Egg noodles vs. Rice noodles — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison

Summary
Egg noodles contain gluten and are richer in proteins, minerals, and vitamins. In comparison, rice noodles have a higher glycemic index but are lower in fats. Taste and texture are different; egg noodles are more savory and salty, and rice noodles are chewier.
Introduction
An essential component of Asian cuisine is noodles. There are different types of noodles, but in this article, we will compare egg noodles to rice noodles based on some general differences, nutritional content, and health impacts.
One of the main differences between them is the ingredients that are used during their preparation.
Egg noodles are prepared with eggs and wheat flour as the base. In comparison, rice noodles are prepared from rice flour. We can say that rice noodles are gluten-free. In contrast, egg noodles are not gluten-free.
Culinary world
In the culinary world, egg and rice noodles can be used to prepare various dishes. Stir fry can be made with the two types of noodles.
Pho, a Vietnamese dish, is prepared with rice noodles.
Noodles are commonly used in soups and salads; also, they can be served with sauces and meats or baked in casseroles.
Taste and texture
Egg noodles have a savory and saltier taste. In comparison, rice noodles usually contain tapioca or corn starch, making them chewier and smoother.
Nutritional content comparison
In this section, we will compare 100g of cooked noodles for each.
Calories
Egg noodles are higher in calories compared to rice noodles. Egg noodles contain 138 calories, and rice noodles contain 108 calories.
Carbs
Both are high in carbs, with a slight difference between one another. That difference is not of high significance.
They contain nearly 25g of carbs per 100g of cooked noodles.
Glycemic index
The glycemic index of egg noodles is lower than that of rice noodles. Egg noodles have a glycemic index of 57. In comparison, rice noodles have a glycemic index of 61. Check our glycemic index chart to find out more about it.
Protein
Egg noodles are richer in protein in comparison to rice noodles. Egg noodles contain 4.5g of protein compared to rice noodles, which contain 1.8g of protein.
Fats
Although they are low in fat, based on the comparison, egg noodles contain higher amounts of fats compared to rice noodles. This is mainly due to the egg that is added.
Minerals
Egg noodles are mineral micronutrient dense compared to rice noodles. They are richer in all minerals in comparison to rice noodles. Egg noodles are richer in copper, zinc, phosphorus, magnesium, iron, and selenium.
In the diagram below, we can see their distribution according to the RDV.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+600%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+200%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+850%
Contains
more
IronIron
+328.6%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+157.9%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+160%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+280%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-73.7%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+176.3%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+431.1%
Vitamins
Like the mineral profile, egg noodles' vitamin profile is richer and denser in most vitamins than rice noodles.
Egg noodles are richer in B complex vitamins.
In the diagram below, we can see their distribution according to the RDV.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+466.7%
Contains
more
Vitamin DVitamin D
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+66.7%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+400%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+455.6%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+2290.9%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+666.7%
Contains
more
Vitamin B12Vitamin B12
+∞%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+600%
Egg noodles have a richer mineral and vitamin content compared to rice noodles.
Health impacts
Eating rice noodles or egg noodles will not adversely or positively affect your health.
However, if you have celiac disease, you should not eat egg noodles since it contains gluten, as mentioned before. (1)
In the case of diabetes, rice noodles have a higher glycemic index than egg noodles, which might cause a sharper spike in blood glucose after eating. It is important to keep track of blood sugar levels and spikes in blood glucose if you are prediabetic or diabetic. (2)
Overall, egg noodles are richer in minerals and vitamins, which gives them more benefits than rice noodles regarding their nutritional aspects.
Gluten Intolerance
Gluten is a protein present in wheat and other grains that provides flexibility to the dough. Celiac disease, an autoimmune disease, prevents certain people from consuming gluten. Your immune system attacks the lining of your small intestine in celiac disease. This can result in anemia, weight loss, diarrhea, constipation, exhaustion, and bloating.
Another advantage of rice noodles is that they are gluten-free, making them an excellent choice for anyone with celiac disease or gluten intolerance. In contrast, egg noodles are often manufactured from wheat flour and contain gluten (3).
