Egg noodles vs. Spaghetti — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison

Summary
Egg noodles are high in choline, magnesium, calcium, mono-, polyunsaturated fats, and vitamins A and D. Moreover, egg noodles have fewer calories.
Spaghetti, on the other hand, provides more protein, net carbs, dietary fiber, potassium, and selenium. It is low-GI food, whereas egg noodles are medium-GI food.
Spaghetti also contains five times less sodium and is cholesterol-free.
Both contain gluten.
Introduction
What are the differences between egg noodles and spaghetti?
Both egg noodles and spaghetti are forms of pasta, but they are different in texture, ingredients, shapes, and origins.
Egg noodles contain eggs, wheat flour, and water. Spaghetti is often cooked using semolina flour and water. When compared to spaghetti, egg noodles are softer and have a tender texture. Spaghetti has a firmer texture.
There are numerous different types of egg noodles, and the sizes vary per nation. Chinese egg noodles are typically long, broad, flat pieces of dough. Egg noodles are thinner than spaghetti, though both are long and cylindrical.
Egg noodles are native to China, whereas spaghetti comes from Italy.
Taste and Use
Spaghetti itself doesn't have a strong flavor. It can have different tastes depending on serving and cooking. The flavor of egg noodles is a little rich and more pronounced.
You can use egg noodles in stroganoff and creamy soups.
Spaghetti is frequently combined with tomato-based sauces or made into foods like aglio e olio or carbonara.
Nutrition
We will compare the nutritional values of egg noodles and spaghetti, concentrating on differences.
Macronutrients and Calories
Egg noodles are high in cholesterol, monounsaturated, and polyunsaturated fats. Furthermore, egg noodles provide fewer calories and saturated fats. Spaghetti, on the other hand, is high in protein, net carbs, and dietary fiber.
Macronutrient Comparison
Contains
more
FatsFats
+122.6%
Contains
more
OtherOther
+78.6%
Contains
more
ProteinProtein
+27.8%
Contains
more
CarbsCarbs
+22.7%
Calories
Compared to egg noodles, spaghetti has more calories. A hundred grams of egg noodles provides 138 calories, whereas the same amount of spaghetti contains 158 calories.
Protein
A hundred grams of egg noodles contain 4.54g of protein. Spaghetti provides 5.8g of protein per 100g. Both have all essential amino acids in small amounts. Moreover, spaghetti is high in tryptophan, threonine, leucine, and valine. Egg noodles, on the other hand, are high in methionine.
Gluten
Traditional egg noodles and spaghetti contain gluten. There are gluten-free flours if you are intolerant to gluten or eat a gluten-free diet.
Fats
Egg noodles provide over two times more fat. The fat content in egg noodles is 2.07g per 100g, whereas spaghetti has 0.93g. Egg noodles are high in monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats. Spaghetti, on the other hand, is less in saturated fats.
Fat Type Comparison
Contains
more
Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat
+343.5%
Contains
more
Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat
+69.3%
Contains
less
Sat. FatSaturated fat
-58%
Carbohydrates
The carb content in egg noodles is 25.16g per 100g. Spaghetti provides 30.86g of carbs per 100g. Spaghetti contains 29.06g of net carbs, whereas egg noodles provide 23.96g.
The main carbohydrate found in spaghetti is starch. Spaghetti provides 26g of starch, whereas egg noodles do not contain it. The other carbohydrates found in spaghetti are sucrose and fructose.
Moreover, spaghetti provides more dietary fiber. The fiber content in egg noodles is 1.2g, whereas spaghetti has 1.8g.
