Prunes vs Dates - Health impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Prune is richer in calcium and potassium. They have 77 times more vitamin A and 21 times more Vitamin K than dates. Prune is also lower in carbs, calories, and glycemic index.
In comparison, dates are richer in folate, selenium, and fiber.
Introduction
Dried fruits are widely used in gastronomy around the world. Dates are among the most common things eaten in the middle east across all cultures. This article compares two dried fruits, prunes, and dates.
We will compare them according to their general differences, nutritional content, and health impacts.
General differences
Deglet Noor dates are one of the most common types of dates that are consumed. It has a semi-dry texture.
Prunes are dried plums that have a semi-dry texture aswell.
Their flavor profiles are quite different from one another. Dates have a more robust flavor compared to prune.
Consumption
Dates are one of the most consumed dried fruits that are consumed all over the world. They are the most famous in the Middle East region.
Palm oil is derived from the processing of the date palm oil fruit.
Nutritional content comparison
The serving size of a prune is one prune which is about 9.5g, and in comparison, the serving size of a date is 7.1g.
The comparison is based on 100g of each.
Calories
Dates are higher in calories compared to prune.
Date contains 282 calories, whereas prune contains 240 calories.
Glycemic index
Dates have a higher glycemic index compared to prune. The glycemic index of date is 42. In comparison, prune has a glycemic index of 29.
Both are classified as low glycemic index foods.
Protein and Fat
They have similar and negligible amounts of proteins and fats.
Carbs
Their carb content is significantly different. Prune contains 64g of carbs, whereas dates contain 75g.
Fiber
Dates have a slightly higher fiber content than prunes. Dates have 8g of fiber, and prunes have 7.1g of it per 100g.
Macronutrient Comparison
Contains
more
ProteinProtein
+12.4%
Contains
more
CarbsCarbs
+17.5%
Contains
more
WaterWater
+50.6%
Contains
more
OtherOther
+65%
Minerals
Prune is richer in calcium and potassium, while dates have a higher amount of selenium.
Below we can see their mineral distributions.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+900%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+10.3%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+11.6%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+36.4%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+51.7%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+11.3%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+14.1%
Vitamins
Prunes are richer in vitamin B2, vitamin K, and Vitamin A. Prunes have 77 times more vitamin A and 21 times more Vitamin K than dates.
In comparison, dates are richer in folate.
Below we can see their vitamin distributions.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+39.6%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+375%
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+50%
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+760%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+181.8%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+47.7%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+24.2%
Contains
more
Vitamin KVitamin K
+2103.7%
Health impacts
Nervous system
Dates benefit the nervous system by decreasing inflammatory markers in brain tissue, decreasing the risks of Alzheimer’s disease. (1)
Diabetes
The glycemic index and glycemic load of dates are low, so they will not spike blood glucose levels and are considered safe for people with diabetes when consumed in moderation.
Dates have been shown to provide glycemic control in diabetic patients. Although they are high in carbs, glycemic control was observed when they consumed dates. (2)(3)
Prunes, on the other hand, also have low GI and GL, so they also will not spike blood sugar levels. However, prunes have an effect on diabetes but with another mechanism. They increase satiety levels and reduce food intake. (11)
Antioxidants
Dates are rich in antioxidants, and they have several benefits regarding overall health. Antioxidant reduces risks of cancer and overall metabolic stress-induced damage. (4)
In addition, phenolic compounds have been shown to decrease the risks of cancer and cardiovascular diseases. (5)
Prune has antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties aswell. In addition, prunes have wound-healing antioxidative properties. (12)
Cardiovascular health
Consumption of prunes is linked with decreased blood lipid levels and overall control of blood lipids. In turn, decreasing the risks of cardiovascular diseases such as atherosclerosis. In addition, prune consumption is linked with decreased risks of cardiovascular diseases in postmenopausal women. (6)(7)
Prune is a richer source of potassium compared to date, and consumption of potassium is linked with more controlled blood pressure levels. Resulting in decreased rates of cardiovascular diseases. (8)
Digestive system
Dates and prunes are rich in fiber, providing several positive impacts on the overall gastrointestinal tract by keeping the microbiome healthy and lowering the risk of several gut diseases. (9)(10)
Vitamin A and K
Prune is richer in vitamins A and K, necessary to maintain normal biochemical and physiological functions regarding the immune system, blood coagulation, cellular metabolism, insulin sensitivity, and bone formation. (13)(14)
Dates do not provide these benefits.
