Cinnamon vs. Ground cloves — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
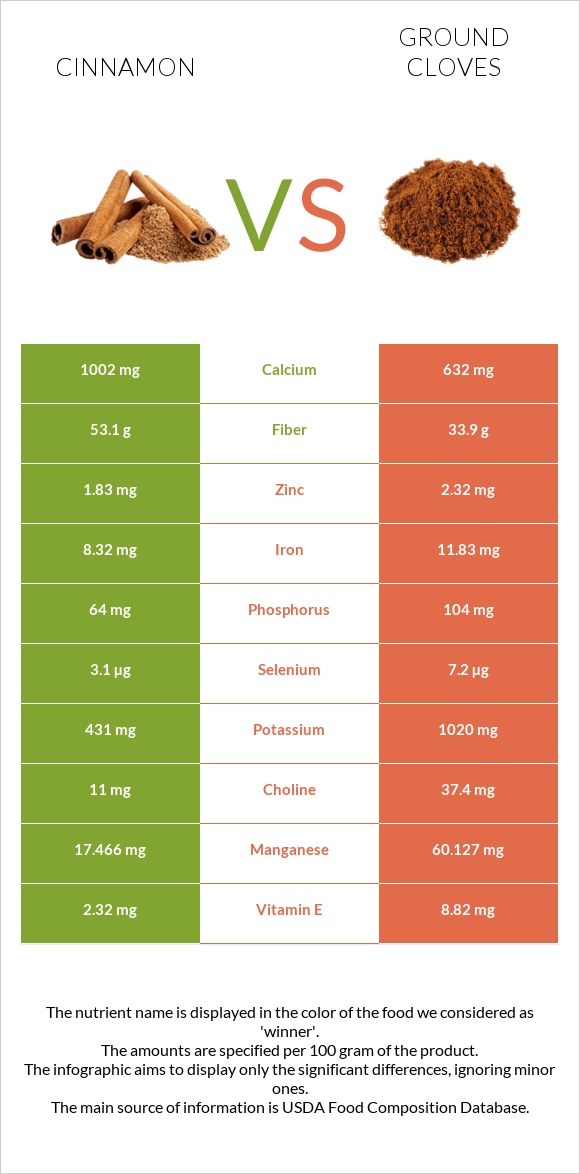
Cinnamon is higher in calcium, vitamins A and E, carbs, and oxalates. On the other hand, cloves are high in magnesium, potassium, manganese, choline, phosphorus, selenium, iron, protein, folate, and monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats. It contains more vitamins E, K, B1, B2, B3, B5, and B6. Moreover, cinnamon has less sodium, saturated fats, and calories.
Introduction
Cinnamon and cloves are spices. They are not similar in taste or origin but complement each other well in many dishes.
Cinnamon is a spice made from the inner bark of trees belonging to the genus Cinnamomum. The two most commonly used types of cinnamon are Ceylon cinnamon and Cassia cinnamon. Ceylon cinnamon originates from Sri Lanka. Cassia cinnamon is native to China and in other areas of Asia, such as Indonesia and Vietnam.
Cloves are dried flower buds from the clove tree (Syzygium aromaticum), endemic to the Maluku Islands in Indonesia, popularly known as the Spice Islands. Other tropical locations where cloves are grown include Madagascar, Tanzania, Sri Lanka, India, Indonesia, and Vietnam.
Nutrition
In this section, we will compare the nutritional values of cinnamon and ground cloves, concentrating on differences. The information below is for a hundred grams of each food.
The typical serving size for cinnamon and ground cloves is 0.25 teaspoons or 0.5 grams. Since the serving size is small, the amount of macronutrients, vitamins, and minerals in each serving is minimal.
Macronutrients and Calories
Cinnamon and ground cloves have similar densities, with cinnamon containing 10.5% water and cloves containing 10% water per 100 g. However, they differ in their macronutrient content. Ground cloves contain slightly more protein and higher amounts of fat than cinnamon, which has a higher carbohydrate content.
Macronutrient Comparison
Contains
more
CarbsCarbs
+23%
Contains
more
ProteinProtein
+49.6%
Contains
more
FatsFats
+948.4%
Contains
more
OtherOther
+56.4%
Calories
Compared to cinnamon, ground cloves have more calories per hundred grams. A hundred grams of cinnamon provides 247 calories, whereas ground cloves have 274 calories. One teaspoon of cinnamon has four kcal, whereas one teaspoon of ground cloves provides six kcal.
Protein
Ground cloves have more protein than cinnamon. A hundred grams of cinnamon has 4g of protein, whereas ground cloves have 6g. Ground cloves are high in all amino acids except for tryptophan.
Fats
Compared to cinnamon, ground cloves have over ten times more fat. A hundred grams of cinnamon has 1.3g of fat, while ground cloves provide 13g. Cinnamon has less saturated fat, whereas ground cloves are high in monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fat. In addition, ground cloves have 0.254g of trans fats per hundred grams, while cinnamon lacks it.
