McDonald's Hamburger vs. McDonald's Cheeseburger - What’s the Difference?


Summary
McDonald’s cheeseburger is higher in vitamin B12, proteins, and iron, while McDonald’s hamburger is higher in phosphorus. Cheeseburger contains 4 times less polyunsaturated fats than a hamburger. Hamburger is lower in sodium content, so it is a better choice for people with hypertension.
Introduction
McDonald's is the world's largest fast-food restaurant chain, and this article compares the two most favorite fast foods in the United States on McDonald’s menu - McDonald’s Hamburger and McDonald’s Cheeseburger. Check the sections of the article to find information about the differences in their nutritional composition and health impact.
Actual differences
The main difference between McDonald’s classical hamburger and cheeseburger is the slice of American pasteurized cheese, which tops the meat in the cheeseburger. Other ingredients are the same: it is a burger patty prepared from ground beef using various condiments. It is topped with slices of a pickle, chopped onions, mustard, and ketchup.
Additionally, hamburger comes from Hamburg, Germany, while cheeseburger has an American origin.
Nutrition
This section will compare the nutritional profiles of a 100g serving of McDonald’s hamburger and cheeseburger. Consider that the serving size for a hamburger equals 95g, while a cheeseburger’s serving size is 119g.
Macronutrient Comparison
Contains
more
FatsFats
+16.8%
Contains
more
OtherOther
+11.5%
Calories
Hamburgers and cheeseburgers are classified as medium-calorie foods. A 100g of each burger provides 264 calories.
Carbohydrates
McDonald's hamburger and cheeseburger are both high in carbs: hamburger contains 30.3g of total carbs, whereas cheeseburger contains 27.8g.
A hamburger and a cheeseburger contain 1.3g and 1.1g of dietary fiber, respectively.
The majority of sugars in both burgers are glucose and fructose, with a comparably higher content of fructose.
Unlike hamburger, cheeseburger also contains some amounts of lactose, which may lead to digestive symptoms, such as abdominal pain and bloating, in people with lactose intolerance.
Carbohydrate type comparison
Contains
more
SucroseSucrose
+∞%
Contains
more
LactoseLactose
+∞%
Contains
more
MaltoseMaltose
+33.3%
Contains
more
FructoseFructose
+27.4%
Protein
Cheeseburger is slightly richer in protein than hamburger; both contain nearly 13g of protein per 100g serving of the food.
Fats
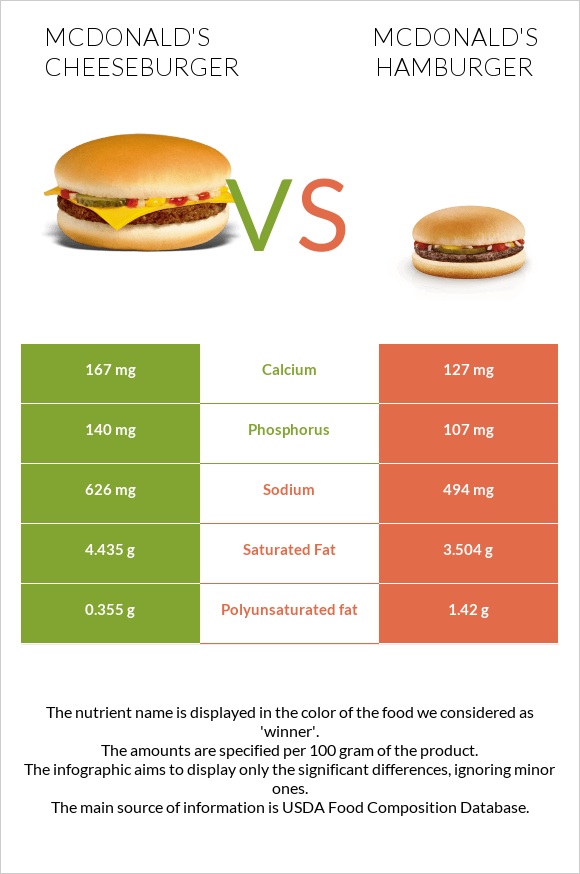
Cheeseburger is higher in fats, providing 11.8g of fats per 100g compared to 10.1g in hamburger. Cheeseburgers are also higher in trans fats, the unhealthiest type of fats, and cholesterol.
Surprisingly, a hamburger contains more monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats than a cheeseburger. It is also lower in saturated fats.
Fat Type Comparison
Contains
less
Sat. FatSaturated fat
-21%
Contains
more
Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat
+300%
Minerals
Cheeseburger is richer in calcium and phosphorus. Hamburger contains more iron and manganese and less sodium.
McDonald's cheeseburger and hamburger are classified as high-sodium products. A 100g of hamburger contains 500mg of sodium, whereas cheeseburger contains 630mg.
100g of McDonald's hamburgers and cheeseburgers cover the RDV of iron by 35% and 30% for men and 16% and 13% for women.
