Clementine vs. Mandarin orange — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
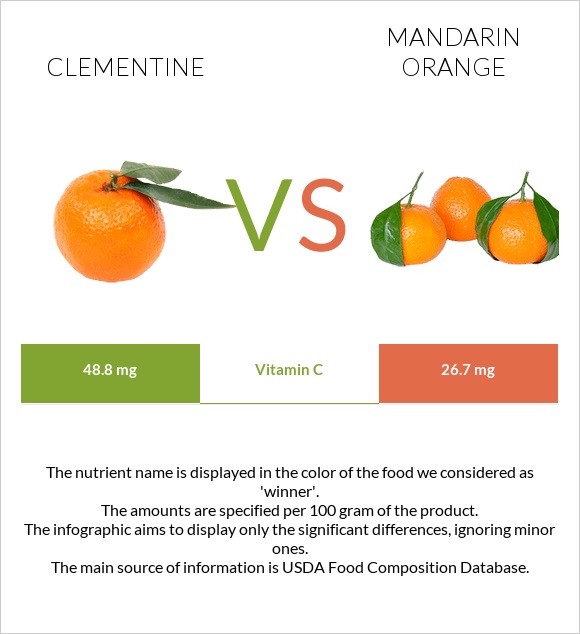
Clementine contains more Vitamin C, Vitamin B1, Vitamin B3, and folate than mandarin orange. It is also lower in sodium, sugars, and saturated fat.
Mandarin is richer in Vitamin B2, Vitamin B5, calcium, magnesium, and zinc.
Introduction
Clementines and mandarin oranges are the most popular citrus fruits, usually confused with each other. Why? Because they are very similar in appearance, they sometimes can also have similar tastes. However, to better understand the main differences, we will look at them individually.
The actual difference
Clementines are a type of mandarin orange. They are a cross between mandarin oranges and sweet oranges.
However, the main difference between clementine and mandarin is that clementines are the smallest mandarin orange variety. Compared to mandarin, clementines have loose skin that makes them easy to peel. They are extremely sweet, seedless, and have smooth and shiny red-orange skin.
Nutrition
Macronutrients and Calories
This article section will compare the nutritional content between a mandarin orange and clementine. Slightly note: both have similar nutritional profiles. At the bottom of this page, you can find a nutrition infographic, which will help you better understand the differences in the nutrition of these fruits.
Calories
Mandarin and clementine are low in calories. On the other hand, mandarin has more calories than clementine: it has roughly 57 calories per 100g, while clementine has 53 calories per 100g (1.2).
Protein
There is little protein in these two fruits. Their protein content is less than 1g per 100g (1.2).
Carbs
The carbohydrate content of mandarin is slightly higher than that of clementine. There are 13.3 grams of carbohydrates in 100 g of clementine, compared with 13.6 grams in 100 g of mandarin. 100g of mandarin contains 2.1 g of dietary fiber, while 100g of clementine contains 1.8 g.
Fats
There is no need to consider the fat content of these fruits, as they have less than 1g of fat per 100g. Mandarin and clementine have no cholesterol.
Vitamins
Clementine is richer in vitamin C, vitamin B1, vitamin B3, and folate. Clementine falls in the range of the top 13% of foods as a source of vitamin C. This vitamin may preserve a strong immune system, promote healing, and have antioxidant activity.
Mandarin orange has more vitamin B2 and vitamin B5.
Both these fruits contain equal amounts of vitamin E and vitamin B6.
Both fruits lack vitamin D, vitamin B12, and vitamin B9.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+82.8%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+48.3%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+69.1%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+50%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+20%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+43%
Minerals
Mandarin has a relatively higher amount of calcium, zinc, and magnesium.
Clementine has less sodium than mandarin.
Both fruits have equal iron, phosphorus, copper, and potassium.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-50%
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+20%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+23.3%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+16.7%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+69.6%
Glycemic Index
According to The International Tables of Glycemic Index Values, the glycemic index of mandarin orange falls in the range of 47±2. Clementines, which are a hybrid of willow leaves mandarin orange with sweet orange, have a low glycemic index, but their glycemic index has not been determined (3).
