Pecan vs. Chestnut — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Pecan contains more vitamins, minerals, fats, and less sodium than chestnuts. It also has a lower GI. On the other hand, chestnuts are lower in sugars, saturated fats, and calories and have more carbs than pecan.
Introduction
Nuts are tasty, healthy, and available all year, and, more importantly, they could be irreplaceable in some diets and health plans. Some nutritionists recommend the daily consumption of nuts for their health benefits.
This article will discover the nutritional value and health impact of two famous nuts: chestnut and pecan. Both nuts are packed with healthy compounds and are edible tree nuts.
What's The Actual Difference?
Taste and Culinary
Chestnuts have a slightly sweet flavor similar to sweet potato rather than another type of nut. Chestnuts are used in desserts, baking, preparing chocolate truffles and salads, and stuffing with cranberries or apples. They go well in winter soups and desserts.
Pecans have a dry and sweet taste. They are widely consumed in raw form and ingredients in pastries, candies, salads, cookies, pasta, and other dishes. Furthermore, nutshells can smoke meats, ground, beauty products, and even be made excellently.
Varieties
Chestnuts are a group of eight or nine species of trees and shrubs that belong to the genus Castanea in the family Fagaceae. The name "chestnut" refers to the nuts produced by this plant. Chestnuts are native to the Northern Hemisphere.
There are four significant types of chestnut: American Chestnut, European Chestnut, Chinese Chestnut, and Japanese Chestnut. They are shiny brown, with a flat bottom and a point.
Pecan originated from South-central America and Mexico. Pecan belongs to the genus Carya in the family Juglandaceae. Pecans come in over 500 varieties with slightly different characteristics such as flavor, texture, size, color, shape, etc. Cape Fear, Desirable, Moreland, Stuart, and Natives are. Pecans have oval or elongated shells colored dark brown.
Nutrition
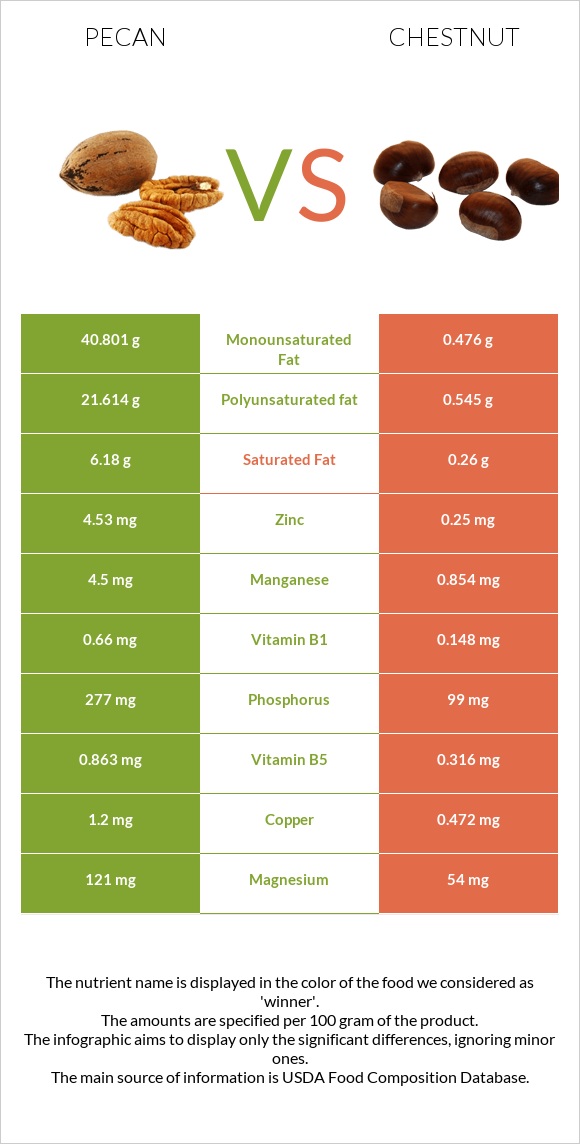
You can find nutritional infographics and tables on this page that visually show the differences between chestnut and pecan.
People prefer to consume raw varieties of pecans and roasted or boiled chestnuts. This is why the food varieties compared in this article are 100g servings of raw pecan nuts and European boiled and steamed chestnuts. However, the actual serving sizes are 1 oz. Equalling 28.35g.
