Pecans vs. Peanuts — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Pecans contain more calories and fats than peanuts, while peanuts contain around 3 times more protein.
While the amount of vitamin B1 is almost the same in peanuts and pecans, the amounts of vitamin B5 and vitamin B6 are around 2 times lower in pecans. Peanuts also provide 6 times more vitamin E, 10 times more vitamin B3, and 11 times more folate when compared to pecans.
The amount of copper found in both is also equal, but pecans contain 2 times more manganese than peanuts.
Introduction
I'm sure you've wondered how your favorite foods stand against each other in terms of nutrition. So let's discuss it.
In this article, you can find a detailed guide about the differences between pecans and peanuts. These nuts are prevalent and used in daily life.
Pecans and peanuts are some of the most loved snacks, and today, we will dig a little deeper and find out their similarities, differences, nutritional values, and health impact.
What's the Actual Difference?
Varieties
Pecan trees are native to South America and Mexico. Pecans have dark brown shells that are oval or elongated. They have over 500 varieties, each with slightly different characteristics such as flavor, texture, size, color, shape, and so on. Cape Fear, Desirable, Moreland, Stuart, and Natives are the most popular types.
Peanut is the edible seed of a legume plant. Despite being a legume, it is commonly classified as an oilseed due to its high oil content. Peanuts are not technically true nuts, but they are used in the kitchen due to their similar nutritional properties.
Taste and Culinary
Peanuts taste more like peas than raw nuts, but they're pretty bland before roasting, salting, grinding, or honey glazing. They are used to make oil, peanut butter, confections, roasted peanuts and snack products, meat product extenders, soups, and desserts.
Pecans have a flavor that is both dry and sweet. Furthermore, the nutshells can be utilized for smoking meats, ground up and incorporated into beauty products, and even used to make delicious ice cream.
Nutrition
In this section, we will be comparing the nutritional compositions of peanuts and pecans, with a specific focus on macronutrients, vitamins, and minerals.
Usually, the serving size for both peanuts and pecans is one ounce or 28.35 grams.
Please note that in this section, we will be referring to 100-gram servings of each to make the comparison easier.
Macronutrients and Calories
The macronutrient composition of pecans and peanuts is quite different. Although the predominant macronutrient found in both pecans and peanuts is fat, pecans contain a significantly higher amount of it compared to peanuts.
Pecans consist of 72% fats, while peanuts only contain 49%. Moreover, peanuts also have a higher protein content than pecans.
Macronutrient Comparison
Contains
more
FatsFats
+46.2%
Contains
more
ProteinProtein
+181.4%
Contains
more
CarbsCarbs
+16.4%
Contains
more
WaterWater
+84.7%
Contains
more
OtherOther
+57.4%
Calories
Both pecans and peanuts contain high amounts of calories; however, pecans contain more calories than peanuts.
In a 1oz serving, pecans contain 196 calories, while peanuts contain 161 calories. Per 100-gram serving, pecans contain 124 more calories than peanuts.
Fats
Pecans have more overall fat content than peanuts. Per 1oz serving of each, pecans provide 20.4 grams of total lipid fat, while peanuts provide only 13.9 grams.
Per 100-gram serving, the difference in total lipid fats between the two equals 22.8 grams.
As can be seen in the fat type coverage comparison charts below, both have the same amounts of saturated fats. Still, pecans have more monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats when compared to peanuts. Monounsaturated fats are the predominant type of fat found in both.
Fat Type Comparison
Contains
more
Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat
+67%
Contains
more
Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat
+38.9%
Protein
Peanuts contain around 3 times more protein than pecans.
Per 100-gram serving, there are 9.17 grams of protein in pecans and 25.8 grams of protein in peanuts.
Cholesterol
Peanuts and pecans have no cholesterol.
Carbohydrates
The amount of carbs is only slightly higher in peanuts than in pecans. Peanuts contain 4.56 grams of carbs, while pecans contain 3.94 grams of carbs per 1oz serving.
This difference equals 2.2 grams per 100-gram serving.
Vitamins
Let's dig deeper into the vitamin content of these nuts. Both pecans and peanuts are full of various vitamins; however, peanuts seem to be dominating in this category. As you refer to the graphs below to observe the visual differences in vitamin contents, keep in mind that an average serving is only about 30 grams, while the graphs are provided for a 300-gram serving.
The predominant vitamins found in peanuts are vitamin E, vitamin B1, vitamin B3, vitamin B5, vitamin B6, and folate. The predominant vitamins in pecans are vitamin B1, vitamin B5, and vitamin B6. While the amount of vitamin B1 is almost the same as the amount of it found in peanuts, the amounts of vitamin B5 and vitamin B6 are around 2 times lower in pecans.
Peanuts provide 6 times more vitamin E, 10 times more vitamin B3, and 11 times more folate when compared to pecans.