A hamburger and a cheeseburger have nearly equal amounts of magnesium, potassium, zinc, and copper.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+31.5%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+30.8%
Contains
more
IronIron
+22.1%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-21.1%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+40%
Vitamins
McDonald's hamburger and cheeseburger are rich in vitamins B1 (thiamine), B2 (riboflavin), B3 (niacin), B9 (folate), and B12. Hamburger is slightly richer in vitamins B1, B3, and folate, whereas cheeseburger is slightly richer in vitamins B2 and B12.
A hamburger and a cheeseburger also contain some amounts of vitamin A, which is higher in a cheeseburger, and vitamin C.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+10.8%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+12.9%
Glycemic Index
Hamburgers and cheeseburgers are considered medium glycemic index foods, with a glycemic index value of 66. However, there are no calculated values for McDonald’s hamburger and cheeseburger.
Acidity
Calculating the PRAL value of foods is another way to look at the food's acidity. The PRAL value shows how much acid is produced in the organism by the given food.
The PRAL values of McDonald's hamburger and cheeseburger are 4.1 and 4.6, respectively, making cheeseburger slightly more acidic or acid-producing.
Health Impact
Metabolic Syndrome
Metabolic syndrome is characterized by high blood pressure, diabetes, and obesity. Long-term consumption of fast food, such as McDonald's hamburger and cheeseburger, on a daily bases, along with an unhealthy diet and sedentary lifestyle, are risk factors for developing metabolic syndrome.
One of the main problems is the sodium concentration of both of these foods. Due to the high sodium level of these foods, nearly one serving of cheeseburger and hamburger combined can exceed the recommended daily value for sodium. Sodium is considered the main risk factor for hypertension, which may lead to the development of cardiovascular disease (1, 2).
As shown by recent meta-analytic studies, foods high in calories, dietary cholesterol, saturated fats, and trans fats are all associated with an increased risk of hyperlipidemia - elevated levels of unhealthy fats in the blood.
Hyperlipidemia is linked to a number of conditions and diseases, such as insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes, fatty liver disease and cirrhosis, atherosclerosis, stroke, high blood pressure, vascular disease, etc. (3, 4, 5, 6, 7).
Anemia
Both hamburgers and cheeseburgers are rich in iron and vitamin B12, decreasing the risks of developing iron deficiency or microcytic anemia and vitamin B12 deficiency or megaloblastic anemia.
Some of the most common symptoms of iron deficiency anemia are dizziness, fatigue, pale skin, and cold hands and feet (8). Vitamin B12 deficiency anemia may also cause tiredness, lack of energy, as well as a sensation of pins and needles in limbs, slow thinking, memory loss, mood changes, irritability, and problems with smell or taste (9).
References
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34579105/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29565029/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26109578/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27739004/
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/agricultural-and-biological-sciences/hyperlipidemia
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4093693/
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1056872713000718
- https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/anemia/iron-deficiency-anemia
- https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/anemia/vitamin-b12-deficiency-anemia
Infographic
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Selenium | 26.2µg | 48% | |
| Iron | 2.35mg | 2.87mg | 7% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.355g | 1.42g | 7% |
| Sodium | 626mg | 494mg | 6% |
| Phosphorus | 140mg | 107mg | 5% |
| Calcium | 167mg | 127mg | 4% |
| Manganese | 0.23mg | 0.322mg | 4% |
| Saturated fat | 4.435g | 3.504g | 4% |
| Fats | 11.79g | 10.09g | 3% |
| Cholesterol | 35mg | 27mg | 3% |
| Vitamin B3 | 4.026mg | 4.544mg | 3% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.223mg | 0.247mg | 2% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.26mg | 0.239mg | 2% |
| Carbs | 27.81g | 30.28g | 1% |
| Fiber | 1.1g | 1.3g | 1% |
| Vitamin B12 | 0.86µg | 0.83µg | 1% |
| Folate | 59µg | 64µg | 1% |
| Fructose | 2.59g | 3.3g | 1% |
| Calories | 263kcal | 264kcal | 0% |
| Protein | 12.97g | 12.92g | 0% |
| Vitamin C | 0.6mg | 0.6mg | 0% |
| Net carbs | 26.71g | 28.98g | N/A |
| Magnesium | 20mg | 21mg | 0% |
| Potassium | 200mg | 192mg | 0% |
| Sugar | 6.22g | 6.03g | N/A |
| Copper | 0.097mg | 0.096mg | 0% |
| Zinc | 1.91mg | 1.95mg | 0% |
| Trans fat | 0.647g | 0.428g | N/A |
| Monounsaturated fat | 3.631g | 3.768g | 0% |
| Omega-3 - EPA | 0.002g | N/A | |
| Omega-3 - ALA | 0.134g | N/A | |
| Omega-3 - DPA | 0.006g | N/A | |
| Omega-3 - Eicosatrienoic acid | 0.001g | N/A | |
| Omega-6 - Gamma-linoleic acid | 0.004g | N/A | |
| Omega-6 - Dihomo-gamma-linoleic acid | 0.011g | N/A | |
| Omega-6 - Eicosadienoic acid | 0.004g | N/A | |
| Omega-6 - Linoleic acid | 1.135g | N/A |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- McDonald's cheeseburger - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/170320/nutrients
- McDonald's hamburger - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/170717/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.




