Burrito vs. Pizza — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Pizza has higher calories, proteins, carbs, fats, sodium and is richer in vitamins and minerals. On the other hand, Burritos have a lower glycemic index, lower saturated fats, but they are higher in trans fats. Both are highly versatile and can be modified to be healthier.
Introduction
Pizza originated in Italy, but today it is spread worldwide and is one of the most common fast foods. The original pizza is not categorized as fast food. The fundamental element of pizza is the dough, the sauce, and the cheese. It is highly versatile and can be vegan, vegetarian, and meat products.
The burrito, on the other hand, is Mexican. It is a tortilla wrapped around various elements: Mexican rice, beans, vegetables, cheese, and meat, which can be beef, chicken, or pork. Burritos are described as savory filling and salsa-rich wraps that have a wide range of tastes and flavors.
Culinary world
Both these can be modified from being healthy foods to junk food. This is due to the various ingredients present in them.
Pizzas are the cornerstone of friend gatherings as there is no gathering without pizza; however, most of the time, delivery pizza is a fast-food pizza that is not considered healthy food. So be careful of the number of slices you eat; they are irresistible.
On the other hand, Burritos are not as famous around the world as much as pizza is. However, they are mostly prepared as fast food and not healthy foods. Some cuisines have taken the burrito concept, made it into a burrito bowl, and turned it into healthy food. We will discuss this in the diet section.
In this article, we will compare the differences between pizza and burritos based on their nutritional data, weight loss and diets, and health impacts.
Nutritional data
In this part of the article, we will discuss the nutritional data based on comparing 100g of pizza and burrito. The pizza taken into consideration is a fast-food pizza with cheese topping and regular crust, and we would compare this to burritos with beans.
The serving size of each is essential. 1 serving of pizza which is 1 slice, is about 107g, and 1 serving of a burrito is 217g
Calories
Pizza and burrito are considered moderate in calories; of course, this is based on 100g.
Pizza has 266 calories compared to burritos which have 206 calories. Pizzas are higher in calories.
Glycemic index
The glycemic index for both has a range depending on the ingredients that are used. It is hard to pinpoint an exact glycemic index. Keeping in mind the portions of the pizza and burrito mentioned above, pizza has a higher glycemic index, which is 60, compared to burritos with a glycemic index of 37.
Carbs
Pizza and burritos have nearly similar carbs. They are high in carbs. Pizza has 33.33g of carbs whereas, burrito has 32.92g of carbs. Nearly 100g of either would satisfy around 11% of the daily required carbs.
Proteins
Pizza has higher protein amounts compared to burritos.
Fats
Pizza has higher amounts of fats, mostly due to the cheese topping.
The saturated fat in pizza fills 20% of the daily value, whereas, in burritos, it is lesser as it is 15% of the daily value.
It is important to take into consideration the amounts of trans fats when it comes to both foods.
Pizza has 0.24g of trans fats, which makes around 12% of the daily required value. However, the burrito has a higher trans fat content of about 1.1g, 55% of the daily value.
Minerals
Pizza and burritos are high in sodium. The recommended daily intake is about 2300 mg, and the sodium amount of pizza is 589mg, filling nearly 25% of the daily value. So 4 slices of pizza would fill 100% of the daily required value. The sodium amount of pizza has to be taken into consideration for hypertensive people and individuals who don’t suffer from any health problems.
In the case of burrito, the sodium content is lesser than pizza, yet it is still considered high since 100g of a burrito would make 19% of the daily value.
The mineral amount can vary, but we will take into consideration the standard types of both foods as mentioned above.
Pizza is richer in calcium, iron, and phosphorus, whereas burrito is richer in magnesium.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+66.7%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+75%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+65.7%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-24.1%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+261.5%
Contains
more
IronIron
+19.2%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+91.4%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+380%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+97%
Vitamins
Pizza is richer in vitamins B1, A, C, and folate. In comparison, the burrito is richer in vitamins B2 and B5. However, these can vary with the toppings and elements added to them.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+43.6%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+75%
Contains
more
Vitamin B12Vitamin B12
+19%
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+55.6%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+34.5%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+104.5%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+132.5%
Weight loss and diets
Both pizza and burrito are not usually associated with weight loss. In a sentence, together, they are considered oxymorons. Although most pizzas and burritos are high in calories, we can make adaptations to make them suitable for people who crave them, even when on a diet.
Pizzas are considered one of the most versatile foods. They can be adjusted to fit a healthy diet if required. However, we would sacrifice most of the good parts of the pizza, like pepperoni, extra cheese, the crust dipping in sauces. Maintaining a specific diet for the long term is to have the least amount of local foods. The more restricted elements are in a specific diet, the more cravings for that particular food will happen.
