Camembert vs. Brie — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Brie has more Vitamin B12, E, B1, and monounsaturated fat than camembert. It is also lower in sodium and sugars.
Camembert has more Vitamin A, Vitamin B3, potassium, and calcium. The amounts of cholesterol and saturated fat are also lower in camembert.
Introduction
In this article, you can find a detailed description of the differences between brie and camembert.
What's The Actual Difference?
Brie and camembert may look similar, be served in similar ways, and even be made from the same recipe, but subtle differences distinguish these two kinds of cheese. Both kinds of cheese are made from cow's milk and have soft, bloomy, edible rinds. They originated in northern France. Brie has a milder flavor with buttery, creamy notes, whereas camembert can have a more intense flavor with deeper earthy notes. Camembert and brie have similar textures, with camembert being denser and brie being runnier. Brie is frequently sold by the slice, a wedge of the giant wheel, whereas camembert is sold whole. The reason for this is because of size. A wheel of brie typically measures between 9 and 17 inches in diameter, whereas a camembert is only 5 inches across.
Nutrition
At the bottom of the page, you can find nutrition infographics that visually demonstrate the differences between these two foods.
Calories
Brie and camembert are high in calories. Brie contains 300 calories per 100g, whereas camembert contains 334 calories per 100g.
Fats
Both types of cheese have good amounts of fat. Brie contains 27.68g, whereas camembert provides 24.26g of fat per 100g.
Accordingly, both are also high in saturated fat. However, brie is higher in mono- and polyunsaturated fats.
Carbs
Both foods are low-carb foods. Brie contains 0.45g of carbs per 100g, and camembert contains 0.46g of carbs per 100g. All these carbs are net.
Cholesterol
Brie is higher in cholesterol than camembert. It has 100mg of cholesterol, while camembert contains 72mg.
Protein
Both foods have equal amounts of protein. Brie has 20.75g of protein, and camembert contains 19.8g of protein per 100g. Both fall in the range of the top 23% of foods as protein sources.
Vitamins
The vitamin content of brie is richer than that of camembert.
Brie contains more Vitamin E, Vitamin D, Vitamin B1, Vitamin B12, and Vitamin K.
On the other hand, camembert contains more Vitamin B3, Vitamin B5, and Vitamin A.
Brie and camembert are equal in Vitamin B2, B6, and folate.
Vitamin Comparison
| Contains more Vitamin AVitamin A | +38.5% |
| Contains more Vitamin B3Vitamin B3 | +65.8% |
| Contains more Vitamin B5Vitamin B5 | +97.7% |
| Contains more Vitamin EVitamin E | +14.3% |
| Contains more Vitamin DVitamin D | +25% |
| Contains more Vitamin B1Vitamin B1 | +150% |
| Contains more Vitamin B12Vitamin B12 | +26.9% |
| Contains more Vitamin KVitamin K | +15% |
Minerals
Brie contains more iron and less sodium than camembert.
Camembert has more calcium, potassium, phosphorus, and copper than brie. Both have equal amounts of magnesium and zinc.
Important notes: both types of cheese are high in sodium, so it is better to consume them in moderation.
Mineral Comparison
| Contains more CalciumCalcium | +110.9% |
| Contains more PotassiumPotassium | +23% |
| Contains more PhosphorusPhosphorus | +84.6% |
| Contains more ManganeseManganese | +11.8% |
| Contains more IronIron | +51.5% |
| Contains less SodiumSodium | -25.3% |
Glycemic Index
Both types of cheese are considered low glycemic index food. The GI of brie and camembert is equal to 27.
Health Impact
Both types of cheese are high in riboflavin and Vitamin B12, essential for energy production. Its calcium content is essential for healthy bone growth, and its Vitamin A content promotes healthy skin and vision [1].
One study [2] shows that brie, camembert, and other ripened cheeses can slow the growth of leukemia cells.
Brie and camembert are high in fat; full-fat dairy consumption is linked to healthier body weight and does not appear to increase your risk of heart disease [3].
The Catholic University of Louvain in Belgium discovered that eating ripened cheese reduced blood sugar levels and fat tissue in obese/diabetic mice [4]. Besides, both cheese types have low glycemic indexes and tiny amounts of carbs, so their consumption will not raise blood glucose levels.
However, more human research is needed.
Side Effects
Camembert contains more sodium than brie. It contains 8% of the daily recommended sodium, which adds up quickly when combined with other salty foods. In salt-sensitive people, too much sodium can cause high blood pressure [5].
