Mulberry vs. Grape — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Mulberry is high in folate, calcium, iron, magnesium, zinc, phosphorus, choline, selenium, protein, fats, and dietary fiber. They also contain more vitamins C, E, B2, and B3. On the other hand, grapes have more net carbs and vitamins K, A, B1, and B6. Moreover, grapes have less sodium, whereas mulberry has less saturated fats and calories.
Introduction
This article compares the nutritional profiles and health effects of mulberry and grape.
Mulberries (Morus) are native to Asia, Europe, Africa, and North America, whereas grapes (Vitis vinifera) are native to the Middle East.
Nutrition
In this part of the article, we will compare the nutritional values of raw mulberry and grapes, concentrating on differences.
Macronutrients and Calories
Grape is denser compared to mulberry. Grapes contain 81% water, whereas mulberry has 88% water.
Macronutrient Comparison
Contains
more
ProteinProtein
+128.6%
Contains
more
FatsFats
+11.4%
Contains
more
OtherOther
+21.1%
Contains
more
CarbsCarbs
+75%
Calories
Grapes have more calories per hundred grams than mulberry. In a 100g serving, mulberry and grape have 43 calories and 67 calories, respectively. One cup (140 grams) of mulberry provides 60 kcal, whereas one cup (92 grams) of grape has 62 kcal.
Protein
Mulberry and grapes are not good sources of protein. Mulberry has a slightly higher protein content than grapes. In a 100g serving, mulberry and grape have 1.44g and 0.63g of protein, respectively.
Fats
Mulberry and grape contain less than 1g of fat in 100 grams. Mulberry provides 0.39g of fats, whereas grape provides only 0.35g. Moreover, mulberries contain more monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, whereas grapes provide more saturated fats.
Fat Type Comparison
Contains
less
Sat. FatSaturated fat
-76.3%
Contains
more
Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat
+192.9%
Contains
more
Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat
+102.9%
Carbohydrates
Grapes are higher in net carbs, whereas mulberry has more dietary fiber.
100g of mulberry contains 9.8g of carbohydrates, of which 1.7g are dietary fiber and 8.1g are net carbs. 100g of grape contains 17.15g of carbohydrates, of which 0.9g are dietary fiber and 16.25g are net carbs.
Cholesterol
Mulberry and grapes do not contain cholesterol.
Vitamins
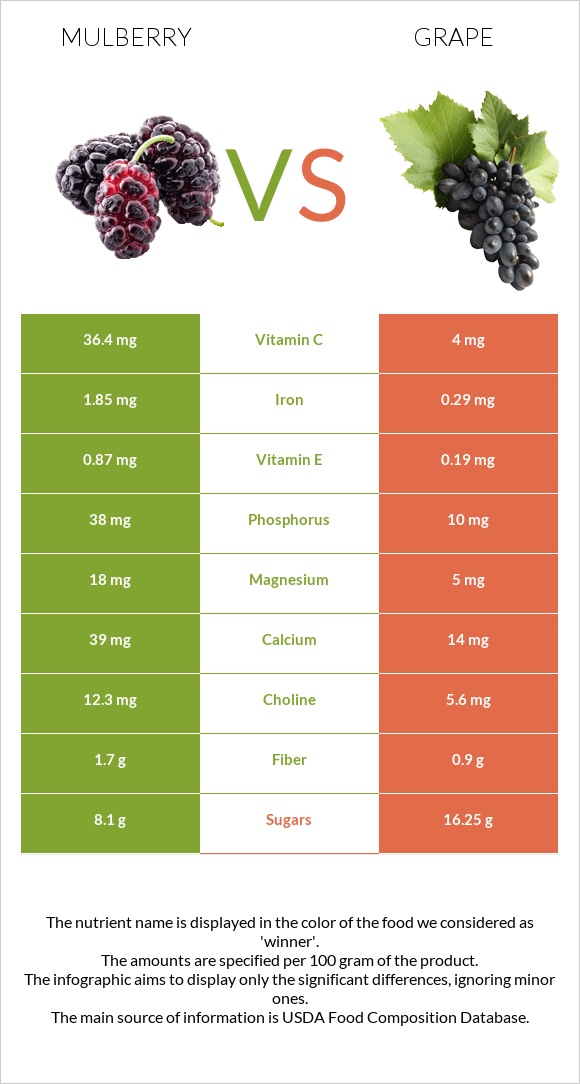
Mulberry has over nine times more vitamin C, whereas the grape provides four times more vitamin A and two times more vitamin K.
