Liver vs. Foie gras — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Foie gras is denser and higher in calories than the liver. While foie gras contains significantly more total fats, it has less protein, lower cholesterol, and more carbohydrates. In terms of vitamins, the liver is superior, offering higher amounts of vitamins A, B12, B3, B5, B2, and folate. The liver also contains more zinc, iron, selenium, and other minerals, whereas foie gras is higher in calcium and sodium.
Introduction
Foie gras (pronounced fwah-grah) is a luxurious French delicacy made from the fattened liver of ducks or geese. The term "foie gras" literally translates to "fatty liver" in French, referring to the enlarged livers produced by a feeding process called gavage.
The birds are fed a diet rich in corn through a feeding tube, resulting in hepatic steatosis, which causes the liver to expand and become fat-laden.
Nutrition
This section will compare the nutritional profiles of foie gras and liver, highlighting their differences.
Macronutrients and Calories
Foie gras is denser than liver. Foie gras contains 37% water, whereas the liver contains 64%.
Macronutrient Comparison
Contains
more
ProteinProtein
+128.2%
Contains
more
WaterWater
+73.7%
Contains
more
FatsFats
+896.4%
Contains
more
CarbsCarbs
+24.2%
Contains
more
OtherOther
+103.3%
Calories
Foie gras provides over 2.8 times calories per hundred grams. In a 100g serving, foie gras and liver have 462kcal and 165kcal, respectively.
Protein
The liver is higher in protein than foie gras. A hundred grams of foie gras provides 11.4g of protein, whereas the liver contains 26.02g.
Fats
Foie gras contains over ten times more total fats compared to the liver.
In a 100g serving, foie gras and liver have 44g and 4.4g of total fats, respectively. Foie gras provides over 40 times more monounsaturated fats, whereas the liver has 1.2 times more polyunsaturated fats and 10 times less saturated fats.
Fat Type Comparison
Contains
less
Sat. FatSaturated fat
-90.2%
Contains
more
Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat
+25%
Contains
more
Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat
+3965.1%
Cholesterol
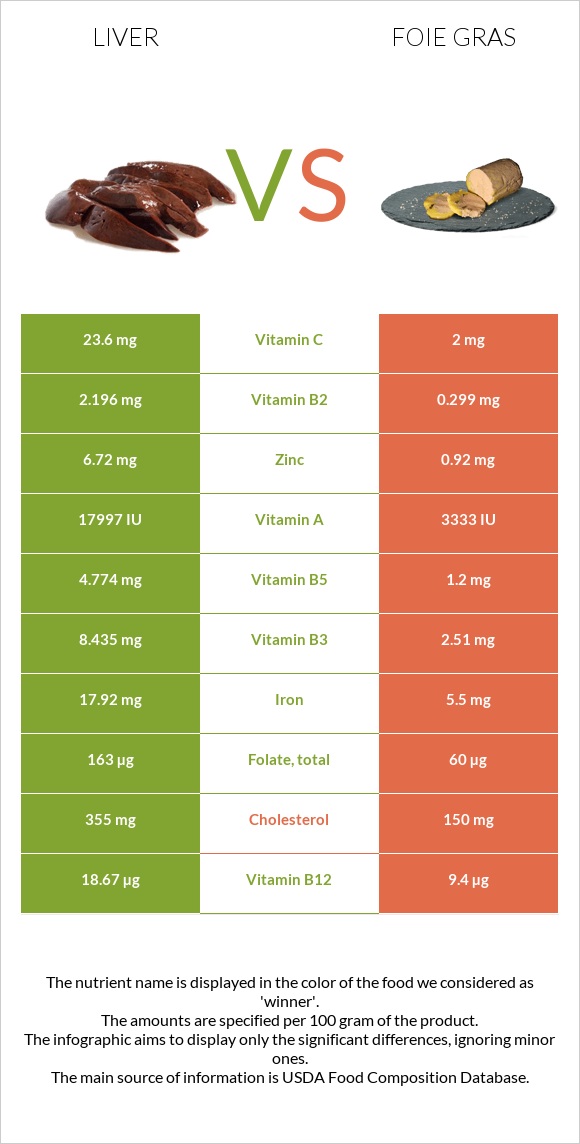
Foie gras has a lower cholesterol level than the liver. In a 100g serving, foie gras and liver contain 150mg and 355mg of cholesterol, respectively.
