Are Kidney Beans Better for Your Health Than Meat?

Summary
In equal serving sizes, beef is 3 times richer in protein; however, when comparing average serving sizes, beef is only 1.4 times higher in protein.
Beef is over 30 times higher in fats, including saturated fats and cholesterol. It is a better source of most B-complex vitamins, especially vitamin B12.
Kidney beans are richer in carbohydrates, including starch and dietary fiber, vitamin B9 or folate, and most minerals.
Kidney beans are overall studied to be the healthier choice, decreasing the risk of cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and colorectal cancer, unlike beef which increases these risks.
Introduction
At first glance, kidney beans and beef seem to have little in common; however, when the question of a good protein source comes up, these two are usually among the top suggestions.
In this article, we will look at how kidney beans and beef compare to each other, mainly focusing on their nutrition and health impact.
Classification
Beef is the meat of domesticated cows or bulls. Due to a high level of iron-containing protein myoglobin, beef is classified as red meat. In fact, beef is the most popular type of red meat.
The kidney bean is a variety of the common bean belonging to the Fabaceae family and the Phaseolus genus. Other types of common beans, such as adzuki beans, pinto beans, and navy beans, should not be confused with kidney beans.
Varieties of kidney beans include red kidney beans, white kidney beans, light-speckled kidney beans, and red-speckled kidney beans.
Nutrition
We will compare the nutritional profiles of mature kidney beans of all types, boiled without salt and broiled ground beef patty, consisting of 85% lean meat and 15% fat.
Macronutrients and Calories
Broiled ground beef is somewhat denser in nutrients compared to boiled kidney beans. Beef consists of 58% water and 42% nutrients, while kidney beans contain 67% water.
The average serving size of kidney beans per person is one cup of boiled beans, weighing around 177g. This serving size for beef is 3 ounces, equal to 85g, or one beef patty weighing 77g.
Calories
Beef is around 2 times higher in calories compared to kidney beans. A 100g serving of beef provides 250 calories, while the same serving of kidney beans contains 127 calories.
However, when looking at average serving sizes consumed, these two provide a similar number of calories. One average serving of kidney beans (177g) contains 225 calories, while one serving size of ground beef (85g) has 213 calories.
Protein
When comparing equal serving sizes, ground beef is 3 times richer in protein compared to kidney beans. However, when comparing average serving sizes consumed per person, beef is only 1.4 times higher in protein.
A 100g of ground beef provides 26g of protein, while beef contains 8.7g. At the same time, three ounces of beef contains 22g of protein, while one cup of kidney beans has 15.4g.
The protein contained in these two foods is of high quality, as they contain some amounts of all the essential amino acids.
Being a type of meat, beef is richer in all of the essential amino acids except for tryptophan.
Fats
Kidney beans contain an insignificant amount of fats, while beef falls in the top 22% of foods as a source of fats.
Naturally, beef is over 30 times higher in fats compared to kidney beans. This includes both saturated and unsaturated fats.
As a plant product, kidney bean does not contain cholesterol, whereas beef is very high in cholesterol, containing 88mg per 100g serving.
Carbohydrates
Like most meats, beef does not contain carbohydrates. Kidney beans, on the other hand, provide almost 28g per 100g serving.
Most of the carb content of kidney beans is made up of starch and only a small amount of sugar.
Kidney beans are a great source of dietary fiber, falling in the top 15% of foods as a source. A 100g serving of these beans provides 6.4g of dietary fiber. Most of this fiber, about 75%, consists of soluble fiber, with only 15% consisting of insoluble fiber (1).
Vitamins
Beef is overall richer in vitamins, especially B-complex vitamins, being 9 times higher in vitamin B3, 3 times higher in vitamins B2, B5, and B6. Beef is also 4 times higher in vitamin E and provides vitamin A, unlike kidney beans.
Beef is a good source of vitamin B12, which kidney beans lack entirely.
Nevertheless, kidney beans are 14 times richer in folate or vitamin B9, 7 times higher in vitamin K, and 3 times higher in vitamin B3. Kidney beans also contain vitamin C.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+247.8%
Contains
more
Vitamin KVitamin K
+600%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+1344.4%
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+300%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+203.4%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+830.4%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+199.1%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+218.3%
Contains
more
Vitamin B12Vitamin B12
+∞%
Minerals
Kidney beans win in this category, providing nearly 3 times more copper and 2 times more calcium and magnesium. Unsalted kidney beans are also lower in sodium.
However, beef is 6 times richer in zinc and provides slightly more iron and phosphorus.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+100%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+94.4%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+27.4%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+154.1%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-98.6%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+3483.3%
Contains
more
IronIron
+17.1%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+531%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+43.5%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+1854.5%
Glycemic Index
The glycemic index of foods with no carbohydrates, such as beef, is considered to be 0.
