Absinthe Nutrition: Calories, Carbs, Ethanol, GI,& More

Summary
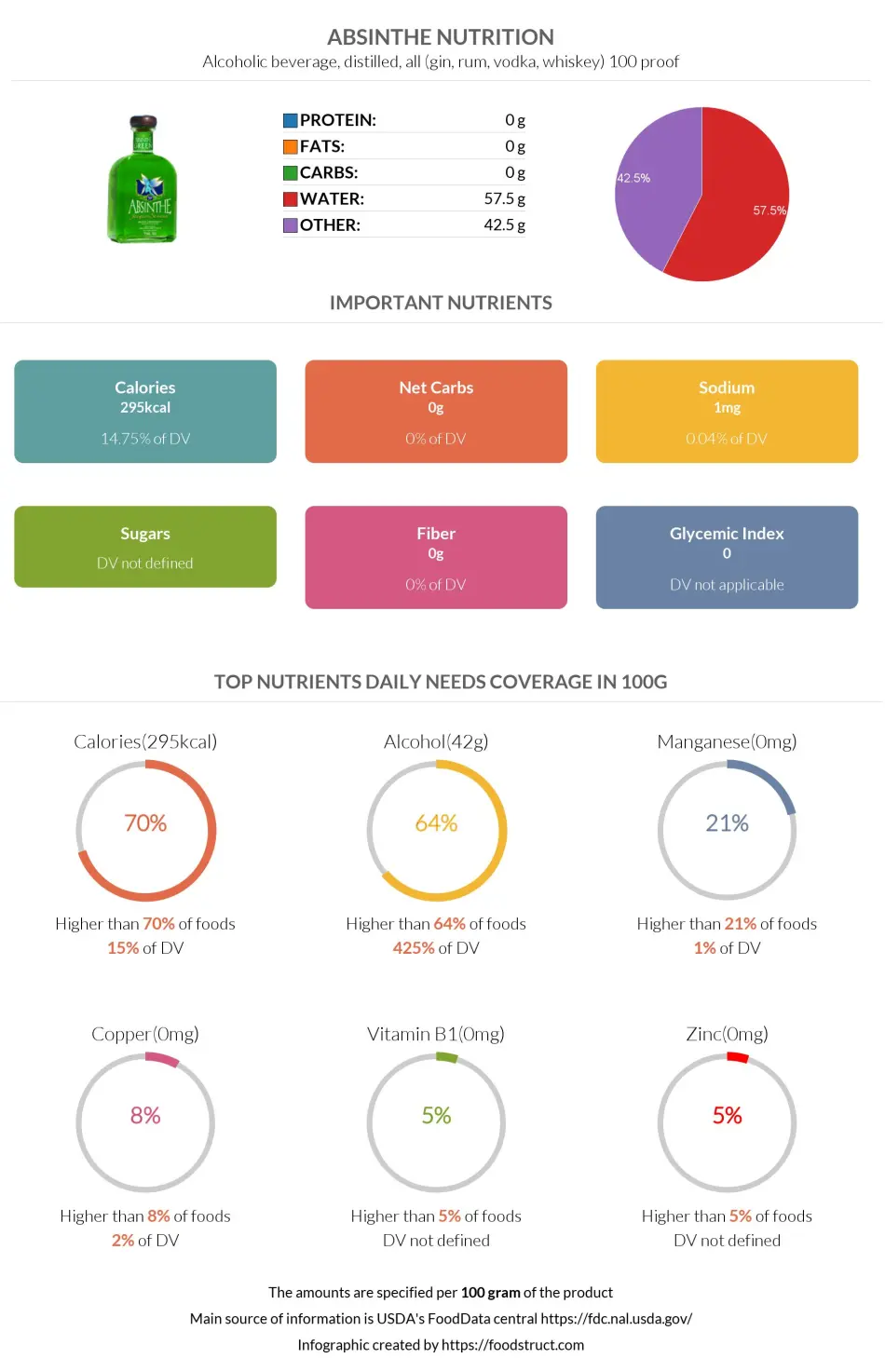
Absinthe is high in calories due to its 42.5% ethyl alcohol content, used as a fuel in the liver, much like fats and carbohydrates. Absinthe is absent in carbs, fats, and proteins and contains trace amounts of several minerals and vitamins.
