Ground chicken vs. Ground beef — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Ground beef and ground chicken contain B vitamins, including vitamin B6, vitamin B5, and vitamin B2. Several vitamins and minerals, including vitamin B3, potassium, and manganese, are abundant in ground chicken. Compared to ground beef, it includes more of these nutrients. Furthermore, the amount of saturated fat in ground chicken is reduced. Contrarily, ground beef is higher in iron, zinc, and vitamin B12 than ground chicken. Compared to ground chicken, it provides 83% more of the recommended daily intake of vitamin B12. The potassium content of ground beef is lower than that of ground chicken.
Introduction
Ground beef and chicken have different tastes, textures, and nutritional profiles, yet they are two of the most popular varieties of ground meat. Burgers, meatballs, meatloaf, tacos, and more foods may all be made using these adaptable components.
Classification
Myoglobin, which gives red meat its crimson hue, is in higher concentrations in red meats like beef. White meat, such as chicken, is lighter in color because it contains less myoglobin.
Ground beef and chicken are not processed meats. Meat that has been salted, cured, fermented, smoked, or subjected to other treatments to increase flavor or improve preservation is processed meat.
Taste and Use
As the name suggests, ground chicken is made by grinding chicken meat, which can include a combination of white and dark meat. It is known for being leaner than ground beef and is often chosen by individuals looking for a lower-fat protein option. Ground chicken offers a mild and slightly sweet flavor, making it a versatile choice for various recipes. Ground beef, on the other hand, is made by grinding beef, typically from cattle. It is known for its robust and savory flavor, which many people find appealing in hamburgers and meat sauces. Ground beef contains a higher fat content than ground chicken, contributing to its rich taste and juiciness.
Nutrition
Macronutrients and Calories
Ground beef contains 40.8% more fat and 171.6% more other components than ground chicken. On the other hand, ground chicken has 11.2% more water content. However, both ground chicken and ground beef provide a similar amount of protein.
Macronutrient Comparison
Contains
more
WaterWater
+11.2%
Contains
more
FatsFats
+40.8%
Contains
more
OtherOther
+171.6%
Calories
A serving of ground chicken contains approximately 189 calories, while a serving of ground beef contains approximately 241 calories.
Protein
The difference is relatively tiny; ground chicken gives roughly 23.28 grams of protein per serving, whereas ground beef supplies around 23.87 grams per dish.
Fats
While ground beef has 6.073 grams of saturated fat, ground chicken has 3.11 grams. This shows that compared to ground beef, ground chicken has 48.8% less saturated fat. However, ground beef has a 50.1% greater quantity of monounsaturated fat than ground chicken, with 7.322 grams as opposed to 4.879 grams. Compared to ground beef, which has 0.408 grams of polyunsaturated fat, ground chicken has 2.08 grams or a 409.8% larger quantity.
Fat Type Comparison
Contains
less
Sat. FatSaturated fat
-48.8%
Contains
more
Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat
+409.8%
Contains
more
Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat
+50.1%
Cholesterol
While ground beef has around 88 mg of cholesterol per serving, ground chicken has about 107 milligrams.
Vitamins
Ground beef contains a higher amount of vitamin A and 2.25 times less vitamin E than ground chicken.
In addition, ground beef offers significantly more folate and vitamin B12. Ground chicken contains noticeably higher amounts of vitamin B1 and vitamin B3. However, neither ground chicken nor ground beef contains significant amounts of vitamin D or vitamin C.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+225%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+137.3%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+76.6%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+76.5%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+159.2%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+73%
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin B12Vitamin B12
+388.2%
Contains
more
Vitamin KVitamin K
+38.1%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+250%
Minerals
Ground beef contains approximately 3.1 times more calcium, 2.4 times more iron, and 3 times more zinc than ground chicken.
On the other hand, ground chicken contains approximately 2.8 times more potassium and 1.8 times more manganese than ground beef. Nearly equal amounts of copper, selenium, magnesium, and phosphorus may be found in ground chicken and beef. The sodium content is similar between the two.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+64.7%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+180.9%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+41%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+77.8%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+312.5%
Contains
more
IronIron
+144.1%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+27.4%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+204.2%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+33.6%
Weight Loss & Diets
- Ground beef and chicken both have a moderate amount of fat and a high amount of protein, making them acceptable for a ketogenic diet.
- Since ground chicken has less saturated fat than ground beef, it may be an excellent option for those following the DASH diet.
- The Paleo diet allows for consuming ground beef and chicken since they are regarded as natural, unprocessed protein sources.
- Because ground chicken often has less fat than ground beef, it is a good option for low-fat and low-calorie diets.
- Ground beef and chicken are suitable for low-carb diets because of their low carbohydrate content.
Health Impact
Compared to chicken meat, the link between eating ground beef and good health is more complicated.
Cardiovascular Health
According to significant research, selecting poultry—such as chicken —instead of red or processed meat can reduce cardiovascular risk (1).
High consumption of red meat, mainly processed red meat, has been linked in certain studies to an increased risk of cardiovascular illnesses (2).
Diabetes
There are observable variations in the effects of red meat, particularly ground beef and chicken, on the risk of type 2 diabetes. Due to their low glycemic and insulin index values, ground chicken has little impact on blood sugar levels and insulin sensitivity. A diet high in vegetables and poultry meat is linked to a lower incidence of obesity, type 2 diabetes, and cardiovascular disease (3).
Conversely, research indicates that consuming large amounts of red meat, including processed and unprocessed forms like ground beef, may be associated with a higher risk of type 2 diabetes. Red meat is higher in saturated fat, heme iron, and possibly hazardous chemicals created during high-temperature cooking techniques. These elements have been linked to insulin resistance, poor glucose metabolism, and inflammation, all of which play a role in the progression of type 2 diabetes (4).