Kidney beans have been calculated to have a glycemic index falling in the wide range of 9 to 51 (2). However, no matter the exact number, the glycemic index of kidneys is low.
If interested, you can find a complete list of glycemic index values of over 600 foods.
Insulin Index
The insulin index is used for foods with low levels of carbohydrates to measure how much the given food raises the insulin levels in the blood after consumption.
Despite the low glycemic index values, beef and kidney beans have relatively high insulin index values.
The insulin index value of lean beef steak is 51, while this value for dried kidney beans is a little higher - 69 (3, 4).
Acidity
Kidney beans and beef have a similar pH value falling in the range of 5.4 to 6. However, the two differ in their potential renal acid load or PRAL values.
Kidney beans have a slightly alkaline PRAL value of -0.7, while beef has an acidic PRAL value of 12.6. This shows that beef is considerably more acid-producing in the body compared to kidney beans.
Diets and Religion
Despite the glaring differences, mashed kidney beans can sometimes substitute for ground beef in vegetarian and vegan versions of foods. This is why kidney bean is considered to be a meat alternative.
Kidney beans are an excellent source of protein and vitamin B9 or folate, among other nutrients, for people who do not consume animal products. However, kidney beans do not provide vitamin B12, low consumption of which can cause vitamin B12 deficiency.
You can find more information about vegan and vegetarian sources of essential nutrients on our page.
Kidney beans are also an excellent choice of nutrients for those following the alkaline diet since kidney beans are alkaline-forming, unlike beef.
Kidney beans are the better choice for low-fat, vegan, vegetarian, and alkaline diets, whereas beef can be the right choice for low-carb, high-protein, and keto diets.
As a respected creature of God, beef consumption is often prohibited in Hinduism. There are various laws in India banning the slaughter of cows. For people following this ban, kidney beans can be a good addition to a healthy diet.
Health Impact
Cardiovascular Health
High intake of red meat, such as beef, has been researched to increase the risk of ischemic heart disease (5). Substituting red meat with high-quality plant products, such as kidney beans, leads to a more favorable profile in cardiovascular health (6).
Research has stated the inverse association between dietary fiber intake and coronary heart disease (7). As mentioned above, kidney beans are abundant in dietary fiber.
Diabetes
Red meat consumption has also been associated with an elevated risk of developing type 2 diabetes and metabolic syndrome (8, 9).
Conversely, kidney beans have been studied to serve as a functional low glycemic index food for the dietary regulation of type 2 diabetes patients (10).
Low-fat, plant-based diets have also been correlated with weight loss and improved insulin sensitivity (11, 12).
Cancer
Eating high amounts of red meat can lead to an increased risk of colorectal and bowel cancer. Red meat is classified as a Group 2A carcinogen, meaning there is probable evidence to support the cancer-causing effect of red meat (13).
Conversely, there is probable evidence that pulses, such as kidney beans, can lead to a decreased risk of colorectal cancer due to their high dietary fiber content (14).
Digestive Health
The soluble dietary fiber found in kidney beans can help normalize stool, while insoluble dietary fiber can increase fecal mass and promote regularity (15). In other words, kidney beans can help improve bowel functions and relieve constipation.
However, they are high in FODMAP, which may cause bloating and flatulence and worsen the symptoms of IBS.
Vitamin B12 Deficiency
Vitamin B12 is a water-soluble vitamin derived from animal products, such as meat, dairy, and eggs, which plays an important role in forming red blood cells and DNA, as well as the function and development of the brain and nerves.
Vitamin B12 deficiency can not manifest for years, as it is stored in excess in the liver; however, it is often seen in those who have followed a strict vegan diet for about three years (16).
Vitamin B12 deficiency symptoms include tiredness, a feeling of pins and needles, mouth ulcers, muscle weakness, disturbed vision, signs of depression, etc.
Beef is an excellent source of vitamin B12, while kidney beans are entirely absent in it.
For people following vegetarian or vegan diets, various forms of vitamin B12 supplements are recommended.
Sources.
