Feta vs. Mozzarella — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
For nutrition, mozzarella is a healthier and better option than feta. Mozzarella is lower in sodium, lower in fat, and cholesterol. Mozzarella is richer in proteins, zinc, phosphorus, calcium, and vitamin A. Feta is richer in B complex vitamins.
Mozzarella is a healthier cheese than feta cheese since nearly all their health impacts are similar, except that feta cheese is high in sodium, which increases the risk factors of developing hypertension and complicates the outcome if hypertension exists.
Introduction
This article will compare two kinds of cheese: feta and mozzarella. We will talk about the difference between these cheeses regarding their nutritional content and health impacts. It is important to answer specific questions that food consumers frequently ask. One of the most important points is understanding which is a healthier cheese. Since both are white cheeses, is feta similar to mozzarella? At the end of this article, this question will be clarified based on nutrition and health impacts.
Nutritional content comparison
Calories
Feta and mozzarella contain similar amounts of calories. They are classified as moderate caloric foods.
Glycemic index
Feta and mozzarella have equal glycemic indices.
Carbs
They are both classified as low-carb foods. The difference between them is negligible.
Fats
Feta contains higher amounts of fat compared to mozzarella.
Cholesterol
Feta contains higher amounts of cholesterol compared to mozzarella.
Saturated fats
Feta contains 1.4 times more saturated fats than mozzarella.
Proteins
Mozzarella contains almost double the amount of proteins compared to feta. The amount of proteins is very significant.
Minerals
Feta is high in minerals such as zinc, phosphorus, and calcium.
Sodium
Feta is high in sodium, whereas mozzarella contains negligible amounts.
In the diagrams below, we can see the distribution of minerals in both foods.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
IronIron
+160%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+18.5%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+∞%
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+36.8%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+48.3%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+53.2%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+55.5%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-98.3%
Vitamins
Feta has a richer vitamin profile, it is richer in B2, B5, B6, and B12. Whereas, mozzarella is richer in vitamin A.
In the diagrams below, we can see the distribution of vitamins in both foods.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+20%
Contains
more
Vitamin DVitamin D
+33.3%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+670%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+148.2%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+725.8%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+430%
Contains
more
Vitamin B12Vitamin B12
+83.7%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+255.6%
Health impacts
Feta cheese health impacts
Feta cheese has both positive and negative health impacts.
It is a rich source of calcium and phosphorus, which promotes overall bone health and reduces osteoporosis damage to bones. (1)
Feta cheese contains lactobacillus bacteria which improves overall gut microflora and helps with digestion. (2)
Feta cheese contains healthy fats such as conjugated linoleic acids with anticarcinogenic and anti-diabetic properties. (3) (4)
Calcium-rich foods such as feta decrease the risk of colorectal cancer. (5)
It is also important to mention some bad health impacts that feta cheese might have.
Feta cheese contains lactose, which may lead to digestive symptoms such as abdominal cramps, diarrhea, bloating, and flatulence in people with lactose intolerance. The sodium content of feta is linked with an increased risk of hypotension development.
There is an increased risk of prostate cancer development when high-calcium foods are consumed. (7)
Mozzarella cheese health impacts
Mozzarella is rich in calcium which, as discussed for feta, promotes bone health and reduces damage caused by osteoporosis on bones. (1)
Calcium-rich foods such as mozzarella decrease the risk of colorectal cancer. (5)
Mozzarella contains lactobacilli which are probiotics that improve microflora and digestion. (8)
The adverse effects of mozzarella have similarities with feta's negative impacts. They may cause digestive symptoms in lactose-intolerant individuals.
Prostate cancer risks are increased when high-calcium foods are consumed. (7)
Cardiovascular system
According to this study, intramuscular vitamin B12 injection in early-lactation dairy cows increases vitamin B12 content in milk and Mozzarella with no adverse effect on cheese quality, but significant vitamin B12 is lost during cheesemaking and rapidly decreases during storage. Vitamin B12 is helpful in controlling homocysteine levels, which are the primary cause of blood vessel inflammation and atherosclerosis (9). These effects are unknown for Feta cheese.
There are a lot of types of Feta and Mozzarella cheese with different amounts of cholesterol (10). This study demonstrated the possibility of producing cholesterol-reduced Feta cheese with little difference in physicochemical and sensory properties compared with regular Feta cheese (11). It should be noted the amount of cholesterol in Mozzarella cheese considerably increased over the course of storage (12).
People taking MAO inhibitors (particularly antidepressants) may experience a hypertensive crisis when eating cheeses, including Feta and Mozzarella, which contain tyramine (13).