Carbohydrate type comparison
Contains
more
GlucoseGlucose
+75%
Contains
more
StarchStarch
+∞%
Contains
more
SucroseSucrose
+125%
Contains
more
FructoseFructose
+∞%
Contains
more
MaltoseMaltose
+33.3%
Vitamins
Egg noodles and spaghetti are not good sources of vitamins. Egg noodles contain a small amount of vitamins A and D, whereas spaghetti does not provide them. Also, egg noodles and spaghetti are equal in vitamins B2, B3, B6, and folate.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+183.3%
Contains
more
Vitamin DVitamin D
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+50%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+134.8%
Contains
more
Vitamin B12Vitamin B12
+∞%
Minerals
Egg noodles contain more calcium, magnesium, and phosphorus. Spaghetti, on the other hand, provides more potassium and selenium.
Egg noodles also are high in choline. Egg noodles contain 25.7mg of choline, whereas spaghetti provides only 6.4mg. Moreover, spaghetti has five times less sodium.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+16.7%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+71.4%
Contains
more
IronIron
+20%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+27.5%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+31%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+15.8%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-80%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+10.5%
Glycemic Index
The glycemic index of egg noodles is 57. Spaghetti has a glycemic index level of 49. Egg noodles are medium-GI foods, whereas spaghetti is low-GI food.
Acidity
The potential renal acid load, or PRAL, is the amount of acid or base produced by the food inside the body. Both have a PRAL value of 3.5. Both are acidic.
Weight Loss & Diets
Egg noodles are not acceptable in a vegan diet because eggs are an animal product. Spaghetti, on the other hand, is vegan.
Traditional egg noodles and spaghetti are high in carbs and are not keto-friendly.
If you are following the Paleo diet, you must avoid egg noodles and spaghetti.
Spaghetti is a good choice for the DASH diet due to its low fat and high protein content. Egg noodles can be part of the DASH diet in moderate amounts.
Health Impact
Cardiovascular Health
Egg noodles contain 29mg of cholesterol. High cholesterol level in the serum is one of the risk factors for cardiovascular diseases(1). Egg noodles are also high in sodium. High sodium intake increases blood pressure. Hypertension is one of the risk factors for heart stroke(2).
According to the study, pasta consumption does not correlate to the deterioration of glucose control, adiposity measurements, or other cardiovascular risk factors in patients with type 2 diabetes(3).
Downsides and Risks
Allergy
Egg allergy is one of the most frequent allergies in children. You must avoid egg noodles from your diet if you have an egg allergy(4).
Egg noodles and spaghetti made from wheat flour. Wheat allergy is common in childhood. Wheat allergy is an IgE-mediated reaction to insoluble gliadin in wheat. You must avoid traditional egg noodles and spaghetti if you are allergic to wheat(5).
Gluten Associated Diseases
