Croissant vs. Bagel — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Bagels and croissants are popular breakfast foods that originated in Europe. Croissants contain around 2 times more calories and 20 times more fat than bagels.
Croissants also contain more Vitamin A, Vitamin B5, Vitamin B2, and folate than bagels. On the other hand, bagels are much richer in minerals, containing 4 times more manganese, as well as slightly more selenium and iron.
Introduction
In this article, we'll go through the main differences between bagels and croissants, focusing on nutrition and health impact.
What's the Actual Difference?
Most of us know that standard white bread has little nutritional value, but what about croissants and bagels? Croissants and bagels are popular breakfast foods, whether eaten with jam or in a breakfast sandwich.
A bagel is a bread product that originated in Polish Jewish communities, whereas croissants are a style of viennoiserie pastries that originated in the Austrian city of Vienna.
Bagels are crisp on the outside, chewy on the inside, slightly sweet, and slightly salty. On the other hand, croissants have a buttery taste with just a hint of yeast. An authentic French croissant has a delicious taste that is difficult to replicate outside France. Both can be eaten with cream cheese, butter, and lox.
Nutrition
The nutritional differences here are depicted for butter croissants and wheat bagels.
The serving sizes for both are usually one piece. Depending on the size, the weight of the croissant will differ. On average, one medium-sized croissant is about 57 grams, while a large one weighs 67 grams. One bagel weighs about 98 grams.
However, to keep the comparison between the two simple, we will sometimes refer to 100-gram servings of each in this section.
Macronutrient and Calories
As can be seen from the macronutrient comparison charts below, bagels and croissants have similar macronutrient compositions. The predominant macronutrients in both are carbs, which make up 46% of the entire macronutrient composition of croissants and 49% of the entire macronutrient composition of bagels.
Bagels also consist of 38% water, while croissants consist of only 23% water.
Macronutrient Comparison
Contains
more
FatsFats
+1272.5%
Contains
more
ProteinProtein
+24.4%
Contains
more
WaterWater
+61.9%
Calories
Both croissants and bagels are high in calories; however, croissants contain around 2 times more calories than bagels.
Per 100-gram serving, croissants contain 406 calories, whereas bagels contain 250 calories.
Fats
Croissants provide 20 times more fat than bagels.
Per 100-gram serving, croissants contain 21 grams of fat, while bagels contain only 1.53 grams.
Carbohydrates
Both bagels and croissants are considered high-carb foods. Per 100-gram servings, they provide similar amounts of carbs. Croissants provide 46 grams of carbs, while bagels provide 49 grams.
Fiber
The amount of fiber in bagels is almost 2 times higher than in croissants.
Bagels contain 4.1g of fiber per 100g, while croissants have only 2.6g.
Vitamins
The vitamin content of croissants is generally richer than that of bagels.
Croissants contain more Vitamin A, Vitamin B5, Vitamin B2, and folate.
On the other hand, bagel contains more Vitamin B3 and Vitamin B6.
Both have equal amounts of Vitamin B1. Moreover, whereas bagels completely lack Vitamin B12, Vitamin A, and Vitamin C, croissants contain some amounts of all these vitamins.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+162.5%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+15.3%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+129.6%
Contains
more
Vitamin B12Vitamin B12
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin KVitamin K
+20%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+15.8%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+54%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+153.4%
Minerals
Bagels are the winner in the mineral category as they contain higher levels of almost all minerals compared to croissants.
Specifically, bagels contain 4 times more manganese, as well as slightly more selenium and iron, when compared to croissants.
Both provide equal amounts of sodium.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+85%
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+218.8%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+39.8%
Contains
more
IronIron
+36%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+118.8%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+46.7%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+35.2%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+333.3%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+26.4%
Glycemic Index
Both croissants and bagels are considered high glycemic index foods.
The glycemic index of croissants is 56, whereas the GI of bagels equals 69. Visit our glycemic index chart page to learn more about the GI values of different foods.
Acidity
One way to understand the acidity of foods is through their potential renal acid load (PRAL) value, which shows how much acid or base the given food produces inside the organism.
Based on our calculations, the PRAL values of croissants and bagels are 4.5 and 5.2, respectively, meaning both values are acidic.
Health Impact
There are many varieties of bagels. Whole grains bagels contain a lot more fiber and antioxidants than other kinds of bagels. They have also been shown to protect against diabetes, cancer, and obesity (1). However, in some countries, bagels and other refined grain products are fortified with some nutrients that were lost during processing, such as B-complex vitamins and iron.
Croissants are extremely versatile and can be paired with various nutrient-dense toppings and fillings; they also provide a small amount of protein per serving. However, croissants are high in calories, sodium, and saturated fat. Research shows that consuming highly processed foods high in both saturated fats and simple carbohydrates, such as croissants, may harm heart health (2). As a result, some people may need to limit their intake and consider consuming low-sodium products.