Carbohydrates
Foie gras is higher in carb content. A hundred grams of foie gras and liver have 4.67g and 3.76g of net carbs, respectively.
Vitamins
In comparison to foie gras, the liver is high in all vitamins. Both have higher amounts of vitamin A, the liver being higher.
The liver contains 17997 IU of vitamin A per hundred grams, while foie gras contains 3333 IU.
The liver also provides two times more vitamin B12, 3.3 times more vitamin B3, four times more vitamin B5, 7.3 times more vitamin B2, and 2.7 times more folate.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+1080%
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+440%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+193.2%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+634.4%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+236.1%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+297.8%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+850%
Contains
more
Vitamin B12Vitamin B12
+98.6%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+171.7%
Minerals
The liver has over 7.2 times more zinc, 3.2 times more iron, and 1.5 times more selenium, whereas foie gras has seven times more calcium. Foie gras has much more sodium content than the liver.
In a 100g serving, foie gras and liver contain 697mg and 49mg of sodium, respectively.
The liver also contains more phosphorus, potassium, manganese, and copper.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
IronIron
+225.8%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+58.5%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+630.4%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+20.5%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-93%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+150%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+53.4%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+600%
Oxalates
Animal products like foie gras and the liver do not contain oxalates.
Acidity
The potential renal acid load (PRAL) is a way to measure the acidity of the food. The PRAL value of foie gras is 8.8, whereas the liver has the PRAL value 18. Both are acid-forming, the liver being more acid-forming.
Health Impact
The liver is rich in vitamin A, a fat-soluble nutrient essential for vision, immune function, cell differentiation, and epithelial barrier health. Vitamin A has two forms: preformed vitamin A (retinol), found in animal products like liver, and provitamin A (beta-carotene), found in fruits and vegetables. A vitamin A deficiency can lead to serious health issues, such as night blindness, immune dysfunction, and problems with the skin and other epithelial tissues.
However, excessive intake of vitamin A can result in toxicity (also known as hypervitaminosis A), which can cause a range of symptoms, and teratogenic effects (harmful to the developing fetus) may occur if consumed during pregnancy. This includes abnormalities like craniofacial, cardiac, and nervous system malformations. For pregnant women, vitamin A intake should not exceed 10,000 IU daily to avoid these risks.
Given the risk of vitamin A toxicity, it's essential to consume liver in moderation to avoid exceeding safe levels of vitamin A intake (1).
Organ meats, including liver (from beef, pork, chicken, or other animals) and foie gras, are high-purine foods. People with disorders that influence uric acid metabolism (such as gout or hyperuricemia) should limit their intake of high-purine foods like liver and foie gras(2, 3).
Excessive cholesterol intake from foods like liver and foie gras can contribute to higher levels of serum cholesterol, especially LDL-C, which is linked to an increased risk of cardiovascular diseases (CVD). If consumed regularly and in large amounts, these foods might elevate LDL-C levels, potentially raising the risk of heart disease (4).
The liver, whether from pork, beef, or lamb, contains higher levels of myoglobin (a protein that stores oxygen in muscle cells), giving it a redder color and classifying it as red meat. Red meat generally tends to have higher iron content compared to white meat. For individuals suffering from iron deficiency anemia, liver and foie gras can be especially beneficial due to their high heme iron content. This type of iron is more easily absorbed by the body, making these foods effective in helping to address iron deficiency and improve hemoglobin levels (5).
Classification
Foie gras is classified primarily by the animal it comes from—duck (foie gras de canard) or goose (foie gras d'oie). The highest quality is whole foie gras (foie gras entier). It can also be found in processed forms such as bloc de foie gras (pressed foie gras) or mousse and pâté de foie gras (spreadable versions).
On the other hand, regular liver comes from various animals, including beef, chicken, pork, and lamb. The most common types of liver are beef liver and chicken liver.