Fat Type Comparison
Contains
less
Sat. FatSaturated fat
-91.3%
Contains
more
Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat
+466.3%
Contains
more
Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat
+5202.9%
Carbohydrates
Cinnamon is high in total carb content. However, cinnamon has a higher dietary fiber content, whereas ground cloves are high in net carbs. A hundred grams of cinnamon contain 80.59g of carbs, whereas ground cloves provide 65.53g.
In a 100g serving, cinnamon and ground cloves have 27.49g and 31.63g of net carbs, respectively.
In a 100g serving, cinnamon and ground cloves have 53.1g and 33.9g of dietary fiber, respectively.
Both contain equal amounts of sucrose, fructose, and glucose. Ground cloves also contain 0.15g of galactose, whereas cinnamon lacks it.
Carbohydrate type comparison
Contains
more
GalactoseGalactose
+∞%
Cholesterol
Cinnamon and ground cloves are cholesterol-free.
Vitamins
Cinnamon has over 1.8 times more vitamin A and 19 times more vitamin C. In a 100g serving, cinnamon and ground cloves have 3.8mg and 0.2 mg of vitamin C, respectively. Unlike it, ground cloves have over 3.8 times more vitamin E, four times more folate, and 4.5 times more vitamin K. Cloves also contain more vitamins B1, B2, B3, B5, and B6.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+1800%
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+87.5%
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+280.2%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+618.2%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+436.6%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+17.1%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+42.2%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+147.5%
Contains
more
Vitamin KVitamin K
+354.5%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+316.7%
Minerals
Cinnamon provides over 1.5 times more calcium, whereas ground cloves contain over 2.5 times more potassium, 4.5 times more magnesium, and 3.5 times more manganese. Cloves are also high in iron, selenium, phosphorus, and choline. On the other hand, cinnamon provides over 28 times less sodium. In a 100g serving, cinnamon and ground cloves have 10 mg and 277 mg of sodium, respectively.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+58.5%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-96.4%
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+331.7%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+136.7%
Contains
more
IronIron
+42.2%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+26.8%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+62.5%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+244.3%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+132.3%
Oxalate content
Both are high in oxalates. However, cinnamon has a higher oxalate content. A 100-gram serving of cinnamon contains 3460mg of oxalate, whereas the oxalate content of ground cloves is 3245mg. Because the serving size is small, each serving contains very few oxalate levels.
Acidity
The potential renal acid load (PRAL) level indicates the food's capacity to degrade into acids or bases within the body. Cinnamon has a PRAL level of -19.3, whereas the PRAL value of ground cloves is -29.6. Both are alkaline-forming.
Health Benefits
Antioxidant Activities
Overall, cinnamon and cloves contain high levels of phenolics and have antioxidant properties (1). Among spices, clove has the highest concentration of antioxidant chemicals (2).
Neuroprotective Activities
Antioxidants play a crucial role in addressing memory deficits induced by oxidative stress. According to the study, clove oil may improve short and long-term memory and learning impairments caused by scopolamine through its antioxidant properties (2).
Sodium benzoate (NaB), a metabolite of cinnamon, has neuroprotective properties. Studies suggest that NaB may reduce the production of proinflammatory chemicals in activated glial cells (3).
Antibacterial Activities
Several studies have indicated the potential effectiveness of cinnamon extracts and essential oils in combating oral cavity infections. Research revealed that cinnamon essential oil exhibited activity against Streptococcus mutans and Lactobacillus acidophilus, which play roles in dental plaque formation and caries development. More recent investigations have explored the antibacterial properties of fresh leaf extract from Cinnamomum zeylanicum against Enterococcus faecalis (4).
Clove oil possesses various biological properties, including antibacterial, antifungal, and insecticidal activities. Furthermore, it serves as an antiseptic in treating oral infections. Studies have indicated that it may inhibit the growth of bacteria, molds, and yeasts (5).
The research found that cinnamon and clove oil have antibacterial properties against wound pathogens such as Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Escherichia coli, and Klebsiella pneumoniae (6, 7).
Anticancer Activities
Cinnamon extract inhibits cancer cells by inducing apoptosis and blocking NFκB and AP1 (8).
β-Caryophyllene (CPO), a key component of cinnamon, has shown potential in altering cancer cell survival pathways. It has antiproliferative effects on prostate and breast cancer cells (9).
Eugenol found in cloves and cinnamon may repress the development of malignant melanoma growth, decrease tumor size, and inhibit melanoma invasion and metastasis (2, 10).
The ethanol extract of clove (EEC) may increase cell growth inhibition in various human cancer cell lines encompassing breast, ovarian, cervical, liver, pancreatic, and colon cells (11).
Classification
Cinnamon belongs to the family Lauraceae and the genus Cinnamomum. Cloves belong to the family Myrtaceae and the genus Syzygium.
