Curry powder vs. Turmeric — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Turmeric is higher in manganese, iron, potassium, and vitamins. Turmeric has a lower glycemic index than curry.
Curry contains more calcium, phosphorus, and magnesium and fewer carbs than turmeric.
Introduction
This article will discuss the main differences in turmeric and cumin seeds' nutrition, focusing on their health impact.
What's The Actual Difference?
Turmeric has a golden yellow color and a bitter taste with a peppery flavor, while the curry is hot due to chili or black pepper and sweet due to spices like cinnamon, often a shade of yellow.
The biggest difference between curry and turmeric is that turmeric is a single spice, while curry powder is a mix of multiple spices, such as ginger, garlic, and turmeric.
Nutrition
You can find nutritional infographics at the bottom of this page that visually show the differences between turmeric and curry.
Calories
Turmeric has 312 calories per 100g, whereas curry contains 325 calories per 100g. However, people usually consume them in tiny amounts, so calories don’t matter much.
Carbs
Turmeric has 67.14g of carbs per 100g, of which 22.7g is fiber and 44.44g are net carbs. Curry powder has 55.83g of carbs per 100g, of which 10.5g is fiber and 33.74g are net carbs.
Here again, these powders are usually consumed in small amounts, so the carb count is also low.
Minerals
In comparison, turmeric has more iron, potassium, and also less sodium than curry. Turmeric falls in the range of the top 2% of foods as a source of iron and can fully convert your daily iron need.
However, curry provides more calcium. Both powders have equal amounts of zinc.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+22.6%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+212.5%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+22.7%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+550%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+77.8%
Contains
more
IronIron
+188%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-48.1%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+138.6%
Vitamins
Curry contains a significantly higher amount of vitamins. It provides more Vitamin A, E, B1, B2, B3, B5, folate, and Vitamin K.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+469.8%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+203.4%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+33.3%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+141.5%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+97.4%
Contains
more
Vitamin KVitamin K
+644.8%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+180%
Glycemic Index
The estimated glycemic index of turmeric is 0, while curry powder has GI equal to 5. Both are considered low-GI foods.
Acidity
Both turmeric and curry are alkaline. Curry powder has a pH of 17.4, while turmeric has a pH of 35.5. With that in mind, taking turmeric in high doses may increase your risk of indigestion and nausea.
Health Benefits
Digestion
Curry powder promotes digestive health due to the presence of turmeric and ginger. Turmeric helps improve your digestive tract's microbiota or the healthy bacteria that aid digestion. Ginger has been shown to relieve nausea and vomiting in pregnant women, help settle upset stomachs, decrease flatulence, bloating, and indigestion, and reduce intestinal cramps [1, 2].
Downsides and Risks
Allergy
Curry powder has some side effects because it combines different spices. In rare cases, people may experience stomach upset, dizziness, or diarrhea.
Turmeric can have serious side effects in rare cases. In rare cases, some people may experience side effects such as stomach upset [3].