Excessive but not moderate absinthe consumption can lead to weight gain.
Despite the misbeliefs, absinthe sold today can be safely consumed if used responsibly and within limits.
Introduction
Absinthe, also known as The Green Fairy, is a highly alcoholic, distilled drink made from various herbs, mainly grande wormwood, green anise, and sweet fennel. This drink has a long and curious history, filled with mysteries. To better understand absinthe, we will look into its nutritional compounds and see how it fits into different diets.
Nutrition
Naturally, depending on the level of alcohol and added ingredients, absinthe’s nutritional values can vary.
The nutritional facts below are presented for a distilled, 100-proof alcoholic beverage.
Macronutrients and Calories
Absinthe can be bottled at different alcohol percentages and distilled with water before drinking. The drink we are discussing contains 57.5% water and 42.5% ethyl alcohol.
One serving size of an absinthe drink equals 1 fluid ounce (27.8 grams).
Macronutrients chart
Calories
A 100-gram absinthe drink contains 295 calories. However, absinthe is not usually consumed in such large quantities.
One serving, or 1 fl oz, of absinthe contains 82 calories.
Ethanol
Ethyl alcohol, or ethanol, is a macronutrient and the primary source of absinthe’s calories; it is used as a fuel in the liver, much like fats and carbohydrates.
According to the World Journal of Gastroenterology, ethanol has the highest energy density aside from fats (1).
Data have shown that heavy drinkers may have altered food intake patterns, resulting in the replacement of alcohol for other nutrients (1).
Protein and Fats
Absinthe completely lacks both proteins and fats.
Carbohydrates
Absinthe contains no carbohydrates unless it has been bottled with added sugars.
Absinthe drinks with added sugars are usually sold as absinthe-liqueur.
Vitamins
Absinthe contains trace amounts of vitamin B1, vitamin B2, vitamin B3, and vitamin B6. It completely lacks the rest of the vitamins.
Minerals
An absinthe drink contains some levels of manganese, copper, zinc, iron, phosphorus, potassium, and sodium.
Absinthe is absent in selenium, magnesium, and calcium.
Mineral chart - relative view
Comparison to Other Alcoholic Beverages
The question of which drink to order often comes up on a night out. To get a better idea of how absinthe compares with some other popular alcoholic drinks, let’s look at the comparisons of their nutritional values.
Absinthe vs. Vodka
Absinthe and vodka, both distilled alcoholic beverages, have similar nutritional compositions. However, absinthe is higher in calories as well as most vitamins and minerals.
You can look at our “Absinthe vs. Vodka” page for a more detailed comparison of these two beverages.
Absinthe vs. Whisky
The nutritional content of absinthe is not so different from that of whisky either. That being said, absinthe contains more calories than whisky. Absinthe is also higher in most minerals, including sodium.
To look into the nutritional differences between these two drinks further, you can visit our “Absinthe vs. Whisky” page.
Weight Loss and Diets
Absinthe, like most other alcoholic drinks, is a high-calorie beverage. Even though it can be used during low-fat and low-carb diets, it is not a good fit for a low-calorie diet.
Alcohol contains what is commonly referred to as “empty calories,” meaning it provides a moderate-to-high level of calories, with very few or no nutrients.
Overall, various studies have shown that excessive alcohol consumption leads to an increased risk of weight gain and the development of obesity. In contrast, light to moderate alcohol intake is not associated with weight gain (2).
