Bratwurst vs. Bockwurst — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Бratwurst and bockwurst are rich in nutrients and vitamins.
Bockwurst contains 485.7% more calcium, 73.3% more magnesium, and 30% more phosphorus, while bratwurst contains 19.3% more zinc.
Bockwurst also contains drastically more vitamin C, vitamin A and 89% more vitamin B6. At the same time, bratwurst contains 96.9% more vitamin B1 and 210% vitamin B12.
Despite this vast nutrient and vitamin content, both foods are connected with the development of different diseases and can affect the cancer development risk.
Introduction
This article will discuss the general differences, nutritional content, and health impacts of bratwurst and bockwurst.
Composition
The main difference between bratwurst and bockwurst is that bratwurst is mainly made of pork, less commonly from veal or beef, while bockwurst is usually made of ground veal, less pork.
Bockwurst is also usually flavored with salt, white pepper, paprika, and some herbs, which may be included in its composition. Both sausages are originally served with beer.
Bratwurst is mixed with salt, pepper, marjoram, and nutmeg.
Nutrition
One serving of bratwurst equals 66 g, and one serving of bockwurst is 91 g.
Calories
Both sausages are high in calories. One serving of bratwurst contains 196 kcal, while the bockwurst calorie content is relatively higher, with about 274 kcal per one serving.
Protein
From the aspect of protein content, the bockwurst is richer in proteins, about 12.7 g per serving, while the bratwurst contains only 8.05 g.
Fats
Bockwurst has higher total fats compared to bratwurst.
CHECK
To sum up, bratwurst is lower in total fats but higher in saturated fat content. Bratwurst contains fewer monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats.
Fat Type Comparison
Contains
less
Sat. FatSaturated fat
-40.7%
Contains
more
Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat
+64.2%
Contains
more
Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat
+47.3%
Carbohydrates
Their carbohydrate content is low. Bratwurst contains 2g per 100g and bockwurst contains about 3g per 100g.
Vitamins
Bratwurst is richer in vitamin B1 and vitamin B12. In comparison, bockwurst is richer in vitamin B3, vitamin B5, vitamin B6, and vitamin K.
Below, we can visualize their vitamin coverage.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+96.9%
Contains
more
Vitamin B12Vitamin B12
+210.5%
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+80.6%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+29.1%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+89%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+325%
Minerals
Bratwurst is richer in selenium and zinc. Bockwurst is richer in manganese, copper, iron, and phosphorus.
They are both high in sodium. However, bockwurst contains less sodium.
You can see another coverage chart for minerals below
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+19.3%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+24.8%
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+73.3%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+485.7%
Contains
more
IronIron
+15%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+25%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+30%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-10.8%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+317.1%
Glycemic Index
The glycemic index of both foods falls under the low GI food category. The glycemic index of bratwurst and bockwurst is equal, estimated at 28.
Acidity
The potential renal acid load (PRAL) of bratwurst and bockwurst varies. While both sausages are considered acidic, the PRAL value of bratwurst is estimated to be 4.4, while this value for bockwurst is higher, estimated to be 6.2. The PRAL shows the capacity of the food to produce acids or bases inside the organism.
Health Impact
Since they are nearly similar, their health impacts are nearly similar aswell.
Cardiovascular Health
When comparing bratwurst and bockwurst in terms of their impact on cardiovascular disease (CVD), there are a few factors to consider.
Saturated fat content: Both bratwurst and bockwurst typically contain high levels of saturated fat, which can contribute to elevated cholesterol levels and increase the risk of CVD.
Sodium content: Processed meats like sausages often contain high amounts of sodium, which can raise blood pressure and increase the risk of heart disease and stroke (1).
Ingredients and processing: The specific ingredients and processing methods used in the production of bratwurst and bockwurst can vary, impacting their overall nutritional profile. Some varieties may contain additives or preservatives that could have negative effects on heart health (2).
Portion size and preparation: The size of the serving and how the sausages are prepared (grilled, fried, etc.) can also affect their health impact. For example, grilling may be a healthier cooking method compared to frying, as it reduces the amount of added fat.
In general, both bratwurst and bockwurst are not considered heart-healthy options due to their high saturated fat and sodium content. However, enjoying them occasionally as part of a balanced diet is unlikely to significantly increase the risk of CVD, especially if paired with plenty of vegetables and whole grains. As always, moderation is key when consuming foods high in saturated fat and sodium.
Diabetes
Consumption of processed foods increases the risk of type 2 diabetes (3).
Cancer
Processed meat is associated with increased risks of cancer, specifically colorectal and esophageal cancer (4).
