Sweet Potato vs. Red Potato - What’s the Difference?


Summary
To sum up, sweet potatoes and red potatoes are only distinctly related to each other, belonging to different families.
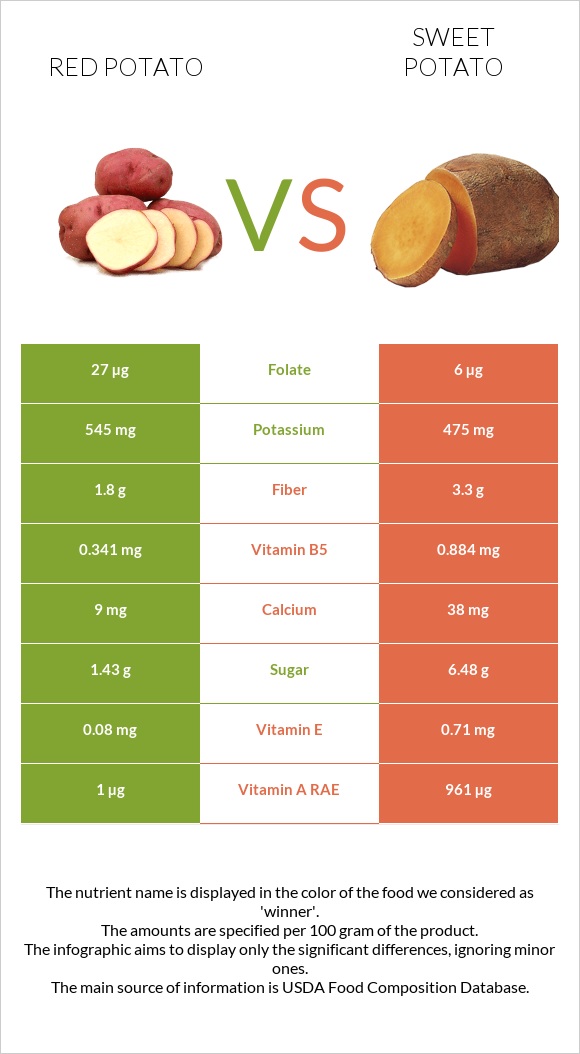
Sweet potatoes are overall richer in carbohydrates, containing slightly more net carbs and almost 2 times more dietary fiber.
Sweet potatoes are a better source of vitamins, being 1921 times higher in vitamin A and falling in the top 3% of foods as a source of this vitamin, and 8 times higher in vitamin E. They are also richer in calcium.
At the same time, red potatoes are richer in vitamin B9 or folate, phosphorus, potassium, and zinc. Red potatoes are lower in sodium.
Sweet potatoes have a lower glycemic index. A few studies suggest that sweet potatoes may have a more beneficial impact on cardiovascular health and the prevention of diabetes.
Introduction
Despite their similarities, sweet potatoes and red potatoes are two different types of vegetables that vary in their taste, texture, and nutritional profile. This article will look at these differences, primarily focusing on nutrition and health impact.
Classification
Red potatoes and sweet potatoes are both tuberous root vegetables. However, they belong to different families and are only distantly related.
Sweet potatoes (Ipomoea batatas) belong to the morning glory or bindweed family, whereas red potatoes are a variety of potatoes (Solanum tuberosum), which belong to the nightshade family.
Sweet potatoes are sometimes confused with yams; however, these are also different root vegetables. On our page, you can learn more about the differences between yams and sweet potatoes.
Appearance, Taste, And Use
Sweet potatoes are usually orange on the inside, with a sweet and slightly nutty flavor. Red potatoes, on the other hand, have white or yellow flesh and thin red skin. They have a mild, earthy flavor and a firmer texture than sweet potatoes.
Thus, they might look similar on the outside, but the flesh of sweet potatoes is orange, while red potatoes have white flesh.
Sweet potatoes are often used in savory dishes but are also popular in sweet dishes like pies and casseroles. Both are often used in potato salads, roasted potatoes, and mashed potatoes. Red potatoes are rarely used in baking.
Potatoes are dairy-free and gluten-free and may be used to make a milk alternative or gluten-free potato bread.
In short, if you want a sweeter flavor and softer texture, you can go for sweet potatoes, while red potatoes may be the better option if you prefer a firmer texture and more neutral flavor.
Nutrition
The nutritional information in this article is provided for 100g servings of baked sweet and red potatoes, with flesh and skin.
The average serving size for one person of these foods can be considered to be one medium potato. An average sweet potato is around 114g, while a medium red potato weighs about 173g.
