Apricot jam vs. Honey — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
In summary, honey is high in calories, whereas apricot jam contains more vitamin C and has a higher GI index. Honey and apricot jam are not good sources of proteins, fats, or vitamins, but both are high in carbs.
Introduction
In summary, honey is high in calories, whereas apricot jam contains more vitamin C and has a higher GI index. Honey and apricot jam are not good sources of proteins, fats, or vitamins, but both are high in carbs.
Appearance
Honey is a natural sweetener. It has a thick sticky texture. Honey has a mild or strong flavor. Darker honey often has a strong flavor than lighter honey, in general.
Apricot jam has a sweet flavor and thick texture. It has a mild flavor, which makes it suitable for savory and sweet meals. You can use apricot jam for cooking and baking.
Nutrition
In this part of the article, we will compare the nutritional values of honey and apricot jam.
Macronutrients
Overall, honey and apricot jam contain fewer amounts of proteins and fats. Honey's primary component is carbohydrates, which account for 95-97% of its dry weight(1).
Macronutrient Comparison
Contains
more
ProteinProtein
+133.3%
Contains
more
FatsFats
+∞%
Contains
more
WaterWater
+101.8%
Contains
more
CarbsCarbs
+28%
Calories
Honey is higher in calories. Honey provides 304 calories per hundred grams, whereas apricot jam contains 242 calories.
Protein
Apricot jam and honey contain less protein. Both have less than 1g of protein.
Carbohydrates
Honey is higher in carbs compared to apricot jam. Honey provides 82.4g of carbs, whereas apricot jam contains 64.4g. The primary sugars in honey are monosaccharides: fructose and glucose.
Honey also contains a small amount of disaccharides, such as sucrose, galactose, and trisaccharides(1).
Honey and apricot jam are cholesterol-free.
Fats
Apricot jam provides only 0.2g of fats, whereas honey does not contain it.
Flavonoid Compounds
The most flavonoid compounds in honey are Luteolin, Quercetin, and Myricetin. Apricot jam, on the other hand, contains more Kaempferol and Catechin(2).
Vitamins
Honey and apricot jam are not good sources of vitamins.
Apricot jam contains high levels of vitamin C. Apricot jam contains 8.8mg of vitamin C, whereas honey only 0.5mg.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+1660%
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+72.7%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+236.1%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+240%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+20%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+100%
Minerals
Honey is not a good source of minerals.
Honey provides 5.5 times more choline and ten times less sodium. Apricot jam contains three times more calcium and 1.5 times more potassium.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+100%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+233.3%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+48.1%
Contains
more
IronIron
+16.7%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+177.8%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+150%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+266.7%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+33.3%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-90%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+100%
Glycemic Index and Glycemic Load
The glycemic index of honey is 61. The glycemic index of apricot jam is 69. On the other hand, apricot jam is a low-GL food, whereas honey is a medium-GL food(3). The glycemic load of honey is 11.
Acidity
The pH value of honey is 3.9, whereas apricot has a pH of 3.69(4)(5). Both are acidic. Another way to measure the acidity of foods is the potential renal acid load (PRAL). The PRAL value of honey is -0.9, whereas apricot jam has a PRAL of -1.5. It means that both are alkaline-forming.
Health Benefits
Diabetes
The study showed that apricot jam is optimal for people with diabetes mellitus, glucose intolerance, and obesity. Moreover, the sugar-free apricot jam with white bread did not affect postprandial glycemic reactions. As apricot jam is a low Gl-food, it is a good option for long-term glycemic control(3).
Honey has antidiabetic effects too. It can cause a lower elevation of plasma glucose level (PGL). Honey also can reduce the complications of diabetes(6).
Cancer
Honey has antimetastatic, antiproliferative, cytotoxic, and anticancer effects. It can decrease the risk of breast, liver, and colorectal cancer(7).
Honey has been shown to inhibit cell proliferation, induce apoptosis, alter cell cycle progression, and cause mitochondrial membrane depolarization in several cancer cells, such as skin cancer cells, cervical cancer cells, endometrial cancer cells, and prostate cancer cells(1).
