Grape seed oil vs. Avocado oil — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Despite containing the same amount of fats, the fat composition of grapeseed and avocado oils differ. Grape seed oil consists predominantly of polyunsaturated fats, while avocado oil contains more monounsaturated fats.
Grape oil is a good source of vitamin E, whereas avocado oil lacks this vitamin.
Refined avocado oil is better for frying, while grape seed oil and unrefined avocado oil are preferably used raw.
Introduction
Edible oils often look indistinguishable and have similar nutritional content. However, each oil has its own distinct physicochemical and nutritional qualities. In this article, we will be looking at the differences between grape seed oil and avocado oil.
Classification
Grape seed and avocado oils are both vegetable oils. Vegetable oils are oils that have been extracted from fruits and plants or their seeds.
Grape seed oil is a by-product of winemaking, extracted from the seeds of grapes, as the name suggests.
Avocado oil, on the other hand, is made from the pulp of the avocado.
Smoke Point, Taste, and Use
The smoke point of cooking oils is one of the most important qualities. It is the temperature at which the oil starts breaking down, smoking, or burning.
Grape seed oil has a moderately high smoke point of around 420°F (216°C). Unrefined avocado oil has a lower smoke point of about 375°F (190°C); however, refined avocado oil has a much higher smoke point of 520°F or 271°C.
Oils with higher smoke points are better to use at high temperatures, such as frying and sauteeing, while oils with low smoke points are better used raw, as dressings.
Thus, refined avocado oil can be used for frying safely, whereas unrefined avocado oil and grapeseed oil are more commonly used as dressings. At the same time, if you’re looking for an unrefined oil to fry with, grape seed oil can be the choice for you.
Avocado oil, especially unrefined avocado oil, has a buttery, grassy taste, much like avocado, while grape seed oil has a much more neutral taste.
Nutrition
Macronutrients and Calories
The average serving size of cooking oils per person is one tablespoon, weighing around 14g, or one teaspoon, equal to 4.5g.
Calories
Grapeseed oil and avocado oil are high-calorie foods, providing an equal amount of calories - 884kcal per 100g serving.
One average serving size of one tablespoon contains 124 calories.
Fats
The macronutrient content of these oils consists of 100% fats. Consequently, one tablespoon of avocado and grape seed oils provides 14g of fats.
However, the two differ in the types of fats they contain.
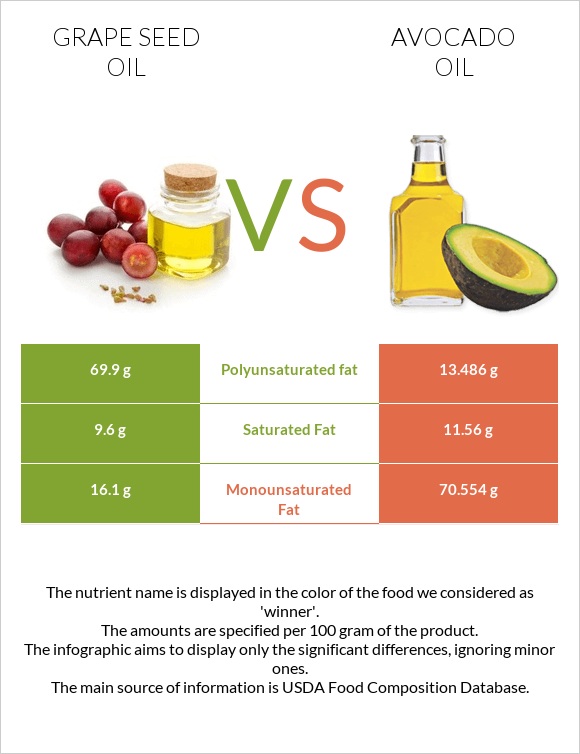
Grape seed oil consists of over 70% polyunsaturated fats and less than 10% of saturated fats. Avocado oil contains over 70% monounsaturated fats and a little over 10% saturated fats.
You can see the fat content comparison in the infographic below.
Fat Type Comparison
Contains
less
Sat. FatSaturated fat
-17%
Contains
more
Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat
+418.3%
Contains
more
Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat
+338.2%
Naturally, being plant products, grape seed, and avocado oil contain no cholesterol.
Protein and Carbohydrates
Grape seed and avocado oils contain no notable amounts of protein and carbohydrates.
Vitamins
Cooking oils are, overall, not a great source of vitamins. Avocado oil provides no vitamins, while grape seed oil is rich in vitamin E.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+∞%
Minerals
Both grape seed and avocado oil contain insignificant amounts of minerals.
Mineral Comparison
Glycemic Index
The glycemic index of foods with no carbohydrates, such as grape seed and avocado oils, is considered to be 0.
Insulin Index
The insulin index is calculated for foods with no carbohydrates to measure how much the insulin levels rise after consumption.
The exact number for the insulin index values of avocado or grape seed oils has not been calculated; however, cooking oils have a very low insulin index value of 3 (1).
Health Impact
Cardiovascular Health
Research finds that replacing saturated fats with unsaturated fats, such as polyunsaturated fats, can reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease (2). Grape seed oil is higher in polyunsaturated fats and lower in saturated fats compared to avocado oil.
Various studies have found rapeseed oil to have cardioprotective and anticancer effects. However, a large amount of oil consumption is required for the beneficial effect to be achieved (3).
A higher intake of avocado oil consumption has also been associated with a lower risk of cardiovascular and coronary heart disease (4)
Diabetes
Grape seed and avocado oils have low glycemic and insulin index values, meaning the intake of these oils does not raise the blood levels of glucose or insulin.
Avocado oil supplementation was found to improve insulin sensitivity and reduce blood lipid levels and inflammation markers in experimental studies (5).
Grape seed extract has also been found to potentially help prevent the development of type 2 diabetes by reducing blood glucose levels after eating (6).
Sources.
- https://ses.library.usyd.edu.au/handle/2123/11945
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4593072/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4988453/
- https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/10.1161/JAHA.121.024014
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9319255/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3466453/
Infographic
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 69.9g | 13.486g | 376% |
| Vitamin E | 28.8mg | 192% | |
| Monounsaturated fat | 16.1g | 70.554g | 136% |
| Saturated fat | 9.6g | 11.56g | 9% |
| Calories | 884kcal | 884kcal | 0% |
| Fats | 100g | 100g | 0% |
Macronutrient Comparison
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Grape seed oil - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/171028/nutrients
- Avocado oil - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/173573/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.