Infographic
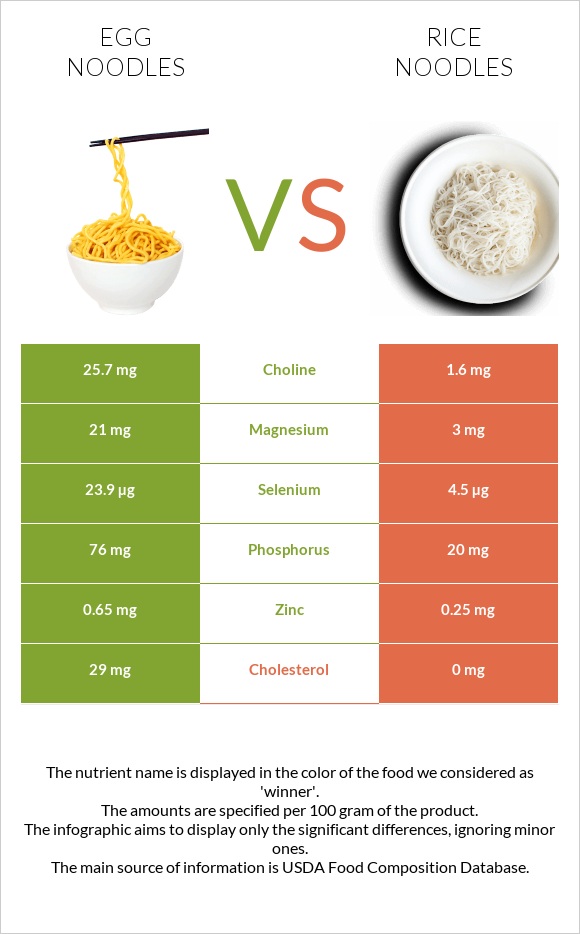
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Selenium | 23.9µg | 4.5µg | 35% |
| Cholesterol | 29mg | 0mg | 10% |
| Manganese | 0.315mg | 0.114mg | 9% |
| Phosphorus | 76mg | 20mg | 8% |
| Copper | 0.098mg | 0.038mg | 7% |
| Protein | 4.54g | 1.79g | 6% |
| Iron | 0.6mg | 0.14mg | 6% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.263mg | 0.011mg | 5% |
| Magnesium | 21mg | 3mg | 4% |
| Zinc | 0.65mg | 0.25mg | 4% |
| Vitamin B12 | 0.09µg | 0µg | 4% |
| Choline | 25.7mg | 1.6mg | 4% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.552g | 0.023g | 4% |
| Fats | 2.07g | 0.2g | 3% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.046mg | 0.006mg | 3% |
| Calories | 138kcal | 108kcal | 2% |
| Vitamin B3 | 0.4mg | 0.072mg | 2% |
| Folate | 7µg | 1µg | 2% |
| Saturated fat | 0.419g | 0.023g | 2% |
| Vitamin D | 4 IU | 0 IU | 1% |
| Calcium | 12mg | 4mg | 1% |
| Potassium | 38mg | 4mg | 1% |
| Fiber | 1.2g | 1g | 1% |
| Sodium | 5mg | 19mg | 1% |
| Vitamin A | 6µg | 0µg | 1% |
| Vitamin E | 0.17mg | 0.03mg | 1% |
| Vitamin D | 0.1µg | 0µg | 1% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.03mg | 0.018mg | 1% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.02mg | 0.004mg | 1% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 0.581g | 0.026g | 1% |
| Net carbs | 23.96g | 23.01g | N/A |
| Carbs | 25.16g | 24.01g | 0% |
| Sugar | 0.4g | 0.03g | N/A |
| Trans fat | 0.029g | N/A | |
| Tryptophan | 0.043mg | 0.022mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 0.138mg | 0.063mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 0.19mg | 0.073mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 0.365mg | 0.147mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 0.137mg | 0.062mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.086mg | 0.043mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 0.24mg | 0.095mg | 0% |
| Valine | 0.22mg | 0.104mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.121mg | 0.045mg | 0% |
Macronutrient Comparison
| Contains more ProteinProtein | +153.6% |
| Contains more FatsFats | +935% |
| Contains more OtherOther | +177.8% |
Fat Type Comparison
| Contains more Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat | +2134.6% |
| Contains more Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat | +2300% |
| Contains less Sat. FatSaturated fat | -94.5% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Egg noodles - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/168926/nutrients
- Rice noodles - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/168914/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.