Macronutrients
The chart below shows that pecan and chestnut significantly differ in their macronutrient content. Pecans primarily consist of fats, while 68% of chestnuts is their water content. Chestnuts are richer in carbs, while pecans are higher in protein. Please, read more in the corresponding sections.
Macronutrient Comparison
Contains
more
ProteinProtein
+358.5%
Contains
more
FatsFats
+5115.2%
Contains
more
OtherOther
+108.5%
Contains
more
CarbsCarbs
+100.3%
Contains
more
WaterWater
+1836.1%
Fats
Pecan provides more overall fat content than chestnut. In particular, it contains 72g of fats per 100g, while chestnut has only 1.4g. Pecans are 40 times richer in monounsaturated fats, 21 times higher in polyunsaturated fats, and 6 times in saturated fats. Hence, most of the pecan fats are heart-healthy monounsaturated fats.
Cholesterol
Chestnuts and pecans have no cholesterol.
Fat Type Comparison
Contains
more
Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat
+8471.6%
Contains
more
Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat
+3865.9%
Contains
less
Sat. FatSaturated fat
-95.8%
Carbs
Chestnuts contain more overall carbs than pecans. They have 27.76 g of carbs in 100g, while pecans have 13.86g.
All that 27.76g in chestnuts are net carbs.
In contrast, pecans contain starch, sugars, and, most importantly, high amounts of fiber. 100g of pecans has 9.6g of dietary fiber, including soluble and insoluble fiber.
Minerals
Pecan is relatively high in minerals.
Pecan has more calcium, iron, magnesium, phosphorus, and copper than chestnut. Moreover, it contains 18 times more zinc and less sodium.
On the other hand, chestnut contains more potassium.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+124.1%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+52.2%
Contains
more
IronIron
+46.2%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+154.2%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+1712%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+179.8%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-100%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+426.9%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+∞%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+74.4%
Vitamins
Overall, the amount of vitamins in pecan is higher than that of chestnut. It contains a significantly higher amount of Vitamin A, Vitamin B1, Vitamin B2, Vitamin B3, Vitamin B5, Vitamin K, and Vitamin E.
Chestnut contains 24 times more Vitamin C, B6, and folate.
Both lack Vitamin B12 and Vitamin D.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+200%
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+345.9%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+25%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+59.6%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+173.1%
Contains
more
Vitamin KVitamin K
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+2327.3%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+11%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+72.7%
Calories
The number of calories in pecans is higher than in chestnuts. It has almost six times more calories per 100g: 691 kcal, whereas chestnut contains only 131 kcal per 100g.
Glycemic Index
The glycemic index of pecan is lower than that of chestnut.
The GI of pecan is equal to 10, while the estimated glycemic index of chestnuts is 54. Pecan is considered a low-glycemic index food.
You can check the glycemic indexes of 350+ foods on our glycemic index chart page.
Weight Loss
Because chestnuts have a low number of calories and fats, they are a good choice in low-calorie and low-fat diets.
Although the pecan has more calories and fats, it can also be used in some diets. Pecans are the better choice if you are on a low carbs diet, such as the Keto diet. Besides, pecan has a low glycemic index, suitable for Low GI or Medium GI diets.
Health Benefits
This section of the article will discover the health impact of pecan and chestnut, the benefits, and the downsides of their consumption.
Cardiovascular Health
According to one study, pecans' high monounsaturated fatty acid content may help reduce triglyceride and low-density lipoprotein (bad cholesterol) levels in the blood, lowering cardiovascular risk. According to this animal study, chestnuts may also lower total cholesterol levels in the blood (1.2).
These studies show that pecans and chestnuts may help reduce arterial blood pressure. It should be noted that pecans have a high arginine content, which is significant since arginine is a precursor to nitric oxide synthesis, which is linked to a decrease in blood pressure (3.4).
Nuts like chestnuts and pecans, which are high in antioxidants and minerals, may help lower the risk of cardiovascular issues like myocardial infarction or stroke (5).
Cancer
Based on research, nuts are rich in antioxidants and anti-cancer properties.
According to the study, pecan contains powerful anti-cancer properties, such as 4-hydroxybenzoic, chlorogenic, vanillic, caffeic, and ellagic acid, which are effective against tumor cell growth and may be considered an alternative to the treatment of cancer (6).
On the other hand, Chestnuts are high in Vitamin C, phenolic acids, flavonoids, and tannins, all of which have anti-cancer properties. According to one study, chestnuts may be beneficial in treating stomach cancer and epistaxis (7).
Boost Immune System
According to research, Vitamin C may help people recover faster from the common cold.