Macronutrients and Calories
Cooked sweet and red potatoes have similar macronutrient compositions, both consisting of around 76% water and 24% nutrients.
Macronutrient Comparison
Contains
more
ProteinProtein
+14.4%
Calories
Sweet and red potatoes are also very alike in the number of calories they provide. Sweet potato provides only one more calorie per every 100g, providing 90 calories.
Carbohydrates
Sweet potatoes are somewhat higher in carbohydrates overall, containing 20.7g per 100g serving, whereas red potatoes have 19.6g in the same serving size.
Red potatoes are slightly higher in net carbs, being over 2 times higher in starch, while sweet potatoes contain nearly 4.5 times more sugar and 2 times more dietary fiber.
To put this information in numbers, sweet potatoes and red potatoes contain 17.4g and 17.8g of net carbs and 3.3g and 1.8g of dietary fiber, respectively.
Sweet potato contains 3g of maltose, which is absent in red potato.
Carbohydrate type comparison
Contains
more
StarchStarch
+114.9%
Contains
more
SucroseSucrose
+406.7%
Contains
more
FructoseFructose
+13.6%
Contains
more
MaltoseMaltose
+∞%
Protein
Red potatoes are slightly higher in protein than sweet potatoes - 0.3g per every 100g serving to be exact.
While both these foods contain some level of all essential amino acids, sweet or red potatoes are not the best source of this nutrient.
Fats
Sweet and red potatoes are equally low in fats, containing insignificant amounts.
Naturally, neither contains cholesterol.
Vitamins
Sweet potatoes are the ultimate winner in the vitamin category.
Sweet potatoes fall in the top 3% of foods as a source of vitamin A and contain 1921 times more of this vitamin than red potatoes, which are nearly absent in it. In fact, 100g of sweet potatoes provides more than 3 times the recommended daily value of vitamin A.
Sweet potato also contains 8 times more vitamin E, 3 times more vitamin B5, 2 times more vitamin B2, and overall more vitamins C, B1, and B6.
Nevertheless, red potatoes provide 4 times more folate or vitamin B9 and more vitamin K.
The potatoes are naturally absent in vitamins B12 and D.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin KVitamin K
+21.7%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+350%
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+55.6%
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+96000%
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+787.5%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+48.6%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+112%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+159.2%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+34.9%
Minerals
Conversely, red potatoes can be considered a better source of minerals. Red potatoes are richer in phosphorus, potassium, and zinc. They are also lower in sodium.
At the same time, sweet potatoes contain 4 times more calcium and 2.8 times more manganese.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+14.7%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+25%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+33.3%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-66.7%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+322.2%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+187.3%
Glycemic Index
The glycemic index of red potatoes, boiled with skin on in salted water, is 89 (1). This is classified as a high glycemic index value.
The glycemic index of sweet potatoes is better researched. Depending on the cooking method, this value can significantly differ. The average glycemic index of roasted sweet potatoes, based on 11 studies, is 88. However, the mean glycemic index of boiled sweet potatoes, based on 13 studies, is 46 (1).
Thus, boiled red potatoes have a high value of 89, while boiled sweet potatoes have a low value of 46.
Insulin Index
The insulin index of foods is another way of looking at the food’s impact on the body. To learn more, you can visit our “Glycemic Index vs. Insulin Index” page.
Despite the low glycemic index, steamed orange sweet potatoes have been researched to have a high insulin index value of 96 (2).
While an exact number has not yet been researched for red potatoes, it can be assumed to be close to potatoes. Boiled Russet potatoes have an insulin index of 121 (3).
Acidity
The PRAL value of foods shows how much acid or base is produced in the organism by the consumed food.
The PRAL values of red and sweet potatoes are -8.5 and -8.2, making both alkaline or base-producing foods.
Health Impact
Cardiovascular Health
Purple sweet potatoes have a high content of phytochemicals called anthocyanins and carotenoids, which is primarily responsible for their potent antioxidant potential. Eating sweet potatoes high in anthocyanins has been linked to increased cognitive performance and reduced risk of cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and cancer (4).
In male obese mice, sweet potatoes have been shown to potentially reduce the risk of obesity and cardiovascular disease by alleviating weight gain, fat tissue expansion, and liver damage and improving insulin sensitivity (5).
However, there is a study linking sweet potato consumption with high blood pressure (6).
There is not enough research on the impact of red potatoes on the cardiovascular system; however, a higher potato consumption overall has been linked negatively to cardiovascular risk factors (7).
