Mung beans vs. Lentil — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Lentils are high in potassium, folate, phosphorus, and protein, whereas mung beans contain more magnesium, calcium, and vitamin A. Compared to mung beans, lentils provide more dietary fiber and calories. Mung beans, on the other hand, contain less calories. Both do not contain gluten content.
Lentils and mung beans contain high levels of polyphenols.
Table of contents
Introduction
Lentils and mung beans are legumes that belong to the same family. However, they can have different nutrition and health impacts.
Appearance
Lentils belong to the genus Lens, whereas mung beans belong to the genus Vigna.
Lentils (Lens culinaris) are small legumes with a lens shape.
There are many varieties of lentils based on color. They can be white, red, yellow, orange, dark brown, and black.
Mung beans(Vigna radiata) are small green legumes with a smooth texture.
Flavor
Mung beans have a nutty and slightly sweet taste.
Light lentils have a nutty flavor, whereas dark lentils have a robust flavor.
Nutrition
This part of the article compares the nutritional values of lentils and mung beans.
Macronutrients and Calories
Lentils are high in calories and proteins. Both contain high content of carbs.
Macronutrient Comparison
Contains
more
ProteinProtein
+28.5%
Calories
Lentils contain 116 calories per hundred grams, whereas the same amount of mung beans provides 105 calories.
Protein
Lentils contain 9.02g of protein, whereas mung beans provide 7.02g. Lentils are higher in all essential amino acids, particularly rich in leucine, lysine, and threonine.
Lentils and mung beans are gluten-free.
Fats
Lentils and mung beans contain less than 1g of fats. Lentils are high in monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, whereas mung beans contain more saturated fats.
Fat Type Comparison
Contains
less
Sat. FatSaturated fat
-54.3%
Contains
more
Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat
+18.5%
Contains
more
Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat
+36.7%
Carbohydrates
Lentils are slightly high in carbs compared to mung beans.
100g of lentils contain 20.13g of carbohydrates, of which 7.9g are dietary fiber and 12.23g are net carbs.
100g of mung beans contain 19.15g of carbohydrates, of which 7.6g are dietary fiber and 11.55g are net carbs.
Both are cholesterol-free.
Vitamins
Lentils and mung beans are not good sources of vitamins.
Lentils contain more vitamins C and B3, whereas mung beans provide three times more vitamin A.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+36.4%
Contains
more
Vitamin KVitamin K
+58.8%
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+50%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+19.7%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+83.7%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+55.6%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+165.7%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+13.8%
Minerals
Lentils provide more potassium, phosphorus, choline, and iron. Mung beans, on the other hand, are higher in calcium and magnesium.
Lentils contain 369mg of potassium and 33mg of choline, whereas mung beans provide 266mg and 29mg, respectively.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+33.3%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+42.1%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+38.7%
Contains
more
IronIron
+137.9%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+60.9%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+51.2%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+81.8%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+65.8%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+12%
Polyphenols
Compared to mung beans, lentils have higher phenolic content(1). The most prevalent polyphenols in lentils are phenolic acids, flavan-3-ol, flavonols, anthocyanidins, proanthocyanidins, and anthocyanins(2). Mung beans, on the other hand, contain more vitexin and isovitexin content(3).
Glycemic Index
Lentils and mung beans are low-GI foods. Lentils have a glycemic index of 29, whereas mung beans have 42.
Glycemic Load
Both have low GL values. The glycemic load of lentils and mung beans is 7(4).
Insulin Index
Lentil's insulin index is 58, whereas the insulin index of mung beans is 38(4).
Acidity
Calculating the potential renal acid load, or PRAL, indicates how much acid or base a specific diet creates inside the body.
The PRAL value of lentils is 2.1, and the PRAL value of mung beans is -0.1. Lentils are acidic, whereas mung beans are neutral.
Weight Loss & Diets
Lentils and mung beans are vegan. Both can be part of the DASH diet. Due to their high carb content, lentils and mung beans can not be part of the keto diet.
Lentils and mung beans can be allowed on the Mediterranean diet.
Both are not paleo-friendly.
Health Impact
Bioactive compounds found in lentils and mung beans have antioxidant, antihypertensive, antidiabetic, and anticancer properties. Moreover, mung beans have hepatoprotective and immunomodulatory effects.
Health Benefits
Cardiovascular Health
Lentils have cardioprotective, anti-cholesterolemic, and antihyperlipidemic properties. Lentil consumption can decrease the risk of coronary heart disease and hypertension(1).
Mung beans have antihypertensive effects. It can decrease plasma angiotensin I and systolic blood pressure levels(5).
Diabetes
According to the studies, regular consumption of lentils may prevent diabetes and diabetic complication. Lentils can improve blood glucose and lipid metabolism. Lentils also can regulate glycemic load and glycemic index(1).