Peanuts also completely lack vitamin K, vitamin A, and vitamin C, which are all present in pecans in small amounts. Both nuts have no Vitamin B12 and Vitamin D.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin KVitamin K
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+495%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+933.9%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+104.8%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+65.7%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+990.9%
Minerals
Both peanuts and pecans are rich in various minerals as well. The predominant minerals found in both are copper and manganese.
The amount of copper found in both is equal, but pecans contain 2 times more manganese than peanuts.
Peanuts also provide slightly more iron, magnesium, phosphorus, and potassium than pecans. On the other hand, pecans contain slightly more zinc.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+38.5%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-100%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+132.7%
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+38.8%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+31.4%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+72%
Contains
more
IronIron
+81%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+35.7%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+89.5%
Glycemic Index
The glycemic index of pecans is slightly lower than that of peanuts. The GI of pecan is equal to 10, while the estimated glycemic index of peanuts is 13.
Both nuts are considered low glycemic index foods.
Acidity
Peanuts have a neutral acidity that varies depending on the type. The pH of raw peanuts is 6.87, while the pH of roasted peanuts is 6.31. Pecan has a pH of 6.6, which is close to neutral.
One way to understand the acidity of foods is through their potential renal acid load (PRAL) value, which shows how much acid or base the given food produces inside the organism. Based on our calculations, the PRAL values of pecans and peanuts are both acidic and equal to 2.1 and 6.2, respectively.
Health Benefits
This section of the article will discover the health impact of pecans and peanuts.
Weight Loss
Both nuts are high in calories and fats, so it is better to avoid them in low-calorie diets. Nevertheless, they are also high in protein, healthy fats, and dietary fiber, making them applicable for a healthy weight-loss diet.
Pecans may be used in the case of a low-carb diet, such as the Keto diet. Besides, both pecans and peanuts have a low glycemic index, which is good in the case of low GI diets.
Diabetes
According to the American Diabetes Association, nuts, especially pecan or peanuts, are diabetes superfoods. Peanuts contain magnesium, fiber, low GI, and do not overly affect your blood glucose (1).
Pecans have a low glycemic index, so they also do not cause a spike in blood sugar, even in people with diabetes (2).
Cardiovascular Health
Both pecans and peanuts contain healthy fats, primarily monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, which can help lower LDL ("bad" cholesterol) levels when consumed in moderation. Pecans contain higher levels of omega-3 fatty acids compared to peanuts (3, 4).
Omega-3s are known for their heart-protective benefits, such as reducing inflammation and lowering the risk of heart disease (5).
Peanuts are generally higher in vitamin E, which is an antioxidant that helps protect cells from damage caused by free radicals. Some research suggests that vitamin E may have a protective effect against atherosclerosis by reducing oxidative stress and inflammation in the arteries. However, the evidence regarding the efficacy of vitamin E supplementation in preventing or treating atherosclerosis and coronary artery disease (CAD) is mixed (6).
Both pecans and peanuts can be healthy choices, but portion size and processing methods matter. Eating too many nuts, regardless of type, can contribute to weight gain due to their high-calorie content. Additionally, roasted and salted varieties of both nuts may contain added sodium and unhealthy fats, which can negate some of their cardiovascular benefits.
Cancer
Resveratrol, a powerful antioxidant found in peanuts, has been shown to reduce the blood supply to growing cancers and inhibit cell growth. Resveratrol, which is found in both raw and roasted peanuts and peanut butter, has been linked to cancer prevention and treating Alzheimer's disease and diabetes (7).
Based on various studies, pecan is a source of powerful anti-cancer properties, such as 4-hydroxybenzoic, chlorogenic, vanillic, caffeic, and ellagic acid, which are effective against tumor cell growth. It can be considered an alternative to the treatment of cancer (8).
Improve Brain Function
Overall, pecans are high in vitamin B, which is directly linked to proper neurological development and function.
Research shows that the monounsaturated fatty acids found in pecans may aid in the prevention of mental decline and inflammation. Furthermore, pecans are high in potassium, which increases blood flow to the brain and promotes nervous system health (9).
Anti-inflammatory Effects
Polyphenols and vitamin E are potent antioxidants and anti-inflammatory compounds found in pecans. Several studies have shown that these compounds play a role in disease initiation and progression, including neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer's and cancer (10).
Moreover, linoleic acid, a type of omega-6 fatty acid found in peanuts, has been shown to reduce inflammation (11).
Downsides and Risks
Allergy
Although pecans and peanuts have potential health benefits, they also have some downsides to consider.
Patients allergic to tree nuts are frequently allergic to pecan. Itching, swelling, and burning in the mouth and throat are some of the most prevalent symptoms.
Peanut allergies are one of the most common food allergens. Peanut allergies can be fatal, and hence, peanuts are sometimes considered the most severe allergen. People who have this allergy should avoid all peanuts and peanut products (12).