Foie gras is most famously associated with France, but it is also produced in other countries, such as Spain, Hungary, and the U.S. However, France is the largest producer and consumer of foie gras. The liver is eaten worldwide, but its popularity and specific types vary by culture. While beef, chicken, and pork liver are common in many countries, lamb liver tends to be favored in Middle Eastern and Mediterranean regions.
Appearance
Foie gras has a rich, creamy, smooth texture and a deep, pale golden to light brown color. It is much fattier than regular liver and has a soft, buttery appearance. Regular liver (like beef, chicken, or pork) is leaner than foie gras and has a darker, reddish-brown color. The texture can be firmer and grainier. It has visible veins and more defined muscle tissue.
Taste
Foie gras has a rich, buttery, delicate, and mildly sweet flavor. The fat content makes it incredibly smooth and melts in your mouth.
Regular liver has a much stronger, more pronounced flavor that can be somewhat gamey or metallic, especially in beef or pork liver.
Culinary Use
Foie gras is considered a delicacy and is used in high-end cuisine. It is often served as pâté, mousse, or as a whole piece, pan-seared to create a crispy exterior while remaining soft inside. You can use it as an appetizer or main course, or in gourmet dishes like foie gras-topped steaks, or serve it with fruit preserves or toasted bread.
The liver is more commonly used in everyday cooking. It can be pan-fried, grilled, or used in stews, soups, and pâtés. Beef liver, for example, is popular in many cultures and is often served with onions.
Availability
Foie gras is considered a luxury delicacy, often more expensive and less widely available due to the intricate and specialized process required for its production. Goose foie gras is traditionally seen as the premium option, known for its delicate texture and refined flavor. On the other hand, duck foie gras is more commonly produced and widely accessible. It is typically more affordable than its goose counterpart, making it a popular choice in many regions. In contrast, liver is more affordable and can be found in most supermarkets and butcher shops.
Infographic
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Vitamin A | 5405µg | 1001µg | 489% |
| Vitamin B12 | 18.67µg | 9.4µg | 386% |
| Iron | 17.92mg | 5.5mg | 155% |
| Vitamin B2 | 2.196mg | 0.299mg | 146% |
| Vitamin B5 | 4.774mg | 1.2mg | 71% |
| Cholesterol | 355mg | 150mg | 68% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 0.63g | 25.61g | 62% |
| Fats | 4.4g | 43.84g | 61% |
| Saturated fat | 1.41g | 14.45g | 59% |
| Zinc | 6.72mg | 0.92mg | 53% |
| Selenium | 67.5µg | 44µg | 43% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.57mg | 0.06mg | 39% |
| Vitamin B3 | 8.435mg | 2.51mg | 37% |
| Protein | 26.02g | 11.4g | 29% |
| Sodium | 49mg | 697mg | 28% |
| Copper | 0.634mg | 0.4mg | 26% |
| Folate | 163µg | 60µg | 26% |
| Vitamin C | 23.6mg | 2mg | 24% |
| Calories | 165kcal | 462kcal | 15% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.258mg | 0.088mg | 14% |
| Manganese | 0.3mg | 0.12mg | 8% |
| Calcium | 10mg | 70mg | 6% |
| Phosphorus | 241mg | 200mg | 6% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 1.05g | 0.84g | 1% |
| Net carbs | 3.76g | 4.67g | N/A |
| Carbs | 3.76g | 4.67g | 0% |
| Magnesium | 14mg | 13mg | 0% |
| Potassium | 150mg | 138mg | 0% |
| Tryptophan | 0.366mg | 0.161mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 1.107mg | 0.507mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 1.32mg | 0.606mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 2.319mg | 1.029mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 2.007mg | 0.863mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.645mg | 0.27mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 1.274mg | 0.567mg | 0% |
| Valine | 1.607mg | 0.719mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.708mg | 0.303mg | 0% |
| Omega-3 - DHA | 0.03g | 0g | N/A |
| Omega-3 - DPA | 0.04g | 0g | N/A |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Liver - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/167863/nutrients
- Foie gras - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/171100/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.