Infographic
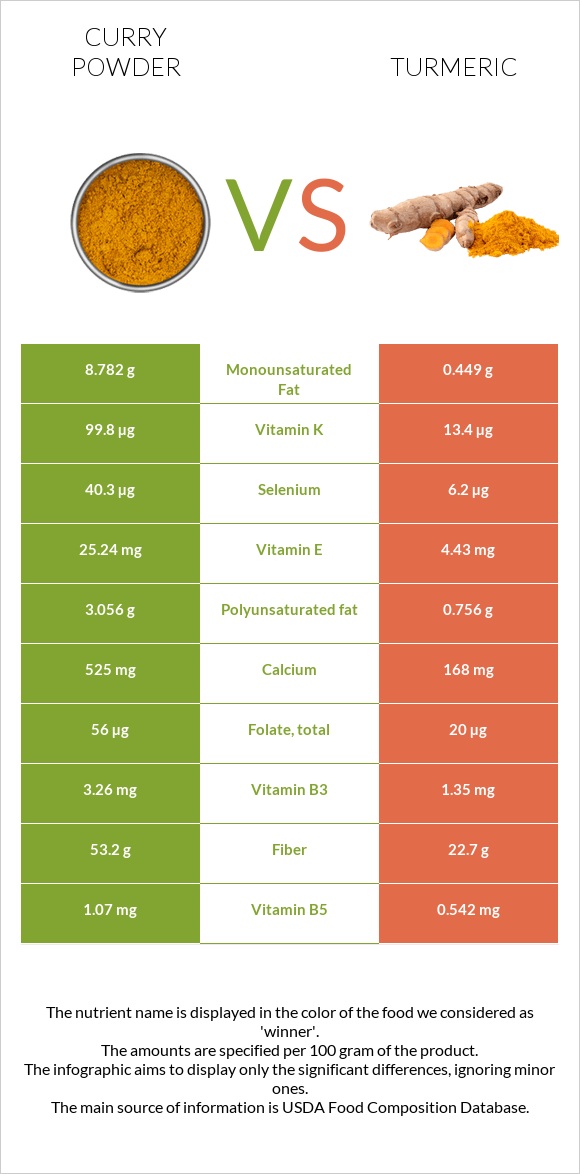
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Manganese | 8.3mg | 19.8mg | 500% |
| Iron | 19.1mg | 55mg | 449% |
| Vitamin E | 25.24mg | 4.43mg | 139% |
| Fiber | 53.2g | 22.7g | 122% |
| Vitamin K | 99.8µg | 13.4µg | 72% |
| Selenium | 40.3µg | 6.2µg | 62% |
| Calcium | 525mg | 168mg | 36% |
| Potassium | 1170mg | 2080mg | 27% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 8.782g | 0.449g | 21% |
| Fats | 14.01g | 3.25g | 17% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 3.056g | 0.756g | 15% |
| Vitamin B3 | 3.26mg | 1.35mg | 12% |
| Magnesium | 255mg | 208mg | 11% |
| Copper | 1.2mg | 1.3mg | 11% |
| Vitamin B5 | 1.07mg | 0.542mg | 11% |
| Phosphorus | 367mg | 299mg | 10% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.176mg | 0.058mg | 10% |
| Protein | 14.29g | 9.68g | 9% |
| Folate | 56µg | 20µg | 9% |
| Carbs | 55.83g | 67.14g | 4% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.2mg | 0.15mg | 4% |
| Choline | 64.2mg | 49.2mg | 3% |
| Zinc | 4.7mg | 4.5mg | 2% |
| Calories | 325kcal | 312kcal | 1% |
| Sodium | 52mg | 27mg | 1% |
| Saturated fat | 1.648g | 1.838g | 1% |
| Vitamin C | 0.7mg | 0.7mg | 0% |
| Net carbs | 2.63g | 44.44g | N/A |
| Sugar | 2.76g | 3.21g | N/A |
| Vitamin A | 1µg | 0µg | 0% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.105mg | 0.107mg | 0% |
| Trans fat | 0g | 0.056g | N/A |
| Tryptophan | 0.11mg | 0.17mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 0.35mg | 0.33mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 0.63mg | 0.47mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 0.89mg | 0.81mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 0.7mg | 0.38mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.19mg | 0.14mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 0.58mg | 0.53mg | 0% |
| Valine | 0.75mg | 0.66mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.29mg | 0.15mg | 0% |
| Fructose | 0.79g | 0.45g | 0% |
| Omega-3 - ALA | 0.255g | 0.003g | N/A |
| Omega-6 - Gamma-linoleic acid | 0.013g | 0.081g | N/A |
Macronutrient Comparison
| Contains more ProteinProtein | +47.6% |
| Contains more FatsFats | +331.1% |
| Contains more CarbsCarbs | +20.3% |
| Contains more WaterWater | +46% |
Fat Type Comparison
| Contains less Sat. FatSaturated fat | -10.3% |
| Contains more Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat | +1855.9% |
| Contains more Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat | +304.2% |
Carbohydrate type comparison
| Contains more GlucoseGlucose | +200% |
| Contains more FructoseFructose | +75.6% |
| Contains more GalactoseGalactose | +∞% |
| Contains more SucroseSucrose | +283.9% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Curry powder - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/170924/nutrients
- Turmeric - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/172231/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.