Aflatoxin Poisoning
Peanuts can sometimes be contaminated with aflatoxin (13). Aflatoxin poisoning is characterized by loss of appetite and yellowing of the eyes, typical of liver problems. The risk of aflatoxin contamination commonly depends on the way peanuts are stored.
References
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4711439/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26561616/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11533266/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4711439/
- https://www.health.harvard.edu/blog/omega-3-fatty-acids-and-the-heart-new-evidence-more-questions-2021032422213
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8874674/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28283884/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28807853/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3098039/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22153059/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29280987/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7811165/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19875698/
Infographic
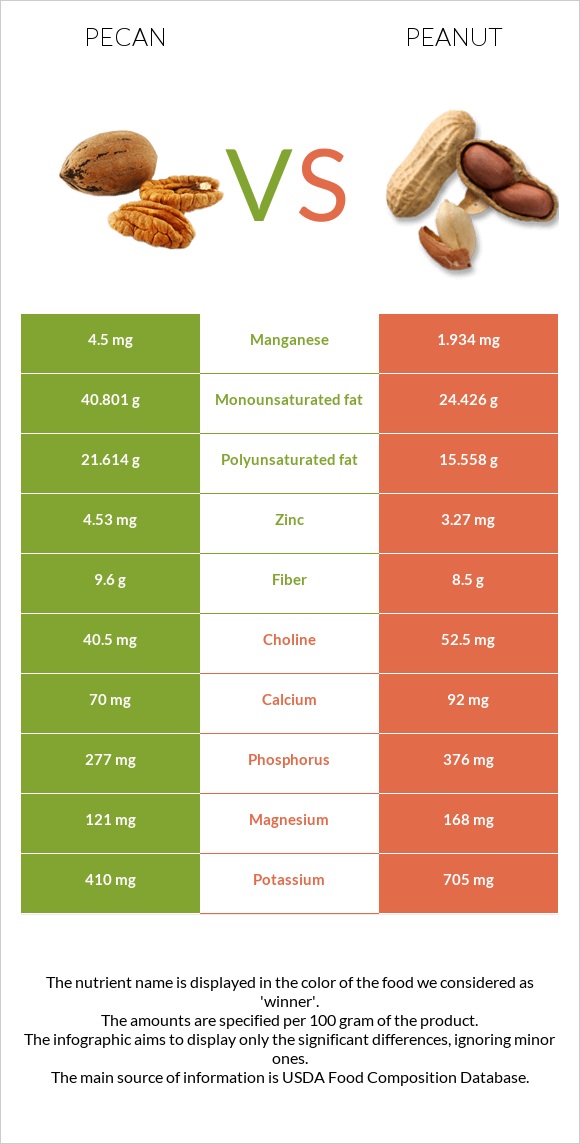
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Manganese | 4.5mg | 1.934mg | 112% |
| Vitamin B3 | 1.167mg | 12.066mg | 68% |
| Folate | 22µg | 240µg | 55% |
| Vitamin E | 1.4mg | 8.33mg | 46% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 40.801g | 24.426g | 41% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 21.614g | 15.558g | 40% |
| Fats | 71.97g | 49.24g | 35% |
| Protein | 9.17g | 25.8g | 33% |
| Iron | 2.53mg | 4.58mg | 26% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.863mg | 1.767mg | 18% |
| Phosphorus | 277mg | 376mg | 14% |
| Magnesium | 121mg | 168mg | 11% |
| Zinc | 4.53mg | 3.27mg | 11% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.21mg | 0.348mg | 11% |
| Potassium | 410mg | 705mg | 9% |
| Calories | 691kcal | 567kcal | 6% |
| Copper | 1.2mg | 1.144mg | 6% |
| Selenium | 3.8µg | 7.2µg | 6% |
| Fiber | 9.6g | 8.5g | 4% |
| Vitamin K | 3.5µg | 0µg | 3% |
| Calcium | 70mg | 92mg | 2% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.66mg | 0.64mg | 2% |
| Choline | 40.5mg | 52.5mg | 2% |
| Vitamin C | 1.1mg | 0mg | 1% |
| Carbs | 13.86g | 16.13g | 1% |
| Sodium | 0mg | 18mg | 1% |
| Net carbs | 4.26g | 7.63g | N/A |
| Sugar | 3.97g | 4.72g | N/A |
| Starch | 0.46g | 0% | |
| Vitamin A | 3µg | 0µg | 0% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.13mg | 0.135mg | 0% |
| Saturated fat | 6.18g | 6.279g | 0% |
| Tryptophan | 0.093mg | 0.25mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 0.306mg | 0.883mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 0.336mg | 0.907mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 0.598mg | 1.672mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 0.287mg | 0.926mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.183mg | 0.317mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 0.426mg | 1.377mg | 0% |
| Valine | 0.411mg | 1.082mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.262mg | 0.652mg | 0% |
| Fructose | 0.04g | 0% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Pecan - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/170182/nutrients
- Peanut - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/172430/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.






