Lemon vs. Kiwi — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Kiwifruits contain eight times more Vitamin E and two times more copper than bananas. They also have higher levels of Vitamin C, Vitamin A, magnesium, and potassium.
On the other hand, lemons contain fewer sugars, fewer fats, and fewer calories than kiwifruits.
Introduction
Kiwifruits and lemons are prevalent fruits and are used worldwide. We will discuss their similarities, differences, and how they stack up against each other in nutrition.
Externally, they are very different. Kiwis have furry brownish-green skin and are 5–8 centimeters in length. Lemons are yellow and oval, usually 7 -12 cm in length. The flavor of lemon is aromatic of rose, lavender, and pine with a slight note of herbaceous. Kiwis are tart, sweet, and complex in flavor.
Varieties
Lemons belong to the Citrus genus. They originated in South Asia, but now lemons are a popular citrus fruit used worldwide. The most popular types of lemons are Lisbon lemons and Eureka lemons. Kiwifruit or Chinese gooseberry belongs to the genus Actinidia. Kiwis are the first known plants exported from New Zealand, but they originated in Asia. The most common variety is the Hayward, grown almost exclusively in California.
Uses
Kiwifruit can be eaten raw or used in juices, garnish, smoothies, cakes, salads, etc. Some people prefer to eat kiwifruit with skin. In China, kiwifruit has been used as a medicine for women to recover after childbirth. Lemon can also be eaten raw or made marmalade, lemon liqueur, cocktails, garnish, and flavor for different dishes. Lemon leaves are also used in culinary to make tea and for preparing meats and seafood.
Nutrition
Both kiwis and lemons have rich nutrition content. You can find the nutrition infographics at the bottom of this page.
Micronutrients
Kiwifruit is richer in protein, carbs, fiber, and fructose. On the other hand, lemon contains fewer sugars. Both fruits contain no cholesterol.
Vitamins
Kiwifruit is relatively high in vitamins. It contains eight times more Vitamin E, two times more Vitamins B3, and Vitamin A than lemon. Vitamin C, Vitamin B2, Vitamin K, and folate levels are also higher in kiwifruit. Lemon, on the other hand, has more Vitamin B1 and Vitamin B6 than kiwifruit. The amount of Vitamin B5 is equal in these fruits. Both fruits lack Vitamin D and Vitamin B12.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+48.1%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+27%
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+74.9%
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+300%
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+873.3%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+25%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+241%
Contains
more
Vitamin KVitamin K
+∞%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+127.3%
Minerals
In comparison, the mineral content of kiwifruit is richer than that of lemon. Kiwifruit has more copper, potassium, magnesium, calcium, zinc, and phosphorus. The level of iron is high in lemon. Also, it has less sodium than kiwifruit.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
IronIron
+93.5%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-33.3%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+100%
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+112.5%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+30.8%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+126.1%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+251.4%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+133.3%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+112.5%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+226.7%
Glycemic Index
The glycemic index of lemon has not yet been measured. Kiwi has a glycemic index equal to 58 (1).
Acidity
The acidity of fruits may change depending on growing conditions. However, most studies show lemons to be more acidic than kiwifruits. The pH of lemons equals 3.1, whereas kiwifruits have a pH of 5.6 (2) (3).
Calories
Overall, kiwifruits have two times more calories than lemons. Kiwifruits contain 61 calories in every 100g serving, while lemons contain only 29 calories in every 100g serving.
Health Impact
Weight Loss
Both kiwifruit and lemon are used in different diets due to their low-calorie content. The lemon detox diet lasts 5 to 10 days, during which people consume only lemon-based mixtures with no solid foods. According to the study, organic maple and palm syrups with lemon juice reduce body fat and insulin resistance (4).
Kiwis are over 90% water, also contain a good amount of fiber and Vitamin C - all additional weight loss benefits.
Cardiovascular Health
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) encompasses various conditions affecting the heart and blood vessels, including coronary artery disease, stroke, and peripheral artery disease. Diet plays a crucial role in the prevention and management of CVD, and both kiwifruit and lemons can be beneficial in this regard.
