Melon vs. Papaya — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Papaya is higher in vitamins and minerals. It has less sodium and a lower glycemic index than melon. On the other hand, melon is richer in Vitamin B6 and Vitamin A and contains fewer sugars and saturated fats.
Introduction
To find the similarities and differences between melon and papaya, we will discuss a comparative analysis of their nutrition features and health impact.
What’s The Actual Difference?
Papayas belong to the Carica genus. They originated in the tropics of America and Mexico. Melons belong to the Cucurbitaceae family, along with watermelons and cucumbers. It is easy to confuse papaya and melon externally; melon is an oblong, oval, yellow plant, 13-17 cm. Papaya is yellow and salmon-colored, about 15–45 cm.
Nutrition
In this article section, we will compare the nutritional content between melon and papaya. Both are mostly made up of water; however, melon contains more water than papaya. At the bottom of this page, you can find a nutrition infographic, which will help you better understand the differences in the nutrition of melon and papaya.
Vitamins
Papaya is relatively high in vitamins than melon. It contains five times more Vitamin E and three times more folate than melon. Vitamin A, Vitamin B3, Vitamin C, Vitamin B5, and Vitamin B1 are also higher in papaya.
Papaya falls in the range of the top 12% of foods as a source of Vitamin C.
On the other hand, melon has more Vitamin B2 and Vitamin B6.
Both papaya and melon contain no Vitamin D and Vitamin B12.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+14.8%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+328.9%
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+179.4%
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+500%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+53.3%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+53.9%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+127.4%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+362.5%
Minerals
Papaya is richer in minerals than melon. It has more calcium, potassium, zinc, magnesium, and less sodium than melon.
On the other hand, melon contains more iron and copper. Both have an equal amount of phosphorus.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
IronIron
+36%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+33.3%
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+90.9%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+81.8%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+14.3%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+100%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-11.1%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+14.3%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+50%
Glycemic Index
The glycemic index of papaya is lower than that of melon. It has a GI equal to 59, whereas the GI of melon is equal to 62.
Insulin Index
Both fruits have almost an equal insulin index. Papayas’ insulin index is 129, and melon’s insulin index is 127.
Acidity
On average, melon has a pH ranging from 6 to 6.7. The pH value of papaya ranges from 5.5 to 5.9.
Calories
Both melon and papaya are considered low-calorie food. Papaya contains more calories than melon. It has 43 calories per 100 g, while melon has 28 calories per 100 g.
Carbs
Papaya has more carbohydrates than melon. It contains 10.82g of carbs per 100g, whereas melon provides 6.58g of carbs per 100g.
Papaya is also richer in fiber: 1.7g of fiber and 9.12g of net carbs. Melon contains 0.9g of fiber and 5.68g of net carbs. Both are considered low-carb foods.
Fats
Both papaya and melon contain tiny amounts of fats.
Health Impact
Cardiovascular Health
A low-sodium diet and appropriate potassium intake can help regulate your blood pressure. Melon is a low-sodium, potassium-rich fruit that may aid in the maintenance of healthy blood pressure levels [1]. Papaya contains a high amount of antioxidants and phenolic compounds, which have protective effects on HDL cholesterol. These antioxidants may also improve the ratio and reduce the risk of heart diseases [2].
Diabetes
Papaya is high in fiber, which can help lower blood glucose levels in type 1 diabetes and maintain blood sugar and insulin levels in type 2 diabetes [3].
One study shows that fermented papaya preparations can help prevent or manage chronic oxidative stress-related diseases, particularly diabetes and cancer. On the other hand, Overeating papaya may negate these health benefits and cause a blood sugar spike [4].
Although melon contains high carbs that can temporarily raise your blood sugar, it also contains fiber and other nutrients that may help improve blood sugar control over time. However, be mindful of melon consumption [5].
Inflammation
Papaya contains two protein-digesting enzymes, papain, and chymopapain. As a result, they can aid digestion and reduce inflammation. They may be especially beneficial for chronic inflammatory diseases like asthma and arthritis [6].
Side Effects
Allergy
If consumed in large quantities, papayas may be unsafe. Individuals who are allergic to latex may also be allergic to papayas. When applied to the skin, papaya latex can cause severe irritation and allergic reactions.
During pregnancy, papayas can be dangerous. The papain found in these fruits has the potential to cause congenital disabilities. People allergic to papain may develop an allergy to papaya in rare cases [7].
Melon allergy is a common food allergy that usually causes an itchy mouth, face, throat, lips, or tongue swelling [8].
