Soybean vs. Peanut — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
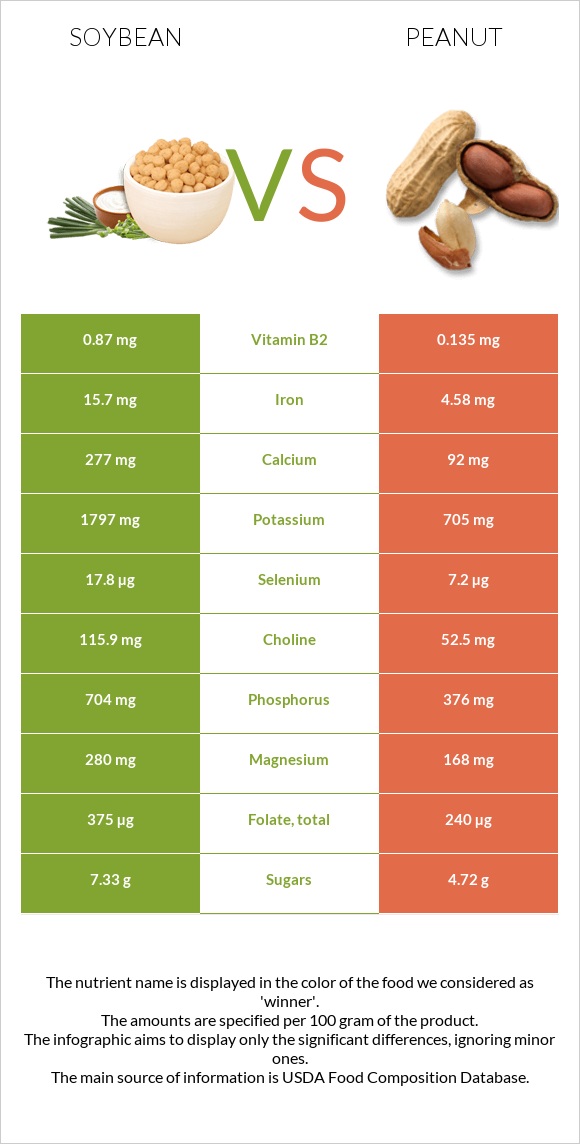
Peanuts contain 30 times more vitamin B3 than soybeans. Peanuts are also higher in copper, vitamin E, vitamins B1, B3, B5, and B6, as well as folate, manganese, and zinc.
The amounts of protein, fats, and carbs are also high in peanuts. In particular, peanuts have 20 times more monounsaturated fats, 3 times more polyunsaturated fats, and more fiber than soybeans.
Soybeans, on the other hand, have more iron and vitamins C, B2, A, and K. Soybeans are also lower in sodium and saturated fats.
Introduction
In this article, we will compare peanuts and soybeans, their nutritional values, and their health impact.
The food types used for comparison are raw peanuts and cooked boiled soybeans (without salt).
Nutrition
Calories
Peanuts have almost 4 times more calories than soybeans. They contain 567 calories per 100g, while soybeans have 172 calories per 100g.
Most of the peanut calories come from its fat content.
Vitamins
Peanuts have a greater vitamin content than soybeans. These nuts contain more vitamin E, vitamin B1, vitamins B2, B3, B5, B6, folate, and choline. The amount of vitamin B is 10 times higher in peanuts.
However, soybeans have more vitamins C, A, B2, and K.
Both lack vitamin D and vitamin B12.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+111.1%
Contains
more
Vitamin KVitamin K
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+2280%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+312.9%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+2924.1%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+887.2%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+48.7%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+344.4%
Minerals
Peanuts contain more magnesium, potassium, phosphorus, copper, zinc, and manganese than soybeans. The amounts of magnesium and potassium are almost 2 times higher in peanuts.
However, soybeans are richer in calcium and iron and have lower sodium content than peanuts.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
IronIron
+12.2%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-94.4%
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+95.3%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+36.9%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+181.1%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+184.3%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+53.5%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+134.7%
Fats
Peanuts contain 20 times more fats than soybeans. They are richer in monounsaturated fats (24g) and polyunsaturated fats (16g) and contain more saturated fats (6g).
Protein
The amounts of protein in peanuts are higher than in soybeans.
Peanuts contain 25.8g, and soybeans have 18.21g of protein per 100g. Both foods contain essential amino acids, such as lysine, histidine, and phenylalanine.
Carbs
And again, peanuts are richer in carbs than soybeans.
Peanuts have almost 2 times more carbs than soybeans.
Soybeans have 8.36g of carbs per 100g, while peanuts have 16.3g of carbs.
However, both are great sources of fiber, containing 8.5g and 6g of fiber, accordingly.
