Lychee vs. Kumquat — Nutrition and Health Impact


Summary
Lychee has a sweet and aromatic taste. It has a lower glycemic index and is richer in manganese, copper, phosphorus, vitamin C, and vitamin B6. In comparison, kumquat is bitter and citrusy. It is richer in fiber, C-glycosides, vitamin A, and vitamin B2.
Both have numerous positive health impacts.
Introduction
Exotic fruits are always interesting to consume, and in this article, we will consider two types of exotic fruits: lychee and kumquat. These fruits are exotic, yet they are widely different from one another. They differ in origin, taste, nutritional content, and health impacts.
In this article, we will examine each of the differences between these fruits, mainly focusing on nutrition and health.
General Differences
These exotic fruits are not commonly found and are available all year round and everywhere. Although kumquat is a citrus fruit that can be cultivated in different regions, its origin is China.
Some people compare them to small, bite-sized mandarines or oranges. However, they are zesty, tangy, and a bit bitter. They are olive-sized, and the interesting thing about kumquats is that you can eat them as a whole with the peel.
In comparison, lychees (litchi) have a peculiar flavor that is aromatic, floral, and sweet with white flesh.
In terms of flavor, eating lychees is more pleasant than eating kumquats.
Nutrition
In this section, we will consider 100g of each fruit.
Calories
Kumquats contain 71 calories, whereas lychee contains 66 calories. Kumquat is slightly higher in calories.
Carbs
They have nearly similar amounts of carbohydrates, about 16g for both. However, the net carb content is very different.
Lychee has more net carbs than kumquat.
Glycemic Index
Kumquat has a glycemic index of 67, whereas lychee has a lower index of 48. However, when considering their glycemic load, they both have glycemic loads of 1.
Fiber
The difference in fiber between them is very significant. Kumquats are richer in fiber than lychees. A kumquat contains 6.5g of fiber, whereas a lychee contains 1.3g of fiber.
Kumquat contains five times more fiber than lychee.
Protein and Fats
Their protein and fat profiles are negligible.
Minerals
Lychee is richer in manganese, copper, and phosphorus. In comparison, kumquat is richer in magnesium and iron.
Here, we can visualize their mineral distribution.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+55.8%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+63.2%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-90%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+∞%
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+100%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+1140%
Contains
more
IronIron
+177.4%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+142.9%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+145.5%
Vitamins
Lychee is richer in vitamin C and vitamin B6. In comparison, kumquat is richer in vitamin A and vitamin B2.
Note that kumquat contains a high amount of vitamin C.
Here, we can visualize their vitamin distribution.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+62.9%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+40.6%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+177.8%
Contains
more
Vitamin KVitamin K
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+114.3%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+236.4%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+38.5%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+21.4%
Health Impacts
Lychee contains many phytochemicals and flavonoids that have numerous positive health impacts, one of the most significant of which is on Alzheimer’s. Flavonol in lychee showcased a slowing down of progression in the early stages of Alzheimer's disease (1).
In addition, lychee phytochemicals have anti-tumor and anti-carcinogenic properties (2)(3).
Lychee contains a very rich amount of vitamin C, which has numerous health benefits and is mainly anti-oxidative (4).
Kumquat is rich in flavonoids, and specifically, they have a richer amount of C-Glycosides, which showcase anti-carcinogenic, anti-diabetes, anti-inflammatory, and anti-oxidative properties.
More research is needed to determine the dosage for their maximal health benefits (5)(6).
Since kumquats are eaten whole, They have a very rich fiber content. The fiber in kumquat has numerous health benefits, including digestive, metabolic, and cardiovascular (7).
References
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26342518/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31603034/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5622752/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29763052/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26462718/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28911534/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33096647/
Infographic
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
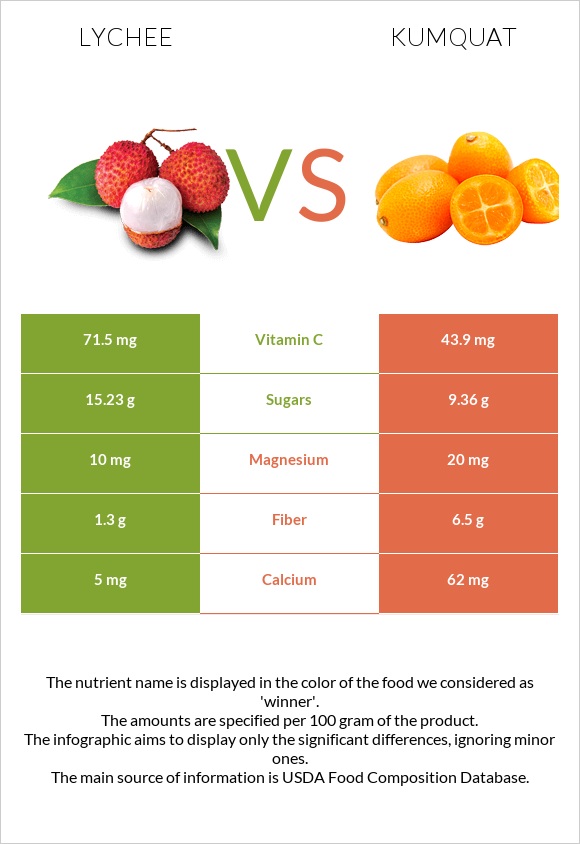
| Vitamin C | 71.5mg | 43.9mg | 31% |
| Fiber | 1.3g | 6.5g | 21% |
| Iron | 0.31mg | 0.86mg | 7% |
| Calcium | 5mg | 62mg | 6% |
| Copper | 0.148mg | 0.095mg | 6% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.1mg | 0.036mg | 5% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.208mg | 4% | |
| Manganese | 0.055mg | 0.135mg | 3% |
| Protein | 0.83g | 1.88g | 2% |
| Magnesium | 10mg | 20mg | 2% |
| Phosphorus | 31mg | 19mg | 2% |
| Vitamin A | 0µg | 15µg | 2% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.011mg | 0.037mg | 2% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.065mg | 0.09mg | 2% |
| Fats | 0.44g | 0.86g | 1% |
| Zinc | 0.07mg | 0.17mg | 1% |
| Vitamin E | 0.07mg | 0.15mg | 1% |
| Selenium | 0.6µg | 0µg | 1% |
| Vitamin B3 | 0.603mg | 0.429mg | 1% |
| Folate | 14µg | 17µg | 1% |
| Calories | 66kcal | 71kcal | 0% |
| Net carbs | 15.23g | 9.4g | N/A |
| Carbs | 16.53g | 15.9g | 0% |
| Potassium | 171mg | 186mg | 0% |
| Sugar | 15.23g | 9.36g | N/A |
| Sodium | 1mg | 10mg | 0% |
| Vitamin K | 0.4µg | 0µg | 0% |
| Choline | 7.1mg | 8.4mg | 0% |
| Saturated fat | 0.099g | 0.103g | 0% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 0.12g | 0.154g | 0% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.132g | 0.171g | 0% |
| Tryptophan | 0.007mg | 0% | |
| Lysine | 0.041mg | 0% | |
| Methionine | 0.009mg | 0% |
Macronutrient Comparison
| Contains more ProteinProtein | +126.5% |
| Contains more FatsFats | +95.5% |
| Contains more OtherOther | +15.9% |
Fat Type Comparison
| Contains more Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat | +28.3% |
| Contains more Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat | +29.5% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Lychee - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/169086/nutrients
- Kumquat - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/168154/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.