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3614039/
- https://academic.oup.com/ajcn/article/114/5/1625/6320814
- https://academic.oup.com/ajcn/article/66/5/1264/4655967
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/19614236
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34284672/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30958719/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3257631/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3942738/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5946175/
- https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fnut.2022.1044427/full
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17890496/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16164885/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK507971/
- https://www.aicr.org/cancer-prevention/food-facts/dry-beans-and-peas-legumes/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3257631/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3257631/
Infographic
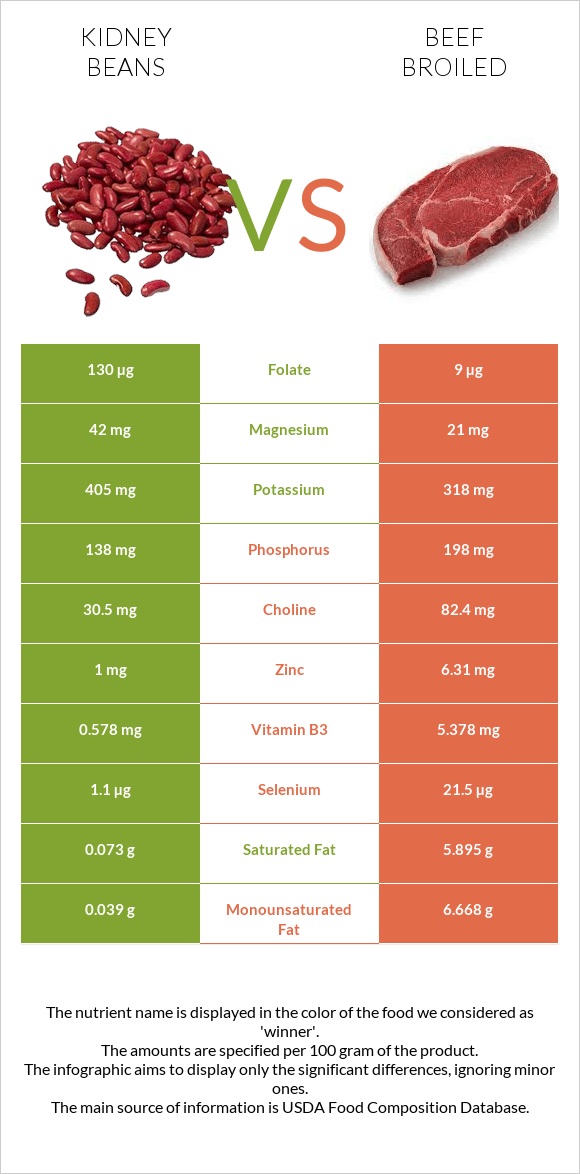
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Vitamin B12 | 0µg | 2.64µg | 110% |
| Zinc | 1mg | 6.31mg | 48% |
| Selenium | 1.1µg | 21.5µg | 37% |
| Protein | 8.67g | 25.93g | 35% |
| Vitamin B3 | 0.578mg | 5.378mg | 30% |
| Folate | 130µg | 9µg | 30% |
| Cholesterol | 0mg | 88mg | 29% |
| Fiber | 6.4g | 0g | 26% |
| Saturated fat | 0.073g | 5.895g | 26% |
| Fats | 0.5g | 15.41g | 23% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.12mg | 0.382mg | 20% |
| Manganese | 0.43mg | 0.012mg | 18% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 0.039g | 6.668g | 17% |
| Copper | 0.216mg | 0.085mg | 15% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.16mg | 0.046mg | 10% |
| Phosphorus | 138mg | 198mg | 9% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.058mg | 0.176mg | 9% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.22mg | 0.658mg | 9% |
| Choline | 30.5mg | 82.4mg | 9% |
| Carbs | 22.8g | 0g | 8% |
| Calories | 127kcal | 250kcal | 6% |
| Vitamin K | 8.4µg | 1.2µg | 6% |
| Magnesium | 42mg | 21mg | 5% |
| Iron | 2.22mg | 2.6mg | 5% |
| Potassium | 405mg | 318mg | 3% |
| Sodium | 1mg | 72mg | 3% |
| Calcium | 35mg | 18mg | 2% |
| Vitamin C | 1.2mg | 0mg | 1% |
| Vitamin E | 0.03mg | 0.12mg | 1% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.278g | 0.484g | 1% |
| Net carbs | 16.4g | 0g | N/A |
| Vitamin D | 0 IU | 2 IU | 0% |
| Sugar | 0.32g | 0g | N/A |
| Vitamin A | 0µg | 3µg | 0% |
| Trans fat | 0g | 0.572g | N/A |
| Tryptophan | 0.104mg | 0.094mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 0.319mg | 0.72mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 0.41mg | 0.822mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 0.736mg | 1.45mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 0.607mg | 1.54mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.113mg | 0.478mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 0.511mg | 0.725mg | 0% |
| Valine | 0.5mg | 0.914mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.238mg | 0.604mg | 0% |
| Omega-3 - EPA | 0g | 0.003g | N/A |
| Omega-3 - DHA | 0g | 0.001g | N/A |
| Omega-3 - ALA | 0.044g | N/A | |
| Omega-3 - DPA | 0g | 0.016g | N/A |
| Omega-6 - Gamma-linoleic acid | 0.012g | N/A |
Macronutrient Comparison
| Contains more CarbsCarbs | +∞% |
| Contains more WaterWater | +15.5% |
| Contains more OtherOther | +60.3% |
| Contains more ProteinProtein | +199.1% |
| Contains more FatsFats | +2982% |
Fat Type Comparison
| Contains less Sat. FatSaturated fat | -98.8% |
| Contains more Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat | +16997.4% |
| Contains more Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat | +74.1% |
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Kidney beans - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/173740/nutrients
- Beef broiled - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/174032/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.