Diabetes
Boiled sweet potatoes have a much lower glycemic index, while roasted sweet potatoes and boiled red potatoes have high glycemic index values. The insulin index of sweet potatoes is also lower than that of potatoes. Thus, boiled sweet potatoes may be the more favorable choice for people with diabetic conditions.
Research has proven that sweet potatoes may be effective in treating high blood glucose conditions and may regulate dyslipidemia, which is an imbalance of blood lipids, such as cholesterol, low-density and high-density lipoproteins (8).
Sweet potato intake may also reduce glycosylated hemoglobin A1c and improve insulin sensitivity (9).
Similarly, not enough research has been carried out on the impact of red potatoes on the development of diabetes. Nonetheless, research finds an association between a high intake of potatoes and type 2 diabetes (10, 11).
Digestive Health
Both sweet and red potatoes, preferably cooked and without skin, are mostly safe to consume for people with inflammatory bowel disease - Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis (12).
½ of sweet potatoes and 1 cup of potatoes are also easily tolerated by most people with IBS, as they are low in FODMAPs in those amounts.
Sweet Potato & Ocular Health
Vitamin A is a fat-soluble vitamin abundant in sweet potatoes. Vitamin A is critical for healthy vision; it is also needed for adequate immunity, cellular functioning, growth and development, reproduction, etc.
Vitamin A deficiency negatively affects the different parts of the eye and several organs. Severe vitamin A deficiency causes xerophthalmia, a type of blindness manifesting with night blindness. It is one of the most common causes of preventable blindness in children (13).
Sources
- https://academic.oup.com/ajcn/article/114/5/1625/6320814
- https://ses.library.usyd.edu.au/handle/2123/11945
- https://academic.oup.com/ajcn/article/66/5/1264/4655967
- https://www.mdpi.com/2076-3921/11/9/1648
- https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fnut.2022.1016020/full
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0261561418311920
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32190135/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8509747/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6486146/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6294859/
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/329790914
- https://www.crohnscolitisfoundation.org/sites/default/files/legacy/assets/pdfs/diet-nutrition-2013.pdf
- https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/VitaminA-HealthProfessional/
Infographic
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Vitamin A | 1µg | 961µg | 107% |
| Manganese | 0.173mg | 0.497mg | 14% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.341mg | 0.884mg | 11% |
| Vitamin C | 12.6mg | 19.6mg | 8% |
| Fiber | 1.8g | 3.3g | 6% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.212mg | 0.286mg | 6% |
| Folate | 27µg | 6µg | 5% |
| Vitamin E | 0.08mg | 0.71mg | 4% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.05mg | 0.106mg | 4% |
| Calcium | 9mg | 38mg | 3% |
| Starch | 15.15g | 7.05g | 3% |
| Phosphorus | 72mg | 54mg | 3% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.072mg | 0.107mg | 3% |
| Potassium | 545mg | 475mg | 2% |
| Protein | 2.3g | 2.01g | 1% |
| Copper | 0.174mg | 0.161mg | 1% |
| Zinc | 0.4mg | 0.32mg | 1% |
| Sodium | 12mg | 36mg | 1% |
| Vitamin B3 | 1.595mg | 1.487mg | 1% |
| Choline | 18.9mg | 13.1mg | 1% |
| Calories | 89kcal | 90kcal | 0% |
| Fats | 0.15g | 0.15g | 0% |
| Net carbs | 17.79g | 17.41g | N/A |
| Carbs | 19.59g | 20.71g | 0% |
| Magnesium | 28mg | 27mg | 0% |
| Iron | 0.7mg | 0.69mg | 0% |
| Sugar | 1.43g | 6.48g | N/A |
| Selenium | 0.2µg | 0% | |
| Vitamin K | 2.8µg | 2.3µg | 0% |
| Saturated fat | 0.026g | 0.052g | 0% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 0.002g | 0.002g | 0% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.043g | 0.092g | 0% |
| Tryptophan | 0.023mg | 0.04mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 0.075mg | 0.107mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 0.074mg | 0.07mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 0.109mg | 0.118mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 0.12mg | 0.084mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.035mg | 0.037mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 0.091mg | 0.114mg | 0% |
| Valine | 0.115mg | 0.11mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.039mg | 0.039mg | 0% |
| Fructose | 0.44g | 0.5g | 0% |
Fat Type Comparison
| Contains less Sat. FatSaturated fat | -50% |
| Contains more Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat | +114% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Red potato - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/170435/nutrients
- Sweet potato - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/168483/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.