Infographic
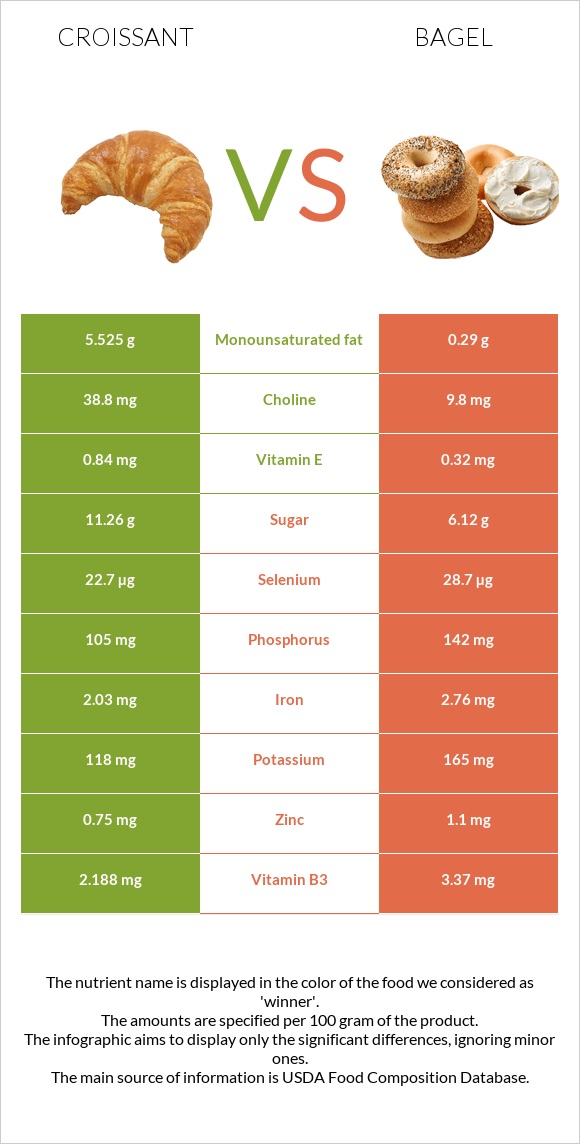
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Saturated fat | 11.659g | 0g | 53% |
| Manganese | 0.33mg | 1.43mg | 48% |
| Fats | 21g | 1.53g | 30% |
| Vitamin A | 206µg | 0µg | 23% |
| Cholesterol | 67mg | 0mg | 22% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 5.525g | 0.29g | 13% |
| Copper | 0.08mg | 0.175mg | 11% |
| Selenium | 22.7µg | 28.7µg | 11% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.861mg | 0.375mg | 10% |
| Iron | 2.03mg | 2.76mg | 9% |
| Calories | 406kcal | 250kcal | 8% |
| Magnesium | 16mg | 51mg | 8% |
| Vitamin B3 | 2.188mg | 3.37mg | 7% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.058mg | 0.147mg | 7% |
| Vitamin B12 | 0.16µg | 0µg | 7% |
| Fiber | 2.6g | 4.1g | 6% |
| Phosphorus | 105mg | 142mg | 5% |
| Choline | 38.8mg | 9.8mg | 5% |
| Protein | 8.2g | 10.2g | 4% |
| Zinc | 0.75mg | 1.1mg | 3% |
| Vitamin E | 0.84mg | 0.32mg | 3% |
| Folate | 88µg | 76µg | 3% |
| Calcium | 37mg | 20mg | 2% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.241mg | 0.209mg | 2% |
| Carbs | 45.8g | 48.89g | 1% |
| Potassium | 118mg | 165mg | 1% |
| Sodium | 467mg | 439mg | 1% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.388mg | 0.403mg | 1% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 1.094g | 0.936g | 1% |
| Protein per 100 calories | 2.0197044334975365g | 4.079999999999999g | N/A |
| Calories per 10 g protein | 495.12195121951225kcal | 245.0980392156863kcal | N/A |
| Vitamin C | 0.2mg | 0mg | 0% |
| Net carbs | 43.2g | 44.79g | N/A |
| Sugar | 11.26g | 6.12g | N/A |
| Vitamin K | 1.8µg | 1.5µg | 0% |
| Tryptophan | 0.099mg | 0% | |
| Threonine | 0.284mg | 0% | |
| Isoleucine | 0.365mg | 0% | |
| Leucine | 0.623mg | 0% | |
| Lysine | 0.329mg | 0% | |
| Methionine | 0.175mg | 0% | |
| Phenylalanine | 0.416mg | 0% | |
| Valine | 0.41mg | 0% | |
| Histidine | 0.187mg | 0% | |
| Omega-3 - EPA | 0.003g | 0g | N/A |
| Omega-3 - DHA | 0.002g | 0g | N/A |
Fat Type Comparison
| Contains more Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat | +1805.2% |
| Contains more Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat | +16.9% |
| Contains less Sat. FatSaturated fat | -100% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Croissant - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/174987/nutrients
- Bagel - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/167533/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.