So a healthy alternative to a classic fast-food pizza would be a homemade one. Knowing what ingredients are being used helps with the process of preparation. A thin dough, less cheese, more vegetable toppings are the way to go. Of course, one should also control the number of slices consumed.
On the other hand, Burrito can be made to be healthier without sacrificing the best parts of it. Some people eat burritos with rice, which is not the normal standard. However, if that is the case, the rice has to be removed. Consider using leaner meat, less cheese, low-fat sour cream, or a little bit of sour cream, and fewer beans.
Vegan
We can make both of them into vegan versions. In the case of pizza, We can use vegan cheese with vegetable toppings. For a burrito, it can be made with mushrooms, or instead of ground beef, you can add extra red beans with the salsa. Sour cream and cheese have to be sacrificed in this case. The point is that you can still have a pizza or a burrito, even on a vegan diet. However, a couple of modifications have to be made.
Keto
Pizza made the keto list, with a couple of modifications, of course. The carb source of pizza is the dough, so the challenge is to change the wheat-based dough. The alternative is cauliflower-based dough or almond flour-based dough. For the cheese, we can consume low-carb, high-fat cheese.
When it comes to toppings, it is important to find alternatives for high-carb toppings, like corn, and you have the green light to stay away from pineapples on top of your pizza.
Burritos, on the other hand, have a challenge with the tortilla wrap. An alternative to that would be a burrito bowl with fewer amounts of carbs sources and more protein.
Gluten-free diet
People with celiac disease and non-celiac gluten sensitivity (gluten intolerance) should follow a gluten-free diet; choose a gluten-free dough not made from wheat.
Common symptoms of celiac disease and gluten intolerance are abdominal pain, bloating, diarrhea or constipation, nausea, anemia-related symptoms (weakness, fatigue, fast heartbeat, lightheadedness, shortness of breath), etc.
Health impacts
Cardiovascular health
Pizza, as fast food, is one of the main concerns of deteriorating cardiovascular health among adults. Pizza has adverse effects on cardiovascular health. (1)
Pizzas are considered high in sodium. If the amount of sodium remains unmonitored over long periods, developing hypertension will increase. (2) (3)
On the other hand, the burrito has nearly 55% of the required daily trans fat, associated with developing cardiovascular diseases. (4)
This paper shows a direct correlation between consuming burritos frequently and having a high BMI. High BMI is associated with an increased risk of hypertension. (5)
Obesity
Pizza consumption has a direct link with increased risks of obesity. (1)
In addition to that, burrito consumption also has a direct link with obesity. High BMI is associated with frequent consumption of burritos. (6)
Diabetes
Measuring blood glucose levels after consuming pizza has shown a high increase in blood sugar levels, resulting in high thresholds of hyperglycemia. This hyperglycemic state on a constant and regular basis would lead to type 2 diabetes. (7)
Similarly, as mentioned above, a direct correlation between burrito consumption and high BMI is present, leading to increased risks of developing diabetes. (8)
Cancer
Consumption of fast foods, including pizza and burrito, over long periods of time and in large amounts are associated with an increased risk of colorectal cancer. (9)
Mental health
Sometimes consuming fast foods is considered a comfort food after a stressful day. However, this is proven to have negative long-term effects associated with depression and stress.
Consumption of fast foods is also associated with violent behavior in children. (10) (11)
Miscellaneous health benefits
Eating well-balanced homemade healthy pizza has its benefits.
Data shows that eating the above-mentioned healthy pizza reduces the risks of obesity. (12)
The baker’s yeast added into pizzas have positive benefits on the overall health. It acts as an immune booster, metabolism booster, and enhancer for digestion and absorption of food. (13)
An alternative to the fast-food burrito is the burrito bowl which is a healthier version. Cutting down the elements that give high fat and high carbs and replacing them with elements that satisfy the macronutrients and essential elements of diets is a better option.
