Quince vs. Guava — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Although guava and quince have similar nutritional structures, they are radically different in the number of nutrients they contain. Guava is richer in fats, protein, and dietary fiber while being lower in sugars than quince.
Guava also contains almost 10 times more vitamins and around 2 times more minerals than quince, making guava nutritionally superior to quince.
Introduction
Quince is often incorporated into our daily lives as an extract, powder, or tea. It is often used as a compressor application for swollen and painful parts, injuries, and cuts. Its lotion is perfect for soothing eyes. This fruit is also available as juice, wine, jelly, jam, pudding, and other sweets.
Guava is a tropical fruit cultivated mainly in Brazil, Venezuela, Colombia, and Mexico. The fruit, its juice, and leaves are often used as medicine. They are usually eaten raw, though they may be used in beverages, jams, and desserts.
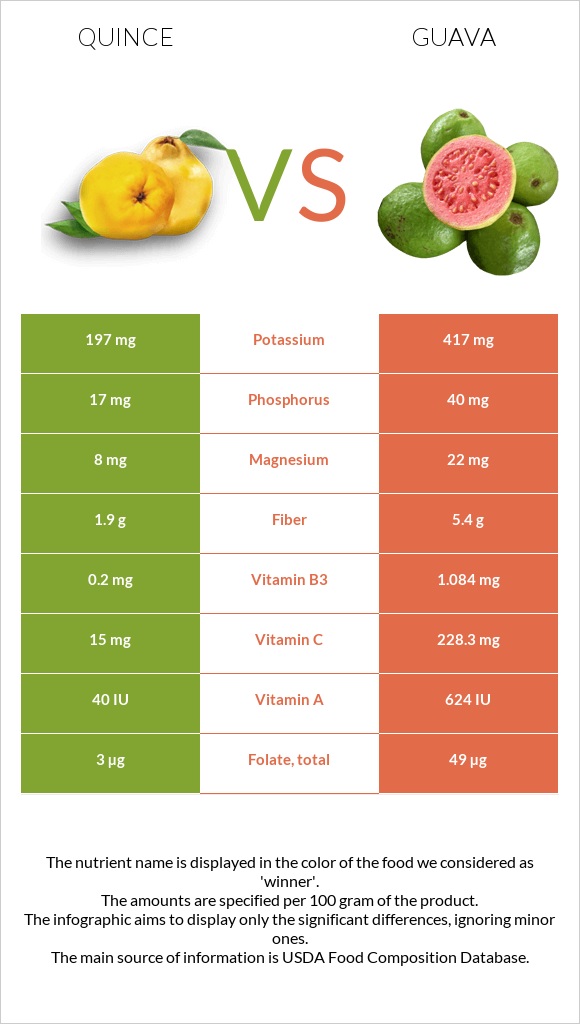
Nutrition
Vitamins and Minerals
Guava has richer vitamin and mineral profiles than quince. It contains 15 times more vitamin A and vitamin C than quince, and it is also significantly richer in all B-group vitamins.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+1422%
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+1450%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+235%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+33.3%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+442%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+456.8%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+175%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+1533.3%
For their mineral content, guava is more affluent in copper, potassium, and zinc, whereas quince is higher in iron.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
IronIron
+169.2%
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+175%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+63.6%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+111.7%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+76.9%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+475%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+135.3%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-50%
Micronutrients
Guava also contains more protein, polyunsaturated fats, and dietary fiber, while quince is higher in net carbs.
Both fruits are low in calories; however, guava contains slightly more calories.
Health Impact
These fruits have been part of the human diet since ancient times, and their health benefits have been known for centuries.
Quince is known for its effects on digestive disorders. Quince may decrease the risk of having stomach ulcers. Quince may beneficially affect nausea, constipation, and hemorrhoids, whereas quince leaves may help with diarrhea. It may also beneficially affect coughing and help heal cuts and injuries (1, 2, 3).
Guava has beneficial effects on diabetes and hypercholesterolemia. It also acts as a cough suppressant. It has protective functions against heart disease and cancer development (4).