Infographic
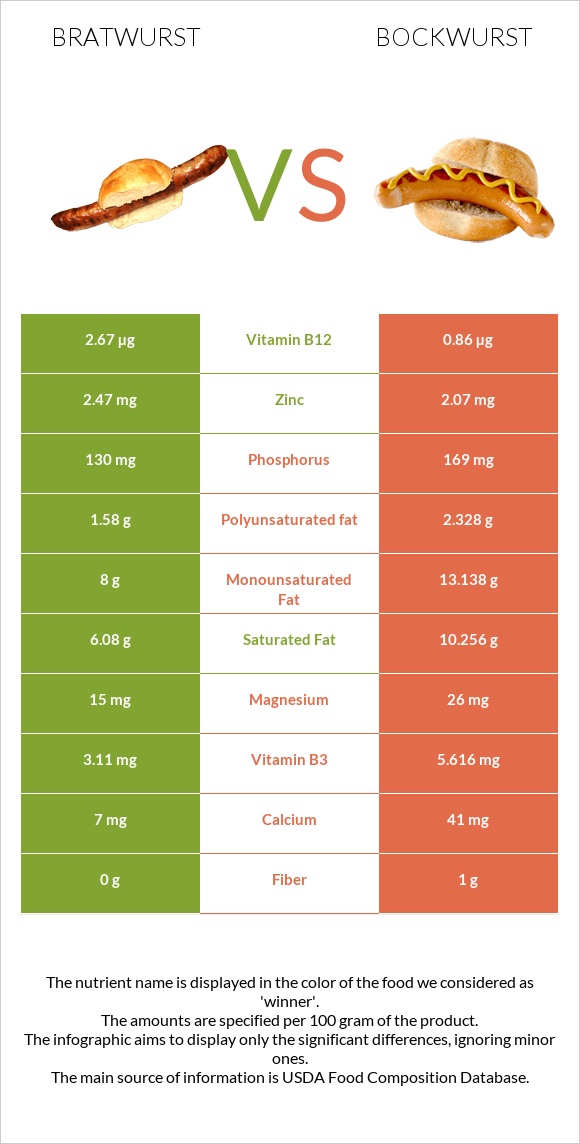
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Vitamin B12 | 2.67µg | 0.86µg | 75% |
| Vitamin K | 70.2µg | 59% | |
| Tryptophan | 0.107mg | 153mg | 55% |
| Saturated fat | 6.08g | 10.256g | 19% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.38mg | 0.193mg | 16% |
| Vitamin B3 | 3.11mg | 5.616mg | 16% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.2mg | 0.378mg | 14% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 8g | 13.138g | 13% |
| Choline | 46.4mg | 8% | |
| Phosphorus | 130mg | 169mg | 6% |
| Manganese | 0.041mg | 0.171mg | 6% |
| Cholesterol | 78mg | 93mg | 5% |
| Selenium | 14.1µg | 11.3µg | 5% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 1.58g | 2.328g | 5% |
| Protein | 12.2g | 14.03g | 4% |
| Vitamin C | 0mg | 3.2mg | 4% |
| Fiber | 0g | 1g | 4% |
| Zinc | 2.47mg | 2.07mg | 4% |
| Sodium | 848mg | 756mg | 4% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.69mg | 0.891mg | 4% |
| Magnesium | 15mg | 26mg | 3% |
| Calcium | 7mg | 41mg | 3% |
| Vitamin E | 0.38mg | 3% | |
| Folate | 4µg | 17µg | 3% |
| Iron | 1mg | 1.15mg | 2% |
| Copper | 0.08mg | 0.1mg | 2% |
| Vitamin A | 0µg | 15µg | 2% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.213mg | 0.233mg | 2% |
| Fats | 26.34g | 25.87g | 1% |
| Calories | 297kcal | 301kcal | 0% |
| Net carbs | 2g | 1.95g | N/A |
| Carbs | 2g | 2.95g | 0% |
| Potassium | 283mg | 270mg | 0% |
| Sugar | 0g | 1.33g | N/A |
| Threonine | 0.465mg | 0.613mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 0.485mg | 0.677mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 0.81mg | 1.107mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 0.903mg | 1.166mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.364mg | 0.333mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 0.405mg | 0.556mg | 0% |
| Valine | 0.464mg | 0.767mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.395mg | 0.513mg | 0% |
| Fructose | 0.01g | 0% |
Macronutrient Comparison
| Contains more ProteinProtein | +15% |
| Contains more CarbsCarbs | +47.5% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Bratwurst - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/172956/nutrients
- Bockwurst - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/171619/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.