References
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4772793/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3381762/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6770596/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23531781/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6316192/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1397859/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8462382/
- https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0229716
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29374411/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25280418/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7041096/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24160252/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18335702/
Infographic
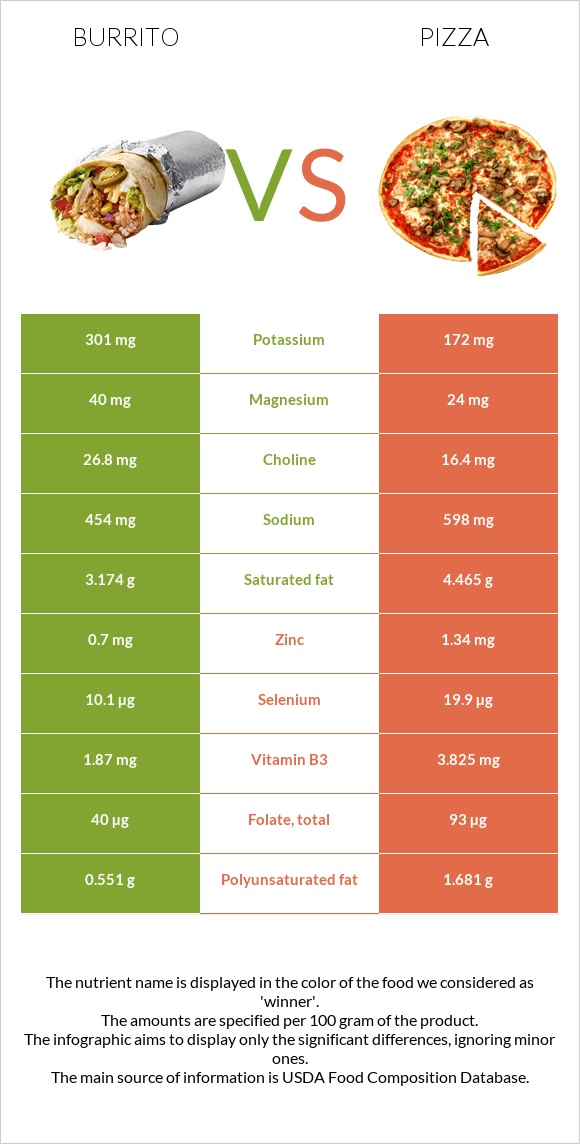
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Phosphorus | 45mg | 216mg | 24% |
| Selenium | 10.1µg | 19.9µg | 18% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.92mg | 18% | |
| Calcium | 52mg | 188mg | 14% |
| Folate | 40µg | 93µg | 13% |
| Vitamin B3 | 1.87mg | 3.825mg | 12% |
| Starch | 26.95g | 11% | |
| Protein | 6.48g | 11.39g | 10% |
| Fiber | 2.3g | 9% | |
| Copper | 0.174mg | 0.105mg | 8% |
| Vitamin A | 69µg | 8% | |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.29mg | 0.39mg | 8% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.551g | 1.681g | 8% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.28mg | 0.195mg | 7% |
| Zinc | 0.7mg | 1.34mg | 6% |
| Sodium | 454mg | 598mg | 6% |
| Vitamin E | 0.83mg | 6% | |
| Vitamin K | 6.7µg | 6% | |
| Saturated fat | 3.174g | 4.465g | 6% |
| Fats | 6.22g | 9.69g | 5% |
| Cholesterol | 2mg | 17mg | 5% |
| Iron | 2.08mg | 2.48mg | 5% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.14mg | 0.08mg | 5% |
| Magnesium | 40mg | 24mg | 4% |
| Potassium | 301mg | 172mg | 4% |
| Calories | 206kcal | 266kcal | 3% |
| Vitamin B12 | 0.5µg | 0.42µg | 3% |
| Manganese | 0.4mg | 0.36mg | 2% |
| Choline | 26.8mg | 16.4mg | 2% |
| Vitamin C | 0.9mg | 1.4mg | 1% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 2.184g | 2.608g | 1% |
| Fructose | 1g | 1% | |
| Net carbs | 32.92g | 31.03g | N/A |
| Carbs | 32.92g | 33.33g | 0% |
| Sugar | 3.58g | N/A | |
| Trans fat | 0.241g | N/A | |
| Tryptophan | 0.079mg | 0% | |
| Threonine | 0.244mg | 0.41mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 0.27mg | 0.564mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 0.504mg | 1.139mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 0.343mg | 0.77mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.107mg | 0.264mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 0.351mg | 0.664mg | 0% |
| Valine | 0.319mg | 0.72mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.172mg | 0.355mg | 0% |
| Omega-3 - EPA | 0.004g | N/A | |
| Omega-3 - ALA | 0.175g | N/A | |
| Omega-3 - DPA | 0.004g | N/A | |
| Omega-6 - Gamma-linoleic acid | 0.003g | N/A | |
| Omega-6 - Dihomo-gamma-linoleic acid | 0.009g | N/A | |
| Omega-6 - Eicosadienoic acid | 0.003g | N/A | |
| Omega-6 - Linoleic acid | 1.367g | N/A |
Macronutrient Comparison
| Contains more WaterWater | +21.7% |
| Contains more ProteinProtein | +75.8% |
| Contains more FatsFats | +55.8% |
| Contains more OtherOther | +30.8% |
Fat Type Comparison
| Contains less Sat. FatSaturated fat | -28.9% |
| Contains more Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat | +19.4% |
| Contains more Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat | +205.1% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Burrito - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/172038/nutrients
- Pizza - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/173292/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.