Acidity
These fruits are alkaline, but exact data is not available. The quality of the produced fruit is determined by the coexistence of internal ripeness (lower acidity, increased sugar/acid ratio) and outward coloring. The PGI (Protected Geographical Indication) specifications require that clementines be harvested when the orange coloration, which occurs naturally on the tree, covers at least 80% of the peel, and have an acid concentration between 0.65g and 1.4g of citric acid per 100g of juice (4).
Weight loss and diets
Clementine and Mandarin orange are low-calorie fruits, so they can be included in a variety of diets.
- Because the Atkins diet is low in carbohydrates, most fruits should be avoided. Clementine and mandarin orange consumption is not recommended during this diet.
- The Dukan diet, like the Atkins diet, is low in carbohydrates and high in protein. Until the third (consolidation) phase, fruits, including these, are off the menu.
- The Mediterranean diet encourages the consumption of fruits and vegetables. Consumption of clementines and mandarin oranges is advised throughout this diet.
- The paleo diet often includes lean meats, fish, fruits, vegetables, nuts, and seeds – foods that may have been gotten through hunting and gathering in the past, thus these fruits are suggested.
- Intermittent fasting is more like an eating habit than a diet because it regulates when you eat rather than what you consume. These fruits are recommended with this diet.
- They can also be included in the DASH diet (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension).
Health impact
Cardiovascular Health
Mandarin orange and clementine’s direct effects on arterial blood pressure are unknown; however, according to this rat study, hesperidin found in citrus fruits may lower blood pressure and cardiac hypertrophies (thickening of the heart's wall, which negatively affects the heart) (5).
Citrus flavonoids are antioxidants that may protect cells from oxidative damage, which is crucial for preventing atherosclerosis. Besides this, some components found in citrus fruits, like naringin, may reduce LDL (bad cholesterol) levels in the blood (5). Based on this, we can say that flavonoids have anti-ischaemic activity and may have a role in preventing myocardial infarction (6).
Citrus flavonoids may reduce platelet activity via a number of routes. This effect is important for preventing atherothrombosis in patients with atherosclerosis, especially after stenting the coronary artery (5).
Citrus fruits contain dietary fiber that may help prevent heart disease by lowering blood pressure and cholesterol. Additionally, it makes you feel full, so you can eat less and possibly lose weight (7). It’s important for this section because obesity was found to be a convincing risk factor for cardiovascular disease and type 2 diabetes, both of which are risk factors for heart disease (8).
Diabetes
Clementine and mandarin orange have anti-diabetic properties.
Citrus fruits containing flavanone glycosides may reduce blood glucose levels in diabetic patients by inhibiting α-amylase and α-glucosidase in the intestinal tract. Several studies have reported that naringenin has neuroprotective properties that could help manage diabetic neuropathy (9).
Satsuma mandarin may suppress liver cell damage and inhibit liver dysfunction caused by chronic hyperglycemia in diabetics, according to this study (10). This effect of clementine is unknown.
According to this study, the consumption of citrus (including clementine and mandarin orange) for a prolonged period of time modulates diabetes-related markers in a positive way (11).
Decreases the transit time of food in the gut, improves gut microflora, and may improve glycemic control. Dietary fibers may also decrease hyperinsulinemia in type 2 diabetes patients (11).
Digestive Health
Dietary fiber in these fruits has been shown to enhance the frequency of bowel movements and may be beneficial in the treatment of constipation (12).
Dietary fiber can change the gut flora to improve digestion, strengthen the immune system, and reduce inflammation. Fiber aids in the production of short-chain fatty acids in the gut, which improves muscle performance and may aid in the prevention of chronic diseases such as ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease (13).
Flavonoids found in these fruits may inhibit pancreatic lipase. When the lipase enzyme is suppressed, total cholesterol levels in the body are reduced, which is important for obesity treatment (14).
Cancer
Both of these fruits include hesperidin and flavonoids, both of which have the potential to be chemoprotective. Hesperidin has been proven to have antioxidant activity, anti-inflammatory properties, and an inhibitory effect on prostaglandin formation. This flavonoid prevents chemically induced carcinogenesis in a variety of organs (15).
Tangeritin, contained in these fruits, has been demonstrated to prevent cancer cell development via increasing intracellular gap junctional communication (15).
According to these studies, high citrus fruit (including mandarin orange and clementine) consumption has a protective effect on the risk of stomach, breast, oral, and pancreatic cancer (16.17.18.19).