Video Summary
References
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24695889/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10849182/
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0002822304004316
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/088915759290037K
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12869397/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5098396/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16522915/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22981567/
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0022030220306627
- https://www.fatsecret.com/calories-nutrition/food/feta-cheese/cholesterol?frc=True
- https://www.cabdirect.org/cabdirect/abstract/20093138342
- https://www.cabdirect.org/cabdirect/abstract/20113003205
- https://europepmc.org/article/med/3283290
Infographic
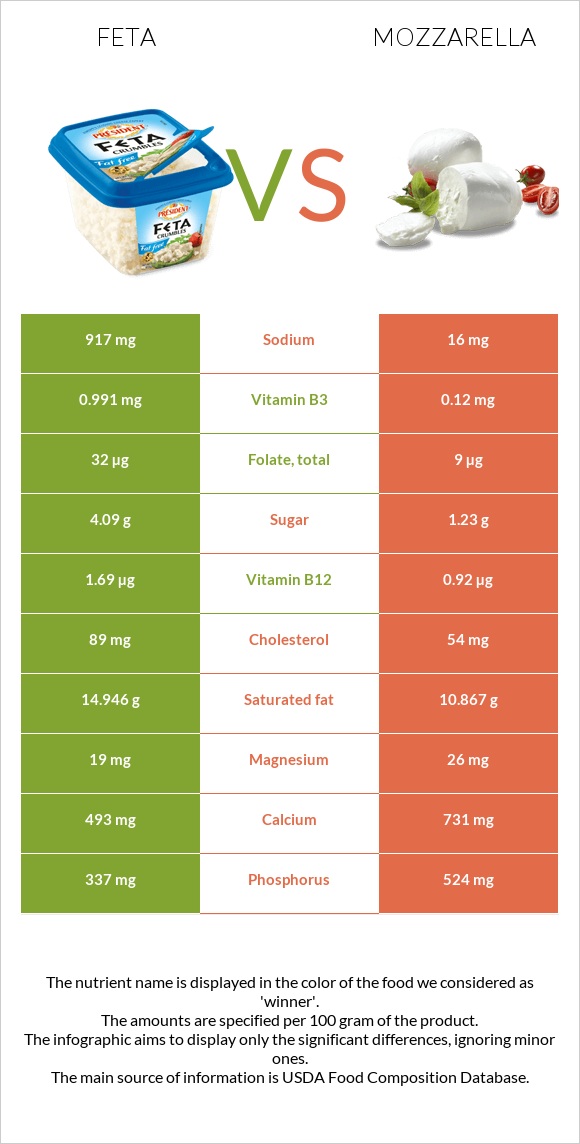
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Sodium | 917mg | 16mg | 39% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.844mg | 0.34mg | 39% |
| Vitamin B12 | 1.69µg | 0.92µg | 32% |
| Protein | 14.21g | 27.5g | 27% |
| Phosphorus | 337mg | 524mg | 27% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.424mg | 0.08mg | 26% |
| Calcium | 493mg | 731mg | 24% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.967mg | 19% | |
| Saturated fat | 14.946g | 10.867g | 19% |
| Cholesterol | 89mg | 54mg | 12% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.154mg | 0.02mg | 11% |
| Fats | 21.28g | 17.1g | 6% |
| Folate | 32µg | 9µg | 6% |
| Iron | 0.65mg | 0.25mg | 5% |
| Vitamin B3 | 0.991mg | 0.12mg | 5% |
| Magnesium | 19mg | 26mg | 2% |
| Zinc | 2.88mg | 3.13mg | 2% |
| Calories | 264kcal | 280kcal | 1% |
| Potassium | 62mg | 95mg | 1% |
| Copper | 0.032mg | 0.027mg | 1% |
| Vitamin A | 125µg | 137µg | 1% |
| Vitamin D | 0.4µg | 0.3µg | 1% |
| Manganese | 0.028mg | 1% | |
| Selenium | 15µg | 15.7µg | 1% |
| Choline | 15.4mg | 18.4mg | 1% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 4.623g | 4.844g | 1% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.591g | 0.509g | 1% |
| Net carbs | 4.09g | 3.1g | N/A |
| Carbs | 4.09g | 3.1g | 0% |
| Vitamin D | 16 IU | 13 IU | 0% |
| Sugar | 4.09g | 1.23g | N/A |
| Vitamin E | 0.18mg | 0.15mg | 0% |
| Vitamin K | 1.8µg | 1.8µg | 0% |
| Tryptophan | 0.2mg | 0% | |
| Threonine | 0.637mg | 0% | |
| Isoleucine | 0.803mg | 0% | |
| Leucine | 1.395mg | 0% | |
| Lysine | 1.219mg | 0% | |
| Methionine | 0.368mg | 0% | |
| Phenylalanine | 0.675mg | 0% | |
| Valine | 1.065mg | 0% | |
| Histidine | 0.397mg | 0% |
Macronutrient Comparison
| Contains more FatsFats | +24.4% |
| Contains more CarbsCarbs | +31.9% |
| Contains more OtherOther | +116.7% |
| Contains more ProteinProtein | +93.5% |
Fat Type Comparison
| Contains more Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat | +16.1% |
| Contains less Sat. FatSaturated fat | -27.3% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Feta - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/173420/nutrients
- Mozzarella - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/167735/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.