Egg noodles and spaghetti contain gluten. Gluten proteins can cause symptoms in persons with coeliac disease multisystem immunological condition. You must avoid these foods if you have celiac disease (CD), non-celiac gluten sensitivity (NCGS), and dermatitis herpetiformis (DH)(6).
References
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31194434/
- https://www.cdc.gov/heartdisease
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7019547/
- https://www.foodallergyawareness.org/food-allergy-and-anaphylaxis/food-allergens/egg/
- https://www.foodallergyawareness.org/food-allergy-and-anaphylaxis/food-allergens/wheat/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK538505/
Infographic
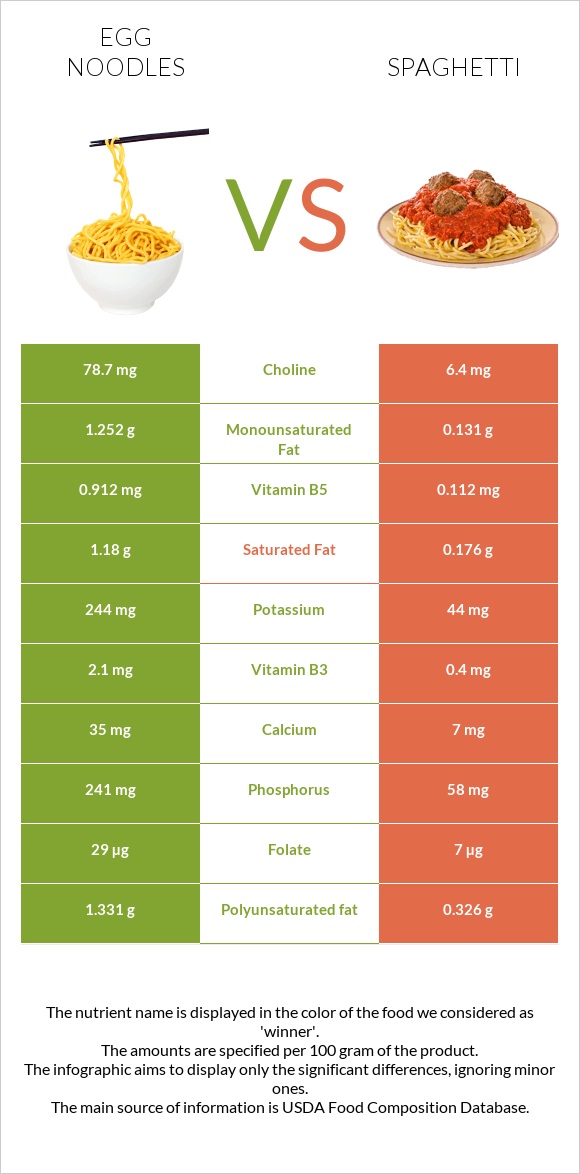
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Starch | 26.01g | 11% | |
| Cholesterol | 29mg | 0mg | 10% |
| Selenium | 23.9µg | 26.4µg | 5% |
| Vitamin B12 | 0.09µg | 0µg | 4% |
| Choline | 25.7mg | 6.4mg | 4% |
| Protein | 4.54g | 5.8g | 3% |
| Phosphorus | 76mg | 58mg | 3% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.263mg | 0.112mg | 3% |
| Fats | 2.07g | 0.93g | 2% |
| Carbs | 25.16g | 30.86g | 2% |
| Fiber | 1.2g | 1.8g | 2% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.552g | 0.326g | 2% |
| Calories | 138kcal | 158kcal | 1% |
| Vitamin D | 4 IU | 0 IU | 1% |
| Magnesium | 21mg | 18mg | 1% |
| Calcium | 12mg | 7mg | 1% |
| Iron | 0.6mg | 0.5mg | 1% |
| Zinc | 0.65mg | 0.51mg | 1% |
| Vitamin A | 6µg | 0µg | 1% |
| Vitamin E | 0.17mg | 0.06mg | 1% |
| Vitamin D | 0.1µg | 0µg | 1% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.03mg | 0.02mg | 1% |
| Saturated fat | 0.419g | 0.176g | 1% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 0.581g | 0.131g | 1% |
| Protein per 100 calories | 3.289855072463768g | 3.670886075949367g | N/A |
| Calories per 10 g protein | 303.9647577092511kcal | 272.41379310344826kcal | N/A |
| Net carbs | 23.96g | 29.06g | N/A |
| Potassium | 38mg | 44mg | 0% |
| Sugar | 0.4g | 0.56g | N/A |
| Copper | 0.098mg | 0.1mg | 0% |
| Sodium | 5mg | 1mg | 0% |
| Manganese | 0.315mg | 0.322mg | 0% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.02mg | 0.02mg | 0% |
| Vitamin B3 | 0.4mg | 0.4mg | 0% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.046mg | 0.049mg | 0% |
| Folate | 7µg | 7µg | 0% |
| Trans fat | 0.029g | 0g | N/A |
| Tryptophan | 0.043mg | 0.083mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 0.138mg | 0.206mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 0.19mg | 0.228mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 0.365mg | 0.44mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 0.137mg | 0.133mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.086mg | 0.065mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 0.24mg | 0.297mg | 0% |
| Valine | 0.22mg | 0.262mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.121mg | 0.132mg | 0% |
| Fructose | 0g | 0.03g | 0% |
| Omega-3 - ALA | 0.024g | N/A |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Egg noodles - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/168926/nutrients
- Spaghetti - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/168928/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.