Appearance
Cinnamon is usually sold in thin, curled sticks (cinnamon sticks) or ground into a fine powder. Cloves are sold whole or ground into a powder. For a fresher flavor, you can grind whole spices (cinnamon and cloves) using a spice grinder or a mortar and pestle.
Whole cinnamon sticks are slender, curled, and reddish-brown. A cinnamon stick is typically about 2 to 4 inches (5 to 10 centimeters) long. In contrast, the cloves are around 1/2 to 3/4 inch (1 to 2 centimeters) in length. The sticks have a rough texture and have multiple layers of rolled bark.
Whole cloves are small, dark brown, and nail-shaped. The texture of cloves has visible ridges and bumps.
Ground cinnamon is a powder with a rich reddish-brown hue. It has a smooth texture, though it may have a slight graininess. Ground cinnamon emits a strong, characteristic aroma. Ground cloves are a dark brown powder. Ground cloves release a potent, aromatic scent. They have a smooth texture, though some fibrous bits may be present.
Taste and Use
Cinnamon's flavor is warm, sweet, and somewhat spicy, with a tinge of woodiness. It has a soothing and fragrant quality.
Ground cloves are robust, spicy, and bitter, with a sweet and peppery undertone. They also have a characteristic warm, spicy scent.
Cinnamon goes nicely with different ingredients, including fruits, chocolate, nuts, and warm spices like nutmeg, cardamom, and cloves. Cloves work nicely with citrus fruits, apples, pumpkins, and ginger.
Cinnamon is a versatile spice employed in both savory and sweet dishes. It finds its way into delectable baked goods like cinnamon rolls and apple pies, adds depth to flavorful curries and stews, and imparts warmth to hot beverages like mulled cider and chai tea.
On the other hand, ground cloves are a staple in sweet recipes like gingerbread, pumpkin pie, cakes, and a range of spiced desserts. They also play a crucial role in savory dishes, enhancing marinades and enriching meat rubs.
Sources
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16190627/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3819475/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3189510/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4586554/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3769004/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35016268/
- https://ifst.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2920880/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5896244/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2920880/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4132639/
Infographic
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Manganese | 17.466mg | 60.127mg | 1855% |
| Vitamin K | 31.2µg | 141.8µg | 92% |
| Fiber | 53.1g | 33.9g | 77% |
| Magnesium | 60mg | 259mg | 47% |
| Iron | 8.32mg | 11.83mg | 44% |
| Vitamin E | 2.32mg | 8.82mg | 43% |
| Calcium | 1002mg | 632mg | 37% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.068g | 3.606g | 24% |
| Fats | 1.24g | 13g | 18% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.158mg | 0.391mg | 18% |
| Potassium | 431mg | 1020mg | 17% |
| Saturated fat | 0.345g | 3.952g | 16% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.041mg | 0.22mg | 14% |
| Sodium | 10mg | 277mg | 12% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.022mg | 0.158mg | 11% |
| Selenium | 3.1µg | 7.2µg | 7% |
| Phosphorus | 64mg | 104mg | 6% |
| Carbs | 80.59g | 65.53g | 5% |
| Folate | 6µg | 25µg | 5% |
| Choline | 11mg | 37.4mg | 5% |
| Protein | 3.99g | 5.97g | 4% |
| Vitamin C | 3.8mg | 0.2mg | 4% |
| Zinc | 1.83mg | 2.32mg | 4% |
| Copper | 0.339mg | 0.368mg | 3% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.358mg | 0.509mg | 3% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 0.246g | 1.393g | 3% |
| Calories | 247kcal | 274kcal | 1% |
| Vitamin A | 15µg | 8µg | 1% |
| Vitamin B3 | 1.332mg | 1.56mg | 1% |
| Net carbs | 27.49g | 31.63g | N/A |
| Sugar | 2.17g | 2.38g | N/A |
| Trans fat | 0g | 0.254g | N/A |
| Tryptophan | 0.049mg | 0.03mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 0.136mg | 0.18mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 0.146mg | 0.24mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 0.253mg | 0.4mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 0.243mg | 0.37mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.078mg | 0.08mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 0.146mg | 0.23mg | 0% |
| Valine | 0.224mg | 0.34mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.117mg | 0.13mg | 0% |
| Fructose | 1.11g | 1.07g | 0% |
| Omega-3 - EPA | 0g | 0.008g | N/A |
| Omega-3 - ALA | 0.011g | 0.585g | N/A |
| Omega-3 - DPA | 0g | 0.184g | N/A |
| Omega-6 - Dihomo-gamma-linoleic acid | 0.008g | N/A | |
| Omega-6 - Eicosadienoic acid | 0g | 0.017g | N/A |
| Omega-6 - Linoleic acid | 2.557g | N/A |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Cinnamon - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/171320/nutrients
- Ground cloves - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/171321/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.