References
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4994443/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8281151/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7019638/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32798862/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8175999/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6130511/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33978491/
- https://www.heart.org/en/health-topics/high-blood-pressure/changes-you-can-make-to-manage-high-blood-pressure/how-potassium-can-help-control-high-blood-pressure
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8153313/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3544045/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24090144/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33801467/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29493984/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26468402/
Infographic
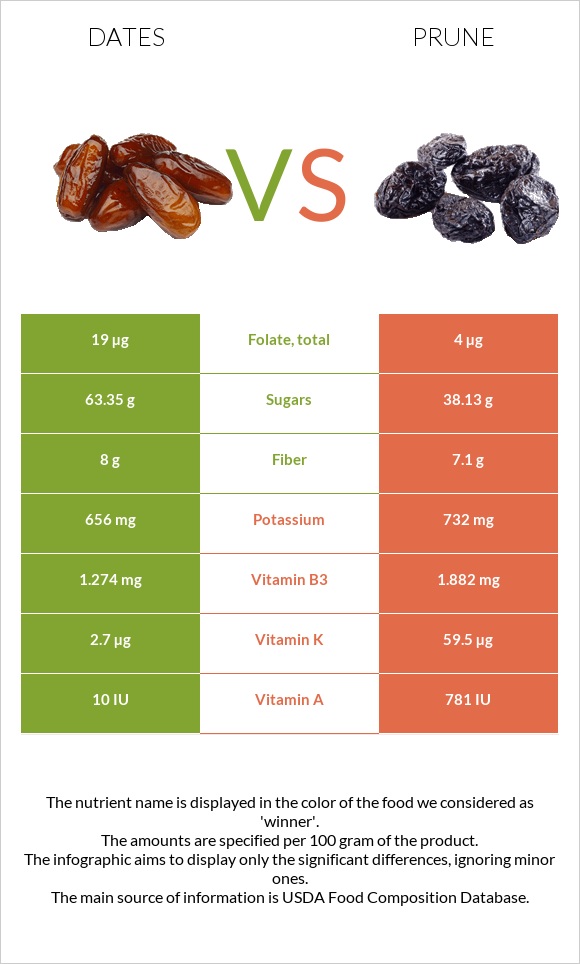
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Vitamin K | 2.7µg | 59.5µg | 47% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.066mg | 0.186mg | 9% |
| Fructose | 19.56g | 12.45g | 9% |
| Copper | 0.206mg | 0.281mg | 8% |
| Selenium | 3µg | 0.3µg | 5% |
| Carbs | 75.03g | 63.88g | 4% |
| Fiber | 8g | 7.1g | 4% |
| Vitamin A | 0µg | 39µg | 4% |
| Vitamin B3 | 1.274mg | 1.882mg | 4% |
| Folate | 19µg | 4µg | 4% |
| Vitamin E | 0.05mg | 0.43mg | 3% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.589mg | 0.422mg | 3% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.165mg | 0.205mg | 3% |
| Calories | 282kcal | 240kcal | 2% |
| Potassium | 656mg | 732mg | 2% |
| Starch | 5.11g | 2% | |
| Manganese | 0.262mg | 0.299mg | 2% |
| Protein | 2.45g | 2.18g | 1% |
| Iron | 1.02mg | 0.93mg | 1% |
| Zinc | 0.29mg | 0.44mg | 1% |
| Phosphorus | 62mg | 69mg | 1% |
| Choline | 6.3mg | 10.1mg | 1% |
| Protein per 100 calories | 0.8687943262411348g | 0.9083333333333334g | N/A |
| Calories per 10 g protein | 1151.0204081632653kcal | 1100.9174311926604kcal | N/A |
| Fats | 0.39g | 0.38g | 0% |
| Vitamin C | 0.4mg | 0.6mg | 0% |
| Net carbs | 67.03g | 56.78g | N/A |
| Magnesium | 43mg | 41mg | 0% |
| Calcium | 39mg | 43mg | 0% |
| Sugar | 63.35g | 38.13g | N/A |
| Sodium | 2mg | 2mg | 0% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.052mg | 0.051mg | 0% |
| Saturated fat | 0.032g | 0.088g | 0% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 0.036g | 0.053g | 0% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.019g | 0.062g | 0% |
| Tryptophan | 0.012mg | 0.025mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 0.043mg | 0.049mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 0.049mg | 0.041mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 0.084mg | 0.066mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 0.066mg | 0.05mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.022mg | 0.016mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 0.05mg | 0.052mg | 0% |
| Valine | 0.071mg | 0.056mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.032mg | 0.027mg | 0% |
Fat Type Comparison
| Contains less Sat. FatSaturated fat | -63.6% |
| Contains more Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat | +47.2% |
| Contains more Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat | +226.3% |
Carbohydrate type comparison
| Contains more SucroseSucrose | +15793.3% |
| Contains more FructoseFructose | +57.1% |
| Contains more MaltoseMaltose | +100% |
| Contains more StarchStarch | +∞% |
| Contains more GlucoseGlucose | +28.1% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Dates - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/171726/nutrients
- Prunes - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/168162/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.