| Keto | The keto diet does not limit ethanolic drink consumption if it's absent in carbs; thus, absinthe can be used during this diet. |
| DASH | Even though absinthe is very low in sodium, the DASH diet limits alcohol consumption to 2 drinks a day for men and one drink a day for women (3). Alcohol consumption has been positively correlated with an increased risk of hypertension (4). |
| Atkins | Alcohol consumption is not encouraged for the first two weeks during the Induction phase. After this period, alcohol consumption is acceptable in moderation (5). |
| Mediterranean | The Mediterranean diet includes daily moderate alcohol consumption (6). |
| Paleo | Conversations about Paleo and alcohol are still inconclusive. Most sources advise avoiding alcohol during this diet (7). |
| Vegan/ Vegetarian/ Pescetarian | As absinthe is made from herbs, it naturally fits into all three diets. |
| Dukan | Alcohol consumption is not allowed during the first two phases of this diet - Attack and Cruise. Afterward, it is strongly advised to keep alcohol intake levels within limits (8). |
| Intermittent Fasting | Like most other foods and beverages, you should refrain from alcohol during fasting periods but consume it in moderation during eating periods. |
| Low Fat & Low Calorie | Absinthe contains no fats. At the same time, it does not fit into a low-calorie diet. |
| Low Carb | Absinthe spirits do not contain carbohydrates; therefore, they can be used during this diet. However, absinthe can be sold with added sugar, which should be avoided. |
| Anti Inflammatory | Moderate alcohol consumption has been researched to be associated with a lower level of inflammation. However, heavy drinking escalates the inflammation process (9). |
| BRAT | Alcohol should be avoided on a BRAT diet (10). |
Daily Values
A one hundred-gram serving of absinthe, equal to about 4 serving sizes of this drink, can make up 11% of the necessary daily value of calories.
The same amount of absinthe also provides 1% of the daily value of phosphorus.
Absinthe does not provide a significant level of other macronutrients, minerals, or vitamins, being deficient in most nutrients.
Glycemic Index
An absinthe drink has a glycemic index equal to 0 unless it has added sugars.
Acidity
The PRAL (potential renal acid load) value demonstrates how much acid or base the given food or beverage produces inside the organism.
Based on the PRAL value, the acidity of absinthe has been calculated to be 0.1, making it slightly acid-forming.
Toxic Compounds
For a long time, absinthe has been considered to have toxic properties. These properties are potentially due to a neurotoxic terpenoid compound called thujone (11). Thujyl alcohol is found in the essential oils of wormwood, one of the main ingredients of absinthe.
Thujone, in high doses, can cause convulsions resembling epilepsy (12). This same compound was responsible for the false belief that absinthe had hallucinogenic properties.
However, available versions of absinthe today contain such a low level of thujone content that it does not pose a threat to health.
Colorings
Absinthe originally got its natural green coloring from herbs. However, the chlorophyll can quickly turn into a light yellow color, especially when exposed to sunlight. Because of this, many green absinthe drinks today are artificially colored.
The most common artificial dyes used for absinthe are mixtures of tartrazine (E102), patent blue V (E131), and brilliant blue FCF (E133) (13).
References
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2928459
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4338356
- https://thedashdiet.net/what-is-the-dash-diet/#10dd
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6627946/
- https://uk.atkins.com/blog/can-you-drink-alcohol-on-a-low-carb-diet/
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S021391111500237X
- Diet Review: Paleo Diet for Weight Loss
- Dukan Diet Update: Can You Drink Alcohol on the Dukan Diet
- https://academic.oup.com/ageing/article/45/6/747/2499235
- https://www.oregonclinic.com/diets-BRAT
- https://www.pnas.org/content/97/8/3826
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1127080/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1475830/
Top nutrition facts for Absinthe

| Calories ⓘ Calories for selected serving | 295 kcal |
|
Glycemic index ⓘ
Source: The food is assumed to have 0 or no glycemic index bason on the fact that it has no carbs and that foods with 0 carbs have no glycemic index
Check out our Glycemic index chart page for the full list.