Kiwifruit and lemon are rich in vitamin C, which acts as an antioxidant, protecting against oxidative stress and inflammation, which are key contributors to cardiovascular damage (5).
The potassium content in lemons and kiwifruits contributes to blood pressure regulation, helping to maintain normal blood pressure levels and reducing the risk of hypertension and its associated complications.
The fiber in kiwifruit can help lower LDL (“bad” cholesterol) levels, thereby lowering the risk of atherosclerosis and coronary artery disease.
According to the study, eating 24 grams of citrus fiber daily for a month reduced total cholesterol and HDL (“good” cholesterol) levels in the blood (6).
On the other hand, flavonoids found in lemons, such as hesperidin, have been shown to have cardioprotective effects by improving endothelial function, reducing blood pressure, and lowering cholesterol levels (7).
It's important to consume them as part of a varied diet and lifestyle that includes other heart-healthy habits such as regular exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, and avoiding smoking.
Diabetes
According to research, lemon juice can slow down the digestion of carbohydrates to sugar.
The results show that adding a drink to diabetics' meals can help level off the spikes in blood sugar. This effect is associated with the acidity of lemon juice slowing down starch digestion.
Kiwifruit contains an enzyme called inositol, which helps control the blood sugar level (8) (9).
Cancer
Researchers suggest that several compounds in lemons, such as limonene or naringenin, have anticancer effects. Moreover, lemon contains antioxidants such as Vitamin C that can fight against free radicals in the human body and lower cancer risk.
On the other hand, kiwifruit contains a good amount of Vitamin C. The flesh of kiwi contains soluble fiber that may promote the growth of good bacteria and reduce colon cancer (10) (11).
Immune System
A lot of studies have shown vitamin C has beneficial effects on typical cold recovery. Moreover, not having enough vitamin C can hurt your immune system, especially if you're elderly. In this case, both lemons and kiwis are good sources of Vitamin C, containing enough Vitamin A and minerals to boost your immune system. Also, Vitamin C can help boost immunity in those undergoing extreme physical activity (12).
Digestive Health
Kiwis are high in dietary fiber. Dietary fiber may act as a bulking agent, improve regularity, and decrease intestinal transit time, thus alleviating constipation symptoms (13).
The dietary fiber in kiwis and lemons may also beneficially affect various gastrointestinal diseases (14).
Kidney Stones
Lemon juice is an excellent source of citric acid, which may help prevent kidney stones by increasing urine volume and pH. As a result, it helps to lower the risk of kidney stone formation. Based on the study, 125 ml of lemon juice daily provides enough citric acid to help prevent stone formation, even in those who already had them (15).
Side Effects
Lemon and kiwifruit have rich nutrition content. However, here are some reasons why you may need to avoid eating these fruits.
Allergy
People who have a citrus allergy may have an allergy to raw lemons. Symptoms usually include intense tingling and itching of the lips, tongue, and throat. People can have an allergy to kiwifruits if they are allergic to latex. When it happens, the symptoms may include itching in the lips, mouth, or throat (16) (17).
Heartburn
Due to their acidic nature, lemons can cause heartburn and aggravation of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) symptoms, which may happen when raw lemons are consumed on an empty stomach. Lemon water effects on GERD symptoms largely depend on the consumer. Some people may feel relief from heartburn, while others may experience it (18) (19).