Apricot induces apoptosis, programmed cell death, and autophagy. Apricot jam, on the other hand, has anti-neoplastic effects on gastric, breast, and colon cancers and hepatocellular carcinoma(8).
Sources.
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5424551/
- https://www.ars.usda.gov/arsuserfiles/80400525/data/flav/flav_r03.pdf
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9574874/
- https://www.clemson.edu/extension/food/food2market/documents/ph_of_common_foods.pdf
- https://www.walshmedicalmedia.com/open-access/functional-properties-and-preparation-of-diet-apricot-jam-2157-7110-1000475.pdf
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5817209/#:~:text=In%20diabetic%20patients%2C%20honey%20compared,and%20CRP%20in%20normal%20subjects.
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24566317/#:~:text=Honey%20is%20highly%20cytotoxic%20against,%2C%20promotion%2C%20and%20progression%20stages.
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9370680/
Infographic
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Fructose | 40.94g | 51% | |
| Vitamin C | 8.8mg | 0.5mg | 9% |
| Copper | 0.1mg | 0.036mg | 7% |
| Carbs | 64.4g | 82.4g | 6% |
| Calories | 242kcal | 304kcal | 3% |
| Sodium | 40mg | 4mg | 2% |
| Manganese | 0.04mg | 0.08mg | 2% |
| Selenium | 2µg | 0.8µg | 2% |
| Protein | 0.7g | 0.3g | 1% |
| Calcium | 20mg | 6mg | 1% |
| Potassium | 77mg | 52mg | 1% |
| Iron | 0.49mg | 0.42mg | 1% |
| Zinc | 0.06mg | 0.22mg | 1% |
| Vitamin A | 10µg | 0µg | 1% |
| Vitamin E | 0.13mg | 0mg | 1% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.022mg | 0.038mg | 1% |
| Vitamin B3 | 0.036mg | 0.121mg | 1% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.02mg | 0.068mg | 1% |
| Fats | 0.2g | 0g | 0% |
| Net carbs | 64.1g | 82.2g | N/A |
| Magnesium | 4mg | 2mg | 0% |
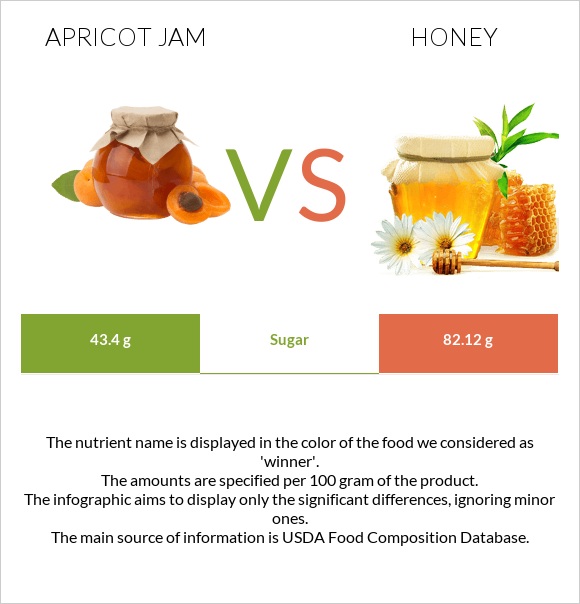
| Sugar | 43.4g | 82.12g | N/A |
| Fiber | 0.3g | 0.2g | 0% |
| Phosphorus | 3mg | 4mg | 0% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.02mg | 0.024mg | 0% |
| Folate | 1µg | 2µg | 0% |
| Choline | 0.4mg | 2.2mg | 0% |
| Saturated fat | 0.01g | 0g | 0% |
| Tryptophan | 0.004mg | 0% | |
| Threonine | 0.004mg | 0% | |
| Isoleucine | 0.008mg | 0% | |
| Leucine | 0.01mg | 0% | |
| Lysine | 0.008mg | 0% | |
| Methionine | 0.001mg | 0% | |
| Phenylalanine | 0.011mg | 0% | |
| Valine | 0.009mg | 0% | |
| Histidine | 0.001mg | 0% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Apricot jam - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/170645/nutrients
- Honey - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/169640/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.