In a 100g serving, mulberry and grape have 36.5 mg and 4 mg of vitamin C, respectively. A hundred grams of mulberry has 25IU of vitamin A, while the grape has 100IU. Moreover, mulberry has more vitamins B2, B3, E, and folate, whereas grapes provide more vitamins B1 and B6.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+810%
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+357.9%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+77.2%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+106.7%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+50%
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+400%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+217.2%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+120%
Contains
more
Vitamin KVitamin K
+87.2%
Minerals
Mulberry is the winner in this category. Mulberry has more calcium, iron, magnesium, copper, potassium, phosphorus, choline, selenium, and zinc. In contrast, the grape has over five times less sodium. In a 100g serving, mulberry and grape have 10mg and 2mg of sodium, respectively.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+260%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+178.6%
Contains
more
IronIron
+537.9%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+50%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+200%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+280%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+500%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-80%
Glycemic Index
The grape has a higher glycemic index than mulberry. The glycemic index of mulberry is 25. The grape has a glycemic index of 49. However, the glycemic index of both falls in the low category.
Glycemic Load
The glycemic load of mulberry is equal to 3, whereas the grape has a glycemic load level of 7. However, the glycemic load of both falls in the low category.
Acidity
The pH level of grapes is 2.8-3.82 (1). Mulberry has a pH value of 4.47-6.79 (2).
Another method for determining the acidity of a food is to measure its potential renal acid load (PRAL), which indicates the food's ability to create acids or bases in the body. Mulberry has a PRAL rating of -2.9, while grape's PRAL level is -3.6. Both are alkaline-forming.
Health Benefits
Antimicrobial Properties
Extract from mulberry leaves (MAE) exhibits anti-inflammatory and antibacterial properties against risk factors associated with oral infectious diseases. MAE can inhibit the growth of bacteria in oral microbes F. nucleatum and S. mutans, known pathogens responsible for periodontal diseases and dental caries, respectively (3).
Grape skin and seeds contain natural antioxidants which have antibacterial and antifungal properties. The study found antibacterial activity against Staphylococcus aureus, Enterococcus faecalis, Enterobacter aerogenes, Salmonella typhimurium, and Escherichia coli, all recognized for their role in foodborne illnesses, and antifungal activity against Penicillium chrysogenum, Penicillium expansum, Aspergillus niger, and Aspergillus versicolor (4).
Anti-obesity Properties
Combining mulberry leaf and fruit extracts may have anti-obesity and anti-diabetic effects by reducing oxidative stress and inflammation induced by obesity. The study found that mulberry fruit water extract may reduce body weight and visceral fat and lower serum triacylglycerol, cholesterol, LDL/HDL ratio, and free fatty acids. It helps regulate the balance between lipolysis and lipogenesis, leading to weight loss (5).
Grape seed proanthocyanidin extract (GSPE) may enhance lipid metabolism, decrease fat accumulation, improve insulin resistance, promote triglyceride (TG) breakdown, enhance heat production in brown adipose tissue (BAT), modulate intestinal flora, decrease appetite, and optimize the peripheral clock, all of which contribute to either reducing obesity or preventing its progression (6).
Bones
Grape and mulberry are rich in bioactive compounds that could benefit your bone health. For example, consuming grape products might help your body use calcium better and inhibit bone turnover (7).
Mulberry water extract (MWE) has the potential to regulate the formation of bone-building cells (osteoblasts) and the activity of bone-resorbing cells (osteoclasts), which could have a positive impact on osteoporosis (8).
Cancer
Extracts from mulberry alba have also exhibited anticancer effects in different human cancer cell lines. According to the study, Albanol B (ABN-B), a compound derived from mulberry alba, demonstrates anticancer properties in vitro and in vivo models of lung cancer by causing cell cycle arrest at G2/M and inducing apoptosis. In addition, the root bark extract of mulberry alba induces growth arrest and apoptosis in human colorectal cancer cells by enhancing ATF3 expression and reducing cyclin D1 levels (9, 10).
Consumption of foods rich in antioxidants, such as grapes, has cancer-prevention effects. Grape skin and seed extracts exhibit strong antioxidant properties, scavenging free radicals and inhibiting lipid oxidation in various models. These extracts may target cancer cells through different pathways, including EGFR and COX-2 inhibition, leading to cell cycle arrest and apoptosis (11).
Grape seed extract has antiangiogenic effects in human breast and prostate cancer cells (12).
Downsides and Risks
Allergy
An allergy occurs when the human body reacts to a foreign substance, known as an allergen, causing the immune system to overreact.
Allergic reactions to mulberry can manifest as food and respiratory allergies, often leading to symptoms like asthma, rhinitis, or anaphylaxis. These reactions also may include oral allergy syndrome, airborne contact urticaria, or food-induced urticaria. Mulberry pollen is a significant trigger for respiratory allergies in many areas, and there is a risk of cross-reactivity with other pollen or fruits. While studies have shown varied results regarding this cross-reactivity, it is essential to be aware of potential reactions in individuals allergic to birch, parietaria, or olive pollens who consume mulberry-containing foods or supplements (13).
Grape allergy is uncommon. Grape lipid transfer protein (LTP) is the primary grape allergen, although other minor allergens can also be allergic. Severe grape allergies typically occur in atopic individuals who may react to other plant-derived foods containing LTP (14).