Downsides and Risks
Allergy
Both mandarin oranges and clementine can cause an allergic reaction․ The symptoms are frequently localized, which means you feel them exactly where the raw fruit touched your skin. Intense tingling and itching of the lips, tongue, and throat are among the symptoms (20).
References
- https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/2503019/nutrients
- https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/2344658/nutrients
- https://academic.oup.com/ajcn/article/114/5/1625/6320814?login=false
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6566537/#:~:text=The%20PGI%20specifications%20constrain%20producers,(European%20Union%2C%202005).
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6431442/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5452232/
- https://www.health.harvard.edu/heart-health/eat-more-fiber-rich-foods-to-foster-heart-health
- https://www.citrusaustralia.com.au/wp-content/uploads/Health-Benefits-of-Citrus-Fruits-CSIRO-Full-Report.pdf
- https://blog.univ-reunion.fr/detroi/files/2015/03/preventive-medecine.pdf
- https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/bpb/29/3/29_3_588/_article/-char/ja/
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S092422442100412X
- https://publications.aap.org/pediatrics/article-abstract/96/5/997/59899/An-Overview-of-the-Effects-of-Dietary-Fiber-on
- https://www.health.harvard.edu/staying-healthy/fabulous-fiber
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0308814620306476
- https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Saravana-Jaganathan/publication/261998860_Role_of_pomegranate_and_citrus_fruit_juices_in_colon_cancer_prevention/links/004635392c841c5856000000/Role-of-pomegranate-and-citrus-fruit-juices-in-colon-cancer-prevention.pdf
- https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10120-007-0447-2
- https://synapse.koreamed.org/articles/1036462
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1043661818304729
- https://journals.lww.com/pancreasjournal/Abstract/2009/03000/Citrus_Fruit_Intake_and_Pancreatic_Cancer_Risk__A.11.aspx
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0091674913018472
Infographic
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Vitamin C | 48.8mg | 26.7mg | 25% |
| Vitamin A | 34µg | 4% | |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.086mg | 0.058mg | 2% |
| Vitamin B3 | 0.636mg | 0.376mg | 2% |
| Folate | 24µg | 16µg | 2% |
| Calcium | 30mg | 37mg | 1% |
| Manganese | 0.023mg | 0.039mg | 1% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.151mg | 0.216mg | 1% |
| Choline | 14mg | 10.2mg | 1% |
| Fructose | 1.64g | 2.4g | 1% |
| Calories | 47kcal | 53kcal | 0% |
| Protein | 0.85g | 0.81g | 0% |
| Fats | 0.15g | 0.31g | 0% |
| Net carbs | 10.32g | 11.54g | N/A |
| Carbs | 12.02g | 13.34g | 0% |
| Magnesium | 10mg | 12mg | 0% |
| Potassium | 177mg | 166mg | 0% |
| Iron | 0.14mg | 0.15mg | 0% |
| Sugar | 9.18g | 10.58g | N/A |
| Fiber | 1.7g | 1.8g | 0% |
| Copper | 0.043mg | 0.042mg | 0% |
| Zinc | 0.06mg | 0.07mg | 0% |
| Phosphorus | 21mg | 20mg | 0% |
| Sodium | 1mg | 2mg | 0% |
| Vitamin E | 0.2mg | 0.2mg | 0% |
| Selenium | 0.1µg | 0.1µg | 0% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.03mg | 0.036mg | 0% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.075mg | 0.078mg | 0% |
| Saturated fat | 0.039g | 0% | |
| Monounsaturated fat | 0.06g | 0% | |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.065g | 0% | |
| Tryptophan | 0.002mg | 0% | |
| Threonine | 0.016mg | 0% | |
| Isoleucine | 0.017mg | 0% | |
| Leucine | 0.028mg | 0% | |
| Lysine | 0.032mg | 0% | |
| Methionine | 0.002mg | 0% | |
| Phenylalanine | 0.018mg | 0% | |
| Valine | 0.021mg | 0% | |
| Histidine | 0.011mg | 0% |
Macronutrient Comparison
| Contains more FatsFats | +106.7% |
| Contains more CarbsCarbs | +11% |
Carbohydrate type comparison
| Contains more GlucoseGlucose | +34% |
| Contains more FructoseFructose | +46.3% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Clementine - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/168195/nutrients
- Mandarin orange - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/169105/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.