Both these fruits are rich in antioxidants that neutralize free radicals and reduce oxidative stress, which lowers inflammation and decreases the risks of multiple diseases. The guava leaf extract is anti-hyperglycemic and widely used in treating diabetes (5).
Cardiovascular health
Studies have shown that extracts from quince leaves at 320mg/kg doses have an antihypertensive effect similar to Captopril. Another study found that an aqueous-methanolic extract from quince seeds was most effective at 600mg/kg and prevented increased blood pressure (6).
Guava also has ACE inhibitory activity similar to antihypertensive drugs like Captopril and Perindopril and antioxidative properties, essential in reducing cardiovascular risk (7, 8).
The quince fruit is packed with quinic acid, shikimic derivatives, procyanidins, and flavonoids, which can help prevent atherosclerosis. Notably, the quince peel extract had the highest antioxidant activity (6).
According to this research, the extract obtained from quince leaves can regulate the levels of lipids in the blood, much like Atorvastatin. However, it did not show significant improvement in atherosclerosis caused by a high-fat diet. Therefore, reducing the intake of high-fat foods in your diet is recommended.
Other studies also found that the aqueous extract of quince fruit and guava may significantly lower serum levels of TG (triglycerides) and LDL (“bad” cholesterol) while increasing the levels of HDL (“good” cholesterol) (6, 9).
References
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16448180/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3746575/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3746946/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5628524/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28347786/
- https://www.hindawi.com/journals/ecam/2022/3185442/
- https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00580-015-2192-y
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27104032/
- https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.1088/1755-1315/276/1/012054/meta
Infographic
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Vitamin C | 15mg | 228.3mg | 237% |
| Fiber | 1.9g | 5.4g | 14% |
| Folate | 3µg | 49µg | 12% |
| Copper | 0.13mg | 0.23mg | 11% |
| Manganese | 0.15mg | 7% | |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.081mg | 0.451mg | 7% |
| Potassium | 197mg | 417mg | 6% |
| Iron | 0.7mg | 0.26mg | 6% |
| Vitamin B3 | 0.2mg | 1.084mg | 6% |
| Vitamin E | 0.73mg | 5% | |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.04mg | 0.11mg | 5% |
| Protein | 0.4g | 2.55g | 4% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.02mg | 0.067mg | 4% |
| Magnesium | 8mg | 22mg | 3% |
| Phosphorus | 17mg | 40mg | 3% |
| Vitamin A | 2µg | 31µg | 3% |
| Zinc | 0.04mg | 0.23mg | 2% |
| Vitamin K | 2.6µg | 2% | |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.05g | 0.401g | 2% |
| Calories | 57kcal | 68kcal | 1% |
| Fats | 0.1g | 0.95g | 1% |
| Calcium | 11mg | 18mg | 1% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.03mg | 0.04mg | 1% |
| Choline | 7.6mg | 1% | |
| Saturated fat | 0.01g | 0.272g | 1% |
| Net carbs | 13.4g | 8.92g | N/A |
| Carbs | 15.3g | 14.32g | 0% |
| Sugar | 8.92g | N/A | |
| Sodium | 4mg | 2mg | 0% |
| Selenium | 0.6µg | 0.6µg | 0% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 0.036g | 0.087g | 0% |
| Tryptophan | 0.022mg | 0% | |
| Threonine | 0.096mg | 0% | |
| Isoleucine | 0.093mg | 0% | |
| Leucine | 0.171mg | 0% | |
| Lysine | 0.072mg | 0% | |
| Methionine | 0.016mg | 0% | |
| Phenylalanine | 0.006mg | 0% | |
| Valine | 0.087mg | 0% | |
| Histidine | 0.022mg | 0% |
Macronutrient Comparison
| Contains more ProteinProtein | +537.5% |
| Contains more FatsFats | +850% |
| Contains more OtherOther | +245% |
Fat Type Comparison
| Contains less Sat. FatSaturated fat | -96.3% |
| Contains more Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat | +141.7% |
| Contains more Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat | +702% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Quince - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/168163/nutrients
- Guava - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/173044/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.