|
0 (low) |
| Net Carbs ⓘ Net Carbs = Total Carbohydrates – Fiber – Sugar Alcohols | 0 grams |
| Default serving size ⓘ Serving sizes are mostly taken from FDA's Reference Amounts Customarily Consumed (RACCs) | 1.5 fl oz (42 grams) |
| Acidity (Based on PRAL) ⓘ PRAL (Potential renal acid load) is calculated using a formula. On the PRAL scale the higher the positive value, the more is the acidifying effect on the body. The lower the negative value, the higher the alkalinity of the food. 0 is neutral. | 0.1 (acidic) |
Absinthe calories (kcal)
| Calories for different serving sizes of absinthe | Calories | Weight |
|---|---|---|
| Calories in 100 grams | 295 | |
| Calories in 1 fl oz | 82 | 27.8 g |
| Calories in 1.5 fl oz | 124 | 42 g |
| Calories for different varieties of absinthe | Calories | Weight |
|---|---|---|
| Alcoholic beverage, distilled, all (gin, rum, vodka, whiskey) 100 proof (this food) | 295 | 100 g |
| Alcoholic beverage, distilled, all (gin, rum, vodka, whiskey) 80 proof | 231 | 100 g |
Absinthe Glycemic index (GI)
Mineral coverage chart
Vitamin coverage chart
Vitamin chart - relative view
All nutrients for Absinthe per 100g
| Nutrient | Value | DV% | In TOP % of foods | Comparison |
| Calories | 295kcal | 15% | 30% |
6.3 times more than Orange
|
| Protein | 0g | 0% | 100% |
N/A
|
| Fats | 0g | 0% | 100% |
N/A
|
| Vitamin C | 0mg | 0% | 100% |
N/A
|
| Carbs | 0g | 0% | 100% |
N/A
|
| Net carbs | 0g | N/A | 75% |
N/A
|
| Cholesterol | 0mg | 0% | 100% |
N/A
|
| Magnesium | 0mg | 0% | 100% |
N/A
|
| Calcium | 0mg | 0% | 100% |
N/A
|
| Potassium | 2mg | 0% | 98% |
73.5 times less than Cucumber
|
| Iron | 0.04mg | 1% | 95% |
65 times less than Beef broiled
|
| Fiber | 0g | 0% | 100% |
N/A
|
| Copper | 0.02mg | 2% | 92% |
6.8 times less than Shiitake
|
| Zinc | 0.04mg | 0% | 95% |
157.8 times less than Beef broiled
|
| Phosphorus | 4mg | 1% | 96% |
45.5 times less than Chicken meat
|
| Sodium | 1mg | 0% | 98% |
490 times less than White bread
|
| Manganese | 0.02mg | 1% | 79% | |
| Selenium | 0µg | 0% | 100% | |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.01mg | 1% | 95% |
44.3 times less than Pea raw
|
| Vitamin B2 | 0mg | 0% | 96% |
32.5 times less than Avocado
|
| Vitamin B3 | 0.01mg | 0% | 96% |
736.4 times less than Turkey meat
|
| Vitamin B5 | 0mg | 0% | 100% |
N/A
|
| Vitamin B6 | 0mg | 0% | 96% |
119 times less than Oats
|
| Vitamin B12 | 0µg | 0% | 100% |
N/A
|
| Trans fat | 0g | N/A | 100% |
N/A
|
| Folate | 0µg | 0% | 100% |
N/A
|
| Saturated fat | 0g | 0% | 100% |
N/A
|
| Monounsaturated fat | 0g | N/A | 100% |
N/A
|
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0g | N/A | 100% |
N/A
|
| Tryptophan | 0mg | 0% | 100% |
N/A
|
| Threonine | 0mg | 0% | 100% |
N/A
|
| Isoleucine | 0mg | 0% | 100% |
N/A
|
| Leucine | 0mg | 0% | 100% |
N/A
|
| Lysine | 0mg | 0% | 100% |
N/A
|
| Methionine | 0mg | 0% | 100% |
N/A
|
| Phenylalanine | 0mg | 0% | 100% |
N/A
|
| Valine | 0mg | 0% | 100% |
N/A
|
| Histidine | 0mg | 0% | 100% |
N/A
|
| Omega-3 - EPA | 0g | N/A | 100% |
N/A
|
| Omega-3 - DHA | 0g | N/A | 100% |
N/A
|
| Omega-3 - DPA | 0g | N/A | 100% |
N/A
|
Check out similar food or compare with current
NUTRITION FACTS LABEL
Serving Size ______________
Health checks
Absinthe nutrition infographic
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.