Classification
Mulberry belongs to the family Moraceae and genus Morus. On the other hand, grapes belong to the family Vitaceae and genus Vitis.
Mulberries grow on trees, often in clusters along the branches. Grapes grow on vines that climb and spread along trellises or other supports.
Appearance
Mulberries are typically small, elongated fruits with a cylindrical or oval shape. They resemble blackberries in appearance. Grapes, on the other hand, are round or oval-shaped berries that grow in clusters on vines. Mulberries are generally smaller than grapes, though their size can vary depending on the variety and ripeness. Grapes come in different sizes, from small, pea-sized berries to larger ones, depending on the cultivar. Mulberries can vary in color depending on the variety, but they are commonly black, red, or white when ripe. Grapes come in different colors, including green, red, blue-purple, and black.
Mulberries have a softer texture compared to grapes. They are juicy and tender, with slightly chewy skin. Grapes have a firm skin that encases a juicy pulp.
Taste
Depending on the variety, mulberries can range from slightly tangy to sweet. They may have subtle variations in flavor depending on factors such as ripeness and growing conditions. Overall, mulberries have a mildly tart and sweet flavor like other berries, such as raspberries and blackberries, with a hint of fig-like sweetness.
Grape tastes vary greatly depending on the varietal. They might be sweet, tart, or a mix of the two. Some grape types have distinct flavor characteristics, such as musky or flowery overtones, while others may have traces of citrus or berry flavors. Furthermore, grapes used for winemaking often have more complex flavor profiles, influenced by factors like terroir, grape variety, and winemaking techniques.
Uses
Mulberry finds its way into various culinary recipes. They are commonly enjoyed fresh as a snack or added to fruit salads for a burst of sweetness. In baking, you can use mulberries in pies, tarts, and cakes, infusing these treats with their delightful flavor. Dried mulberries are a nutritious alternative to baked goods, lending their unique taste to granola bars and muffins. You can also use them for making jams and jellies. Additionally, mulberries can be blended into smoothies or sauces, adding depth and sweetness.
You can use fresh grapes as a snack or dessert fruit. In addition, grapes make delightful additions to salads, meat marinades, and cheese platters, adding a sweet and refreshing contrast to savory dishes. Dried grapes, or raisins, are a pantry staple, lending their sweetness to baked goods like cookies and bread or enjoyed as a wholesome snack. Grapes are also juiced to make refreshing beverages, such as grape juice, or blended into smoothies. They play a central role in winemaking, where different grape varieties are cultivated, from robust reds to crisp whites and sparkling varieties.
Sources
- https://www.clemson.edu/
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/330914405
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9099889/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4689022/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5981255/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7250358/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25644345/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27805229/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7764986/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4074313/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22919383/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2728696/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7029495/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17228170/
Infographic
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Vitamin C | 36.4mg | 4mg | 36% |
| Manganese | 0.718mg | 31% | |
| Iron | 1.85mg | 0.29mg | 20% |
| Vitamin K | 7.8µg | 14.6µg | 6% |
| Vitamin E | 0.87mg | 0.19mg | 5% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.029mg | 0.092mg | 5% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.05mg | 0.11mg | 5% |
| Phosphorus | 38mg | 10mg | 4% |
| Magnesium | 18mg | 5mg | 3% |
| Calcium | 39mg | 14mg | 3% |
| Fiber | 1.7g | 0.9g | 3% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.101mg | 0.057mg | 3% |
| Protein | 1.44g | 0.63g | 2% |
| Carbs | 9.8g | 17.15g | 2% |
| Copper | 0.06mg | 0.04mg | 2% |
| Vitamin B3 | 0.62mg | 0.3mg | 2% |
| Calories | 43kcal | 67kcal | 1% |
| Zinc | 0.12mg | 0.04mg | 1% |
| Selenium | 0.6µg | 0.1µg | 1% |
| Folate | 6µg | 4µg | 1% |
| Choline | 12.3mg | 5.6mg | 1% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.207g | 0.102g | 1% |
| Fats | 0.39g | 0.35g | 0% |
| Net carbs | 8.1g | 16.25g | N/A |
| Potassium | 194mg | 191mg | 0% |
| Sugar | 8.1g | 16.25g | N/A |
| Sodium | 10mg | 2mg | 0% |
| Vitamin A | 1µg | 5µg | 0% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.024mg | 0% | |
| Saturated fat | 0.027g | 0.114g | 0% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 0.041g | 0.014g | 0% |
| Tryptophan | 0.003mg | 0% | |
| Threonine | 0.017mg | 0% | |
| Isoleucine | 0.005mg | 0% | |
| Leucine | 0.013mg | 0% | |
| Lysine | 0.014mg | 0% | |
| Methionine | 0.021mg | 0% | |
| Phenylalanine | 0.013mg | 0% | |
| Valine | 0.017mg | 0% | |
| Histidine | 0.023mg | 0% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Mulberry - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/169913/nutrients
- Grape - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/174682/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.