Cancer
According to research, overeating red and processed meat, especially ground beef, increases your chance of developing various illnesses, especially colon cancer (5). In contrast, white meat, such as chicken, can help lower cancer risk (6).
Potential health risks
A danger of bacterial contamination, such as Salmonella or E. coli, exists in both ground chicken and ground beef. Ground beef must be handled and prepared correctly to lower the danger of foodborne infections. To guarantee food safety, ground beef must be cooked to the proper internal temperature (7).
Sources
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34542332/
- https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/10408398.2016.1158148
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4462824/
- https://academic.oup.com/ajcn/article/94/4/1088/4598110
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4698595/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4462824/
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0890850803000562
Infographic
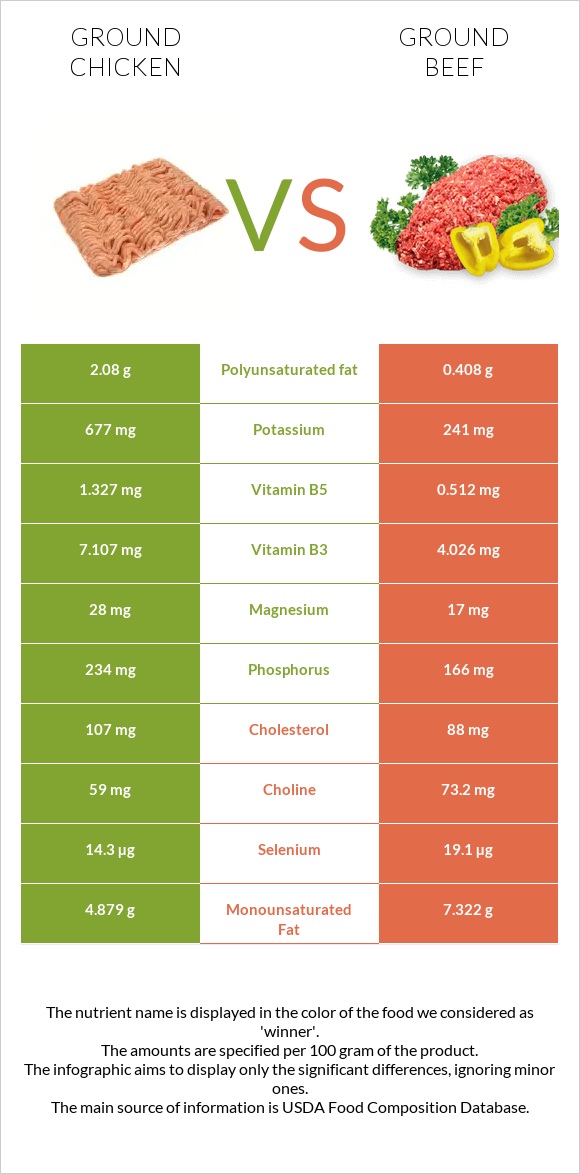
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Vitamin B12 | 0.51µg | 2.49µg | 83% |
| Zinc | 1.92mg | 5.84mg | 36% |
| Vitamin B3 | 7.107mg | 4.026mg | 19% |
| Iron | 0.93mg | 2.27mg | 17% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.538mg | 0.311mg | 17% |
| Vitamin B5 | 1.327mg | 0.512mg | 16% |
| Potassium | 677mg | 241mg | 13% |
| Saturated fat | 3.11g | 6.073g | 13% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 2.08g | 0.408g | 11% |
| Phosphorus | 234mg | 166mg | 10% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.302mg | 0.171mg | 10% |
| Selenium | 14.3µg | 19.1µg | 9% |
| Fats | 10.92g | 15.37g | 7% |
| Cholesterol | 107mg | 88mg | 6% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.121mg | 0.051mg | 6% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 4.879g | 7.322g | 6% |
| Calories | 189kcal | 241kcal | 3% |
| Magnesium | 28mg | 17mg | 3% |
| Calcium | 8mg | 33mg | 3% |
| Choline | 59mg | 73.2mg | 3% |
| Copper | 0.062mg | 0.079mg | 2% |
| Vitamin E | 0.39mg | 0.12mg | 2% |
| Protein | 23.28g | 23.87g | 1% |
| Vitamin K | 2.1µg | 2.9µg | 1% |
| Folate | 2µg | 7µg | 1% |
| Vitamin D | 2 IU | 0% | |
| Sodium | 75mg | 73mg | 0% |
| Vitamin A | 0µg | 3µg | 0% |
| Manganese | 0.016mg | 0.009mg | 0% |
| Trans fat | 0.087g | 1.173g | N/A |
| Tryptophan | 0.196mg | 0.121mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 0.97mg | 0.923mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 1.06mg | 1.055mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 1.816mg | 1.861mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 2.014mg | 1.976mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.596mg | 0.614mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 0.912mg | 0.931mg | 0% |
| Valine | 1.102mg | 1.172mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.706mg | 0.775mg | 0% |
| Omega-3 - EPA | 0.008g | 0g | N/A |
| Omega-3 - DHA | 0.031g | 0g | N/A |
| Omega-3 - ALA | 0.081g | N/A | |
| Omega-3 - DPA | 0.016g | 0g | N/A |
| Omega-6 - Gamma-linoleic acid | 0.02g | 0.008g | N/A |
| Omega-6 - Eicosadienoic acid | 0.015g | N/A | |
| Omega-6 - Linoleic acid | 1.787g | N/A |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Ground chicken - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/171117/nutrients
- Ground beef - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/169474/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.