Infographic
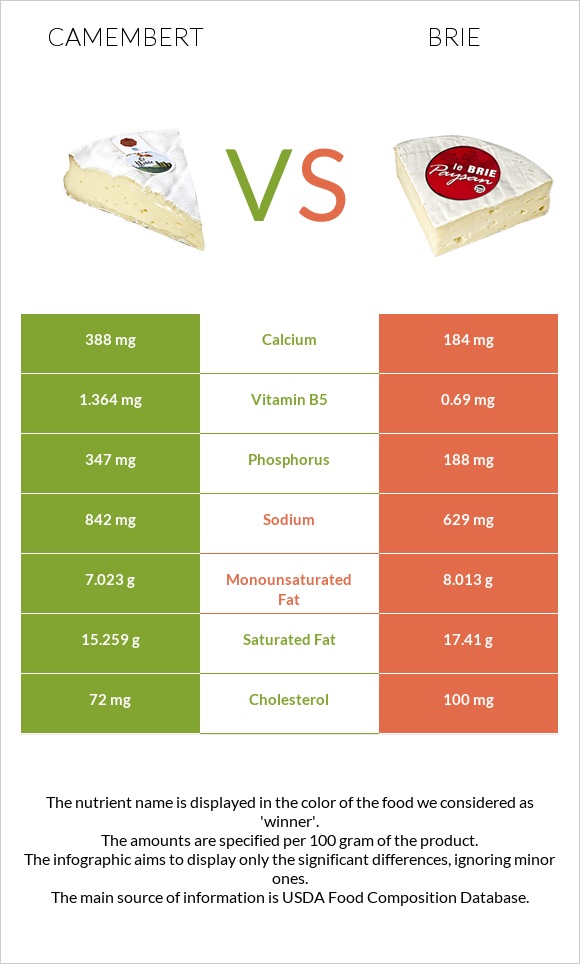
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Phosphorus | 347mg | 188mg | 23% |
| Calcium | 388mg | 184mg | 20% |
| Vitamin B12 | 1.3µg | 1.65µg | 15% |
| Vitamin B5 | 1.364mg | 0.69mg | 13% |
| Saturated fat | 15.259g | 17.41g | 10% |
| Cholesterol | 72mg | 100mg | 9% |
| Sodium | 842mg | 629mg | 9% |
| Vitamin A | 241µg | 174µg | 7% |
| Fats | 24.26g | 27.68g | 5% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.028mg | 0.07mg | 4% |
| Calories | 300kcal | 334kcal | 2% |
| Protein | 19.8g | 20.75g | 2% |
| Iron | 0.33mg | 0.5mg | 2% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.488mg | 0.52mg | 2% |
| Vitamin B3 | 0.63mg | 0.38mg | 2% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 7.023g | 8.013g | 2% |
| Potassium | 187mg | 152mg | 1% |
| Vitamin D | 0.4µg | 0.5µg | 1% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.227mg | 0.235mg | 1% |
| Folate | 62µg | 65µg | 1% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.724g | 0.826g | 1% |
| Net carbs | 0.46g | 0.45g | N/A |
| Carbs | 0.46g | 0.45g | 0% |
| Vitamin D | 18 IU | 20 IU | 0% |
| Magnesium | 20mg | 20mg | 0% |
| Sugar | 0.46g | 0.45g | N/A |
| Copper | 0.021mg | 0.019mg | 0% |
| Zinc | 2.38mg | 2.38mg | 0% |
| Vitamin E | 0.21mg | 0.24mg | 0% |
| Manganese | 0.038mg | 0.034mg | 0% |
| Selenium | 14.5µg | 14.5µg | 0% |
| Vitamin K | 2µg | 2.3µg | 0% |
| Choline | 15.4mg | 15.4mg | 0% |
| Tryptophan | 0.307mg | 0.322mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 0.717mg | 0.751mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 0.968mg | 1.015mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 1.84mg | 1.929mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 1.766mg | 1.851mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.565mg | 0.592mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 1.105mg | 1.158mg | 0% |
| Valine | 1.279mg | 1.34mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.683mg | 0.716mg | 0% |
Macronutrient Comparison
| Contains more OtherOther | +36.3% |
| Contains more FatsFats | +14.1% |
Fat Type Comparison
| Contains less Sat. FatSaturated fat | -12.4% |
| Contains more Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat | +14.1% |
| Contains more Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat | +14.1% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Camembert - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/172178/nutrients
- Brie - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/172177/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.