Mung beans have hypoglycemic and hypolipidemic properties. It has a beneficial effect on serum glucose(3). Mung bean consumption can lower glycated hemoglobin and BGL levels(6).
Antimicrobial effects
Lentils and mung beans have antifungal properties. Lentils have antifungal effects on Aspergillus niger, whereas mung beans can inhibit the growth of Fusarium solani and Pythium aphanidermatum(1). Mung beans also have antibacterial effects on Staphylococcus aureus(5).
Cancer
Lentils consumption can decrease the risk of breast, prostate, colon, and thyroid cancer. It causes cancer cell apoptosis and autophagy and inhibit the growth of cells(1).
Mung beans also have anti-proliferative effects on the digestive system cells, leukemia, tongue squamous cell carcinoma, and colon cancer cells(3)(5).
Infographic
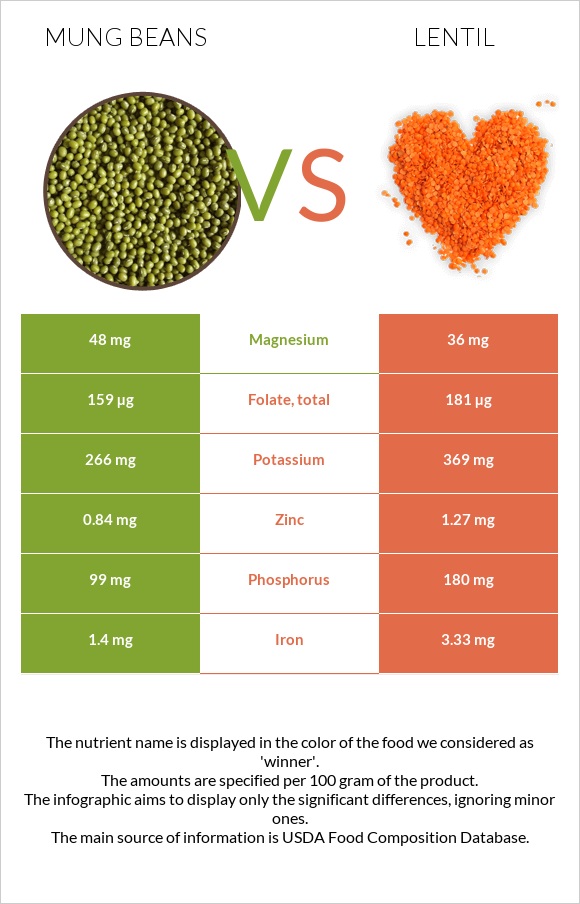
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Iron | 1.4mg | 3.33mg | 24% |
| Phosphorus | 99mg | 180mg | 12% |
| Copper | 0.156mg | 0.251mg | 11% |
| Manganese | 0.298mg | 0.494mg | 9% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.067mg | 0.178mg | 9% |
| Folate | 159µg | 181µg | 6% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.41mg | 0.638mg | 5% |
| Protein | 7.02g | 9.02g | 4% |
| Zinc | 0.84mg | 1.27mg | 4% |
| Magnesium | 48mg | 36mg | 3% |
| Potassium | 266mg | 369mg | 3% |
| Vitamin B3 | 0.577mg | 1.06mg | 3% |
| Calories | 105kcal | 116kcal | 1% |
| Vitamin C | 1mg | 1.5mg | 1% |
| Calcium | 27mg | 19mg | 1% |
| Fiber | 7.6g | 7.9g | 1% |
| Selenium | 2.5µg | 2.8µg | 1% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.061mg | 0.073mg | 1% |
| Vitamin K | 2.7µg | 1.7µg | 1% |
| Choline | 29.4mg | 32.7mg | 1% |
| Fats | 0.38g | 0.38g | 0% |
| Net carbs | 11.55g | 12.23g | N/A |
| Carbs | 19.15g | 20.13g | 0% |
| Sugar | 2g | 1.8g | N/A |
| Sodium | 2mg | 2mg | 0% |
| Vitamin A | 1µg | 0µg | 0% |
| Vitamin E | 0.15mg | 0.11mg | 0% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.164mg | 0.169mg | 0% |
| Saturated fat | 0.116g | 0.053g | 0% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 0.054g | 0.064g | 0% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.128g | 0.175g | 0% |
| Tryptophan | 0.076mg | 0.081mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 0.23mg | 0.323mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 0.297mg | 0.39mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 0.544mg | 0.654mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 0.49mg | 0.63mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.084mg | 0.077mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 0.425mg | 0.445mg | 0% |
| Valine | 0.364mg | 0.448mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.205mg | 0.254mg | 0% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Mung beans - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/174257/nutrients
- Lentil - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/172421/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.






