Haddock vs. Halibut — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Overall, haddock is richer in protein, while halibut contains 25 times more fats. Both contain almost equal amounts of minerals, whereas halibut is higher in vitamins than haddock.
Both haddock and halibut can be beneficial during various health problems and are invaluable for the formation and repair of nails and hair.
The final choice is up to personal taste.
Introduction
Haddock is a white, flaky, lean fish with a mild taste. This type of fish is an excellent choice for beginners, as it doesn’t have a strong fish flavor. Haddock is a common fish in the North Atlantic and is fished for commercial aims. You can find them in supermarkets fresh or frozen. It is a good source of protein and is very low in fat. It cooks well when grilled, broiled, or baked.
Halibut is one of the largest flat and saltwater fishes, and it has been a vital food source for Native Americans and Canadians for thousands of years. Its meat is perfect for fish lovers due to its delicate flavor and high nutritional value. It is often served baked, broiled, and grilled. Fresh halibut is available in summer, whereas frozen ones are available all year round.
Nutrition
Macronutrients and Calories
Both halibut and haddock are incredibly rich in nutrients while containing no notable amount of carbohydrates.
Halibut provides more than 2 times more calories compared to haddock.
Macronutrient Comparison
Contains
more
WaterWater
+28.7%
Contains
more
FatsFats
+3125.5%
Contains
more
OtherOther
+∞%
Protein
Per every 100g serving, haddock contains almost 1.5g more protein than halibut.
Both of these fishes contain all essential amino acids. However, haddock is richer in all of these.
Fats
On the other hand, halibut is 32 times richer in fats, mostly due to its monounsaturated fatty acid content. That being said, halibut also contains higher levels of saturated and polyunsaturated fats.
Surprisingly, halibut is slightly lower in cholesterol than haddock despite the fat content.
Fat Type Comparison
Contains
less
Sat. FatSaturated fat
-96.4%
Contains
more
Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat
+14416.2%
Contains
more
Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat
+759.3%
Minerals
When looking at the comparison chart of minerals, it becