Peach vs. Mango — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Mangoes are higher in calories and carbohydrates, mostly due to net carbs.
Mangoes are a better source of vitamins, providing 11 times more folate or vitamin B9, 6 times more vitamin C, and 3 times more vitamin A.
Peaches are a better source of zinc and iron, while mangoes are richer in selenium, calcium, and copper.
Peaches are cheaper than mangoes, although both are seasonal fruits.
Introduction
This article will discuss the differences and similarities between mango and peach, focusing on their general characteristics, nutrition, weight loss properties, and health impacts.
General Characteristics
Mango is a stone fruit that grows in tropical regions. It is native to South Asia. Nowadays, they are also cultivated in the South American tropical regions.
Mangoes have a distinct smell, flavor, and texture, with an orange-to-yellow fleshy part surrounding the stone. Due to their seasonal availability and specific growing conditions, they are considered luxury fruit. Thus, the price is higher compared to peach.
Peach is also a stone fruit. Its origin is traced back to China. Nowadays, it is found all over the world, though it is only seasonally available.
Different types of peaches are available during the peach season, which is during summer. The different types are related to size, flavor, juiciness, and taste.
Even though both are seasonally available, peach is cheaper than mango, and this is due to its distribution in nearly most types of regions.
Culinary Use
Mangoes can be used in a variety of ways by different cultures. In Bangladesh, unripe mangoes are pickled. In Indian cuisine, they are used for main course preparations. Mangoes can also be made into jam, compotes, dried, squeezed to juice, and eaten raw.
Peach is eaten raw, made into compote, dried, and squeezed into juice. Peach is less versatile in its usage in the culinary world.
Nutrition
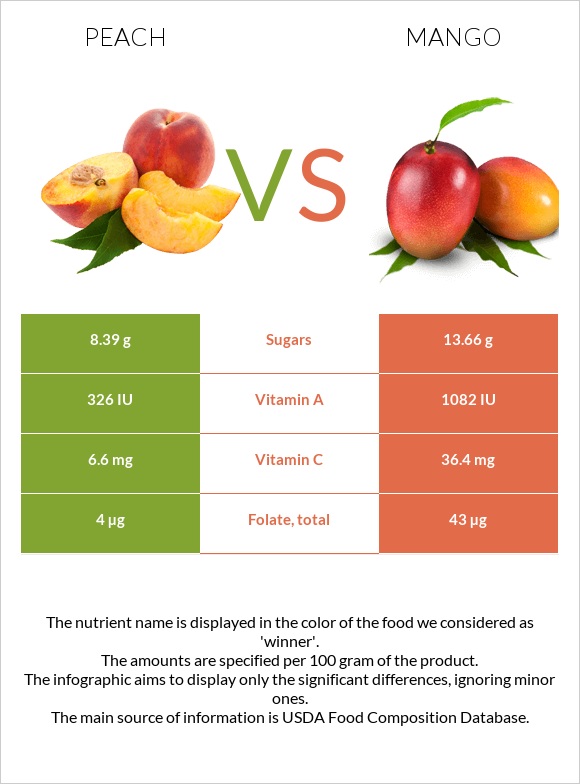
In this article section, we will compare the nutritional content between raw mango and raw yellow peach, based on 100g of each. It is important to note that they are both mostly made up of water. Peach contains slightly more water than mango.
However, one average peach is equal to around 147g, while one cup of cut mangoes weighs 165g.
Mango is made up of 83% water and 27% nutrients, while peach consists of 89% water and 21% nutrients.
The main macronutrient in both these foods is carbohydrates.
Macronutrient Comparison
Contains
more
OtherOther
+19.4%
Contains
more
FatsFats
+52%
Contains
more
CarbsCarbs
+57%
Calories
Peach is lower in calories compared to mango. However, both are considered low-calorie foods.
Mango provides 60 calories per 100g serving, while the same amount of peach has 39 calories.
Carbs
Mango is higher in carbohydrates compared to peach, mostly due to net carbs. Mangoes and peaches contain 13.4g and 8g of net carbs, respectively.
Even though they have different amounts of carbohydrates, they have similar fiber content. Both cover 8% of the daily value of dietary fiber, containing about 1.5g per 100g.
The predominant carbohydrate type found in both fruits is sucrose, making up over 50%. The next carbohydrate type by percentage is fructose in mangoes and glucose in peaches.
Carbohydrate type comparison
Contains
more
MaltoseMaltose
+∞%
Contains
more
GalactoseGalactose
+∞%
Contains
more
SucroseSucrose
+46.4%
Contains
more
FructoseFructose
+205.9%
Protein and Fats
Both mango and peach have negligible amounts of proteins and fats - less than 1g per 100g serving.
Vitamins
The vitamin profile of mangoes is richer than that of peaches. Mango is richer in vitamin C, covering 61% of the daily value per 100g serving. They are 11 times richer in folate and 3 times richer in vitamin A.
Mangoes also provide higher levels of vitamins B1, B2, B5, and B6 and vitamins E and K.
Peach also contains vitamin C, but it only provides 11% of the daily value per 100g. That being said, peaches are a relatively better source of vitamin B3.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+20.5%
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+451.5%
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+237.5%
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+23.3%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+16.7%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+22.6%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+28.8%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+376%
Contains
more
Vitamin KVitamin K
+61.5%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+975%
Minerals
Mangoes and peaches have roughly similar mineral profiles, both not being very rich in these micronutrients.
However, mangoes provide 6 times more selenium and are richer in calcium, copper, and magnesium. Peaches, on the other hand, are a better source of zinc, iron, phosphorus, and potassium.
Both these fruits are very low in sodium.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+13.1%
Contains
more
IronIron
+56.3%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+88.9%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+42.9%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-100%
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+11.1%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+83.3%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+63.2%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+500%
Glycemic Index and Glycemic Load
Peaches and mangoes are both low glycemic index foods. The glycemic index of peaches is 42, only slightly lower than that of mangoes - 51.
However, when calculating their glycemic load values, we can see that peaches have a glycemic load of 5, while this value for mangoes is 11. This difference is due to their different average serving size portions.
On our website, we have detailed articles about the glycemic index of peaches and the glycemic index of mangoes.
Weight Loss and Diets
In moderation, mangoes and peaches can fit perfectly in weight loss diets. They are ideal for replacing sweet snacks like chocolate. These fruits are low in calories, most of their weight is water, and are rich in dietary fiber, thus, keeping you fuller for more extended time periods.
As mentioned before, peaches have a lower calorie content compared to mangoes.
Keto
Mangoes cannot be consumed on the keto diet. Their carbohydrate levels are relatively high for the carbohydrate limit in keto diets - usually 20g per day.
Peaches, on the other hand, can be consumed but in only low amounts.
Vegan
Mangoes and peaches can naturally be eaten on vegan diets without any restrictions.
Health Impacts
Cardiovascular Health
Mango and peach have beneficial effects on blood pressure control. According to this study, long-term consumption of mangoes may decrease systolic blood pressure (1). An experimental study on rats found that peach extracts were more effective as a therapeutic method for controlling blood pressure in hypertension (2).
Physiologically active substances in peach extract effectively improve lipid metabolism, which is vital in reducing the risk of developing cardiovascular disease (2). However, when mango pulp was added to the diet, it significantly increased plasma triglyceride levels, unlike peaches, which contain flavonoids that lower triglyceride levels in the blood (3, 4, 5).
Diabetes
Consumption of mango is associated with decreased blood glucose levels and regulation of blood glucose for obese individuals without negatively impacting body weight. This decreases the risk of developing type 2 diabetes for people who suffer from obesity (6)․
Peach is associated with reducing risks of type 2 diabetes and obesity. This is due to the inhibitory effect of their constituents on digestive enzymes associated with obesity and type 2 diabetes. However, these effects can greatly differ depending on the cultivar due to varying phenolic acid, flavonol, and carotenoid acid contents (7)․
Cancer
Dietary changes, such as high consumption of fruits like peaches and mangoes, have been researched to decrease the risk of cancer by nearly 32% (8)․
Mangoes are rich in polyphenolic compounds with anticarcinogenic and chemotherapeutic properties, thus reducing cancer risk (9)․
Peaches have been studied to have an effect on breast cancer. Phenolic compounds found in peaches have inhibitory properties on the tumor. In addition, these compounds can help slow down the development of lung metastasis (10)․
Antioxidant Effects
Phenolic compounds and ascorbic acid are potent antioxidants that can be found in mango. In addition to phenolic compounds and ascorbic acid, mangiferin is an antioxidant found in mangoes with anti-scavenging properties. These give mangoes strong antioxidative properties to protect against oxidative stress and free radicals. These effects can protect against numerous diseases (11, 12)․
Peaches also contain very potent antioxidant phenolic compounds that have protective roles against oxidative stress (13)․
Drug Interactions
Mangoes interact with warfarin and some anticoagulants. They alter the effects of warfarin (14)․ This effect is assumed to be due to the high vitamin A content of mangoes. Thus, mango consumption should be avoided or moderated when taking warfarin.
References
- https://cdnsciencepub.com/doi/full/10.1139/apnm-2021-0637
- https://koreascience.kr/article/JAKO200606140783486.page
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0268005X20311905
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5490577/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32556180/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4155986/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30284108/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8741778/
- Anticarcinogenic Effects of Polyphenolics from Mango (Mangifera indica) Varieties
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24745759/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3249901/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24374812/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12060270/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12014354/
Infographic
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Vitamin C | 6.6mg | 36.4mg | 33% |
| Folate | 4µg | 43µg | 10% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.025mg | 0.119mg | 7% |
| Copper | 0.068mg | 0.111mg | 5% |
| Vitamin A | 16µg | 54µg | 4% |
| Fructose | 1.53g | 4.68g | 4% |
| Carbs | 9.54g | 14.98g | 2% |
| Calories | 39kcal | 60kcal | 1% |
| Calcium | 6mg | 11mg | 1% |
| Potassium | 190mg | 168mg | 1% |
| Iron | 0.25mg | 0.16mg | 1% |
| Zinc | 0.17mg | 0.09mg | 1% |
| Phosphorus | 20mg | 14mg | 1% |
| Vitamin E | 0.73mg | 0.9mg | 1% |
| Selenium | 0.1µg | 0.6µg | 1% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.031mg | 0.038mg | 1% |
| Vitamin B3 | 0.806mg | 0.669mg | 1% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.153mg | 0.197mg | 1% |
| Vitamin K | 2.6µg | 4.2µg | 1% |
| Protein | 0.91g | 0.82g | 0% |
| Fats | 0.25g | 0.38g | 0% |
| Net carbs | 8.04g | 13.38g | N/A |
| Magnesium | 9mg | 10mg | 0% |
| Sugar | 8.39g | 13.66g | N/A |
| Fiber | 1.5g | 1.6g | 0% |
| Sodium | 0mg | 1mg | 0% |
| Manganese | 0.061mg | 0.063mg | 0% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.024mg | 0.028mg | 0% |
| Choline | 6.1mg | 7.6mg | 0% |
| Saturated fat | 0.019g | 0.092g | 0% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 0.067g | 0.14g | 0% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.086g | 0.071g | 0% |
| Tryptophan | 0.01mg | 0.013mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 0.016mg | 0.031mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 0.017mg | 0.029mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 0.027mg | 0.05mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 0.03mg | 0.066mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.01mg | 0.008mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 0.019mg | 0.027mg | 0% |
| Valine | 0.022mg | 0.042mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.013mg | 0.019mg | 0% |
Fat Type Comparison
| Contains less Sat. FatSaturated fat | -79.3% |
| Contains more Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat | +21.1% |
| Contains more Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat | +109% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Peach - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/169928/nutrients
- Mango - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/169910/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.