References
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4224208/
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0924224416305271
- https://nutritionandmetabolism.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12986-015-0057-7
- https://www.mdpi.com/2311-5637/4/4/83
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5388466/
- https://www.atsjournals.org/doi/full/10.1164/ajrccm.164.10.2104061
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29723936/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7899184/
Infographic
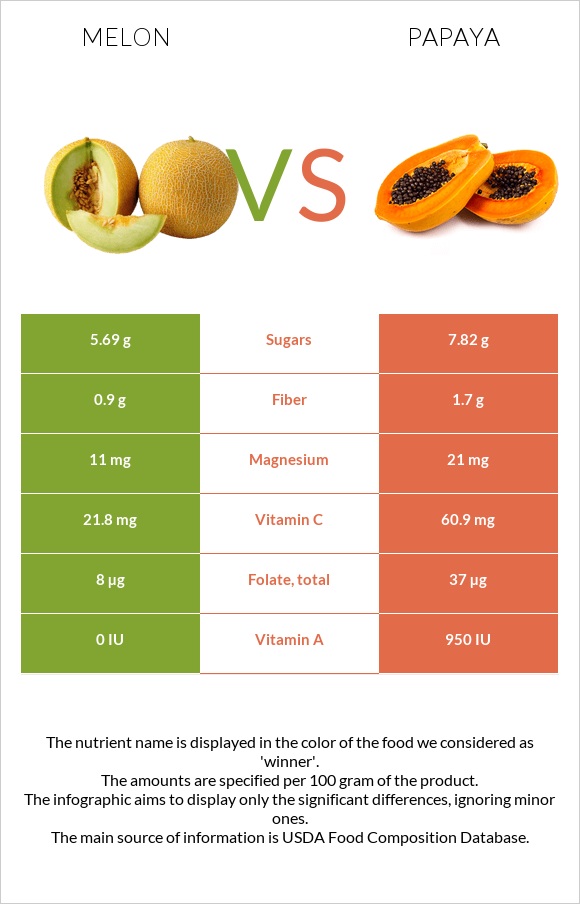
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Vitamin C | 21.8mg | 60.9mg | 43% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.163mg | 0.038mg | 10% |
| Folate | 8µg | 37µg | 7% |
| Vitamin A | 0µg | 47µg | 5% |
| Fructose | 3.73g | 5% | |
| Fiber | 0.9g | 1.7g | 3% |
| Magnesium | 11mg | 21mg | 2% |
| Copper | 0.06mg | 0.045mg | 2% |
| Vitamin E | 0.05mg | 0.3mg | 2% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.084mg | 0.191mg | 2% |
| Calories | 28kcal | 43kcal | 1% |
| Protein | 1.11g | 0.47g | 1% |
| Carbs | 6.58g | 10.82g | 1% |
| Calcium | 11mg | 20mg | 1% |
| Iron | 0.34mg | 0.25mg | 1% |
| Phosphorus | 5mg | 10mg | 1% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.015mg | 0.023mg | 1% |
| Vitamin B3 | 0.232mg | 0.357mg | 1% |
| Fats | 0.1g | 0.26g | 0% |
| Net carbs | 5.68g | 9.12g | N/A |
| Potassium | 182mg | 182mg | 0% |
| Sugar | 5.69g | 7.82g | N/A |
| Zinc | 0.07mg | 0.08mg | 0% |
| Sodium | 9mg | 8mg | 0% |
| Manganese | 0.035mg | 0.04mg | 0% |
| Selenium | 0.4µg | 0.6µg | 0% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.031mg | 0.027mg | 0% |
| Vitamin K | 2.5µg | 2.6µg | 0% |
| Choline | 7.6mg | 6.1mg | 0% |
| Saturated fat | 0.025g | 0.081g | 0% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 0.002g | 0.072g | 0% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.039g | 0.058g | 0% |
| Tryptophan | 0.008mg | 0% | |
| Threonine | 0.011mg | 0% | |
| Isoleucine | 0.008mg | 0% | |
| Leucine | 0.016mg | 0% | |
| Lysine | 0.025mg | 0% | |
| Methionine | 0.002mg | 0% | |
| Phenylalanine | 0.009mg | 0% | |
| Valine | 0.01mg | 0% | |
| Histidine | 0.005mg | 0% |
Macronutrient Comparison
| Contains more ProteinProtein | +136.2% |
| Contains more FatsFats | +160% |
| Contains more CarbsCarbs | +64.4% |
Fat Type Comparison
| Contains less Sat. FatSaturated fat | -69.1% |
| Contains more Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat | +3500% |
| Contains more Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat | +48.7% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Melon - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/169093/nutrients
- Papaya - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/169926/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.