References
- https://care.diabetesjournals.org/content/diacare/suppl/2008/09/18/dc08-1239.DC1/TableA1_1.pdf
- https://www.idosi.org/abr/7(2)13/7.pdf
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S092552140300231X
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25912765/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23394985/
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0271531705801757
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35889917/
- https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00394-020-02228-x
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780123942944000146
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10082788/
- https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/01635581.2019.1650190
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17636648/
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1021949816301429
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24876314/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18946667/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28721824/
- https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/j.1398-9995.1998.tb03889.x
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35047433/
- A Comparative Analysis of Antimicrobial and Antioxidant Activity between Green Tea, Green Coffee, Pine Apple and Lemon Juice
Infographic
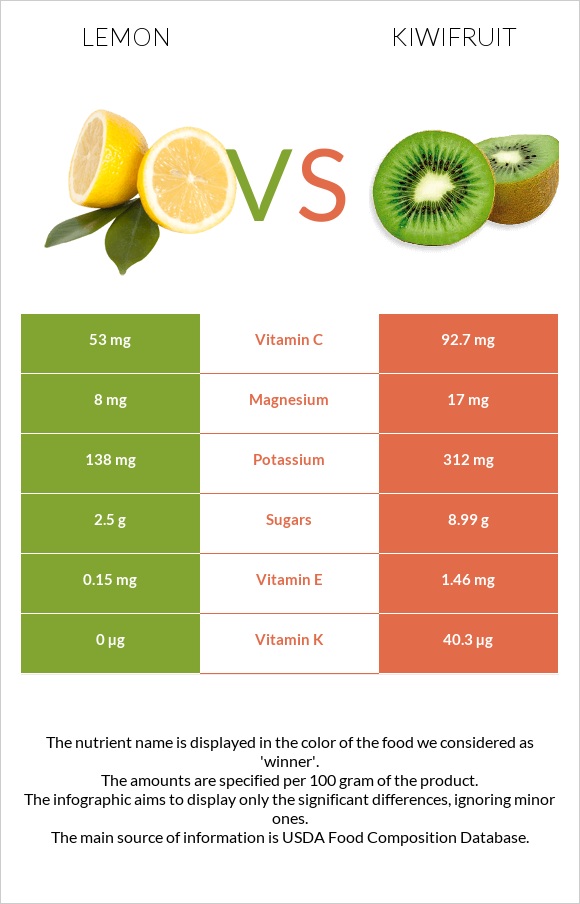
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Vitamin C | 53mg | 92.7mg | 44% |
| Vitamin K | 0µg | 40.3µg | 34% |
| Copper | 0.037mg | 0.13mg | 10% |
| Vitamin E | 0.15mg | 1.46mg | 9% |
| Potassium | 138mg | 312mg | 5% |
| Fructose | 4.35g | 5% | |
| Iron | 0.6mg | 0.31mg | 4% |
| Folate | 11µg | 25µg | 4% |
| Phosphorus | 16mg | 34mg | 3% |
| Manganese | 0.03mg | 0.098mg | 3% |
| Calories | 29kcal | 61kcal | 2% |
| Carbs | 9.32g | 14.66g | 2% |
| Magnesium | 8mg | 17mg | 2% |
| Vitamin B3 | 0.1mg | 0.341mg | 2% |
| Calcium | 26mg | 34mg | 1% |
| Fiber | 2.8g | 3g | 1% |
| Zinc | 0.06mg | 0.14mg | 1% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.04mg | 0.027mg | 1% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.08mg | 0.063mg | 1% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.089g | 0.287g | 1% |
| Protein | 1.1g | 1.14g | 0% |
| Fats | 0.3g | 0.52g | 0% |
| Net carbs | 6.52g | 11.66g | N/A |
| Sugar | 2.5g | 8.99g | N/A |
| Sodium | 2mg | 3mg | 0% |
| Vitamin A | 1µg | 4µg | 0% |
| Selenium | 0.4µg | 0.2µg | 0% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.02mg | 0.025mg | 0% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.19mg | 0.183mg | 0% |
| Choline | 5.1mg | 7.8mg | 0% |
| Saturated fat | 0.039g | 0.029g | 0% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 0.011g | 0.047g | 0% |
| Tryptophan | 0.015mg | 0% | |
| Threonine | 0.047mg | 0% | |
| Isoleucine | 0.051mg | 0% | |
| Leucine | 0.066mg | 0% | |
| Lysine | 0.061mg | 0% | |
| Methionine | 0.024mg | 0% | |
| Phenylalanine | 0.044mg | 0% | |
| Valine | 0.057mg | 0% | |
| Histidine | 0.027mg | 0% |
Macronutrient Comparison
| Contains more FatsFats | +73.3% |
| Contains more CarbsCarbs | +57.3% |
| Contains more OtherOther | +103.3% |
Fat Type Comparison
| Contains less Sat. FatSaturated fat | -25.6% |
| Contains more Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat | +327.3% |
| Contains more Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat | +222.5% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Lemon - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/167746/nutrients
- Kiwi - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/168153/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.