Oxalates
Soybeans have 3 times more oxalates than peanuts. Soybeans have 224mg of oxalates per 100g, while peanut offers 76mg of oxalates.
If you are on a low-oxalate diet, it is better to avoid these foods.
Glycemic Index
Both foods have similar glycemic indexes. The glycemic index of soybeans is equal to 15, and peanuts have a GI of 13. The insulin index of peanuts is also low, equal to 20.
Soybeans’ glycemic load is equal to 1, meaning it will not raise your blood glucose level after eating.
Health Benefits
Cardiovascular Health
- Peanuts: A study published in Frontiers in Nutrition found that peanut consumption may improve lipid profiles, as the total cholesterol/HDL-cholesterol and LDL-cholesterol/HDL-cholesterol ratios were slightly lower in the peanut consumption group compared to the control group after a 6-month intervention (1).
- Soybeans: Research in The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition concluded that soy isoflavones significantly reduced serum total and LDL cholesterol, indicating benefits for cardiovascular health (2).
Diabetes Management
- Peanuts: The American Diabetes Association classifies peanuts and other nuts as excellent foods for managing diabetes. This is due to their high content of magnesium, fiber, and heart-healthy oils, along with their minimal impact on blood sugar levels (3).
- Soybeans: A study in Diabetes Care demonstrated that soy protein combined with isoflavones can improve glycemic control, insulin resistance, and lipid profiles in patients with type 2 diabetes (4).
Cancer Prevention
- Peanuts: Research in Food Science & Nutrition indicated that resveratrol, a compound found in peanuts, has inhibitory effects on human breast cancer cells, suggesting potential anti-cancer properties (5).
- Soybeans: A meta-analysis in JAMA found that among women with breast cancer, soy food consumption was significantly associated with decreased risk of death and recurrence, highlighting the protective role of soy isoflavones (6).
References
- https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/nutrition/articles/10.3389/fnut.2022.853378/full
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17413118/
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4711439/
- https://diabetesjournals.org/care/article/30/7/1871/26510/Effects-of-Isoflavone-Dietary-Supplementation-on
- https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/fsn3.3590
- https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/fullarticle/185034
Infographic
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Copper | 0.407mg | 1.144mg | 82% |
| Vitamin B3 | 0.399mg | 12.066mg | 73% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 5.064g | 15.558g | 70% |
| Fats | 8.97g | 49.24g | 62% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 1.981g | 24.426g | 56% |
| Vitamin E | 0.35mg | 8.33mg | 53% |
| Manganese | 0.824mg | 1.934mg | 48% |
| Folate | 54µg | 240µg | 47% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.155mg | 0.64mg | 40% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.179mg | 1.767mg | 32% |
| Saturated fat | 1.297g | 6.279g | 23% |
| Calories | 172kcal | 567kcal | 20% |
| Magnesium | 86mg | 168mg | 20% |
| Zinc | 1.15mg | 3.27mg | 19% |
| Phosphorus | 245mg | 376mg | 19% |
| Vitamin K | 19.2µg | 0µg | 16% |
| Protein | 18.21g | 25.8g | 15% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.285mg | 0.135mg | 12% |
| Fiber | 6g | 8.5g | 10% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.234mg | 0.348mg | 9% |
| Iron | 5.14mg | 4.58mg | 7% |
| Potassium | 515mg | 705mg | 6% |
| Carbs | 8.36g | 16.13g | 3% |
| Vitamin C | 1.7mg | 0mg | 2% |
| Calcium | 102mg | 92mg | 1% |
| Sodium | 1mg | 18mg | 1% |
| Choline | 47.5mg | 52.5mg | 1% |
| Net carbs | 2.36g | 7.63g | N/A |
| Sugar | 3g | 4.72g | N/A |
| Selenium | 7.3µg | 7.2µg | 0% |
| Tryptophan | 0.242mg | 0.25mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 0.723mg | 0.883mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 0.807mg | 0.907mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 1.355mg | 1.672mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 1.108mg | 0.926mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.224mg | 0.317mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 0.869mg | 1.377mg | 0% |
| Valine | 0.831mg | 1.082mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.449mg | 0.652mg | 0% |
Macronutrient Comparison
| Contains more WaterWater | +862.3% |
| Contains more ProteinProtein | +41.7% |
| Contains more FatsFats | +448.9% |
| Contains more CarbsCarbs | +92.9% |
| Contains more OtherOther | +22% |
Fat Type Comparison
| Contains less Sat. FatSaturated fat | -79.3% |
| Contains more Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat | +1133% |
| Contains more Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat | +207.2% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Soybean - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/174271/nutrients
- Peanut - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/172430/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.