Pecans are an excellent immune-boosting food because of their high Vitamin C content. Vitamin C increases the production of white blood cells and acts as an antioxidant, lowering the risk of free radical formation and neutralizing them before they cause healthy cells to mutate or cause oxidative stress near vital organs (8).
Diabetes
According to studies, nuts, such as pecan or chestnut, can help to reduce blood sugar levels.
Pecans have a low glycemic index, so they do not cause a spike in blood sugar, even in people with diabetes. When eaten as part of a meal, pecans can even offset the effects of foods with a higher glycemic index (9).
Other Health Benefits
Several pecan compounds, such as polyphenols and Vitamin E, have potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. Several studies have demonstrated the role of these compounds in disease initiation and progression, including neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's and various types of cancer (10).
Chestnuts contain folic acid, which can aid in the prevention of congenital disabilities in newborns. However, eating chestnuts in moderation to avoid gaining too much weight is unfavorable during pregnancy (11).
Improve Brain Function
First, pecans are rich in the Vitamin B family, which is directly linked to proper neurological development and function.
According to the study, monounsaturated fatty acids in pecan may help to decrease mental decline and reduce inflammation. Besides, pecans are also rich in potassium, increasing blood flow to the brain and promoting good nervous system health (12).
Downsides and Risks
Allergy
Although pecans and chestnuts have potential health benefits, they also have downsides.
Patients allergic to tree nuts are frequently allergic to pecan and chestnut. Itching, swelling, and burning in the mouth and throat are symptoms.
In cases of chestnut allergy, the allergen responsible for the reaction is most likely one of the lipid transfer proteins. Thirty percent of chestnut-allergic patients have severe anaphylactic reactions to ingestion. Common symptoms are wheezing throat swelling, and difficulty breathing (13).
References
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11533266
- https://koreascience.kr/article/JAKO200914852872120.page
- https://www.proquest.com/openview/a22fea86c2f147573d959c16aba8dfa7/1?pq-origsite=gscholar&cbl=18750&diss=y
- https://www.hindawi.com/journals/omcl/2013/471790/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24398275/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28807853/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3133749/
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0308814611003943
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26561616/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22153059/
- https://www.atsjournals.org/doi/full/10.1164/rccm.200710-1544OC
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3098039/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7811165/
Infographic
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Manganese | 4.5mg | 0.854mg | 159% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 21.614g | 0.545g | 140% |
| Fats | 71.97g | 1.38g | 109% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 40.801g | 0.476g | 101% |
| Copper | 1.2mg | 0.472mg | 81% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.66mg | 0.148mg | 43% |
| Zinc | 4.53mg | 0.25mg | 39% |
| Fiber | 9.6g | 38% | |
| Calories | 691kcal | 131kcal | 28% |
| Vitamin C | 1.1mg | 26.7mg | 28% |
| Saturated fat | 6.18g | 0.26g | 27% |
| Phosphorus | 277mg | 99mg | 25% |
| Magnesium | 121mg | 54mg | 16% |
| Protein | 9.17g | 2g | 14% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.863mg | 0.316mg | 11% |
| Iron | 2.53mg | 1.73mg | 10% |
| Potassium | 410mg | 715mg | 9% |
| Vitamin E | 1.4mg | 9% | |
| Selenium | 3.8µg | 7% | |
| Choline | 40.5mg | 7% | |
| Carbs | 13.86g | 27.76g | 5% |
| Folate | 22µg | 38µg | 4% |
| Vitamin B3 | 1.167mg | 0.731mg | 3% |
| Vitamin K | 3.5µg | 3% | |
| Calcium | 70mg | 46mg | 2% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.13mg | 0.104mg | 2% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.21mg | 0.233mg | 2% |
| Sodium | 0mg | 27mg | 1% |
| Net carbs | 4.26g | 27.76g | N/A |
| Sugar | 3.97g | N/A | |
| Starch | 0.46g | 0% | |
| Vitamin A | 3µg | 1µg | 0% |
| Tryptophan | 0.093mg | 0.022mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 0.306mg | 0.071mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 0.336mg | 0.079mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 0.598mg | 0.118mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 0.287mg | 0.118mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.183mg | 0.047mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 0.426mg | 0.084mg | 0% |
| Valine | 0.411mg | 0.112mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.262mg | 0.055mg | 0% |
| Fructose | 0.04g | 0% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Pecan - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/170182/nutrients
- Chestnut - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/170168/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.






