Salmonberry vs Cloudberry - Health impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Cloudberries are higher in protein and vitamin C, while Salmonberries are richer in carbs and vitamin A. Salmonberries provide 17 times less vitamin C than Cloudberries.
Introduction
This article will compare the nutritional content and health impact of raw Salmonberry (1) and Cloudberry (2).
Actual differences
Rubus spectabilis, also known as salmonberry, is native to west-central Alaska. Rubus chamaemorus is the Latin name of the cloudberry; this berry is also native to Alaska. Salmonberry has red, orange, or yellow berries, while cloudberries have golden-yellow coloring. Salmonberry has a more subtle flavor, and it is tart, whereas cloudberry’s taste combines tart and sweet flavors. Salmonberries and cloudberries differ in their usage: salmonberries are commonly used to flavor wine and beer, but cloudberry is usually used for making jams, tarts, and desserts.
Macronutrients
Both salmonberry and cloudberry are members of the Rosaceae family and tend to have many similarities, yet there are differences in how the macronutrients are distributed in each.
Calories
Salmonberry and Cloudberry are plant food products. Hence, these two are considered low-calorie foods. However, Cloudberry is higher in calories.
Carbs
Salmonberry is higher in carbs compared to Cloudberry.
Salmonberry provides 1.9g of dietary fiber per 100g, while the same amount of Cloudberry does not contain fiber.
Salmonberry is rich in soluble fiber.
Protein
These two berries are not supposed to contain much protein. Still, Cloudberry is three times higher in proteins than Salmonberry.
Fats
Both berries have less than 1g of fat per 100g, so we can neglect the fat amounts. Salmonberry and Cloudberry do not contain any amount of cholesterol.
Vitamins
Salmonberry and Cloudberry are rich in different vitamins.
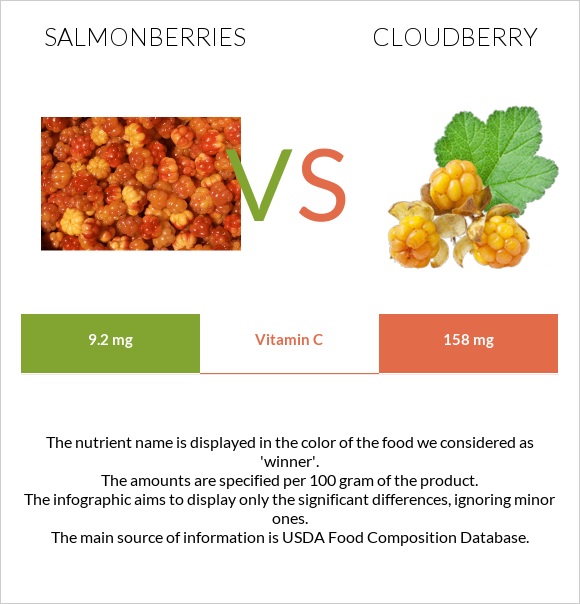
Cloudberries are an excellent source of vitamin C: they are 17 times higher in vitamin C (158mg per 100g) than Salmonberries (9.2mg per 100g).
Salmonberry is richer in vitamins A, E, K, and folate, while Cloudberry provides more B1 and B3.
Salmonberry covers 37% of the DV of vitamin K and 33% of the DV of vitamin E, while Cloudberry does not provide any amounts of these vitamins.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin KVitamin K
+∞%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+1617.4%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+22%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+12.9%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+93.1%
Minerals
Salmonberry is higher in magnesium and zinc.
Cloudberry is richer in calcium and phosphorus.
You can compare the mineral composition of these two berries in the chart below.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+∞%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+∞%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+∞%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+∞%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+∞%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+38.5%
Contains
more
IronIron
+75%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+29.6%
Health impact
Both salmonberry and cloudberry have powerful plant compounds that have beneficial effects on the human organism.
Cloudberries are packed with vitamin C and ellagitannins - powerful antioxidants that protect the cells from oxidative damage. According to some studies (3) (4), ellagitannins may fight against inflammation and have anticancer effects.
Salmonberry is a depo of manganese. This mineral plays a crucial role in metabolism and bone health. In addition, manganese has antioxidant properties (5) (6).
REFERENCES
- https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/168048/nutrients
- https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/169802/nutrients
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27187472/
- https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/elsc.201400069
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22072939/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29293455/
Infographic
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Vitamin C | 9.2mg | 158mg | 165% |
| Manganese | 1.1mg | 48% | |
| Vitamin K | 14.8µg | 12% | |
| Vitamin E | 1.61mg | 11% | |
| Fiber | 1.9g | 8% | |
| Vitamin A | 50µg | 6% | |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.078mg | 6% | |
| Magnesium | 15mg | 4% | |
| Iron | 0.4mg | 0.7mg | 4% |
| Folate | 17µg | 4% | |
| Protein | 0.85g | 2.4g | 3% |
| Potassium | 110mg | 3% | |
| Copper | 0.03mg | 3% | |
| Zinc | 0.28mg | 3% | |
| Vitamin B3 | 0.466mg | 0.9mg | 3% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.167mg | 3% | |
| Fructose | 1.75g | 2% | |
| Fats | 0.33g | 0.8g | 1% |
| Calcium | 13mg | 18mg | 1% |
| Phosphorus | 27mg | 35mg | 1% |
| Sodium | 14mg | 1% | |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.041mg | 0.05mg | 1% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.062mg | 0.07mg | 1% |
| Calories | 47kcal | 51kcal | 0% |
| Net carbs | 8.15g | 8.6g | N/A |
| Carbs | 10.05g | 8.6g | 0% |
| Sugar | 3.66g | N/A |
Macronutrient Comparison
| Contains more CarbsCarbs | +16.9% |
| Contains more ProteinProtein | +182.4% |
| Contains more FatsFats | +142.4% |
| Contains more OtherOther | +114.3% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Salmonberries - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/168048/nutrients
- Cloudberry - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/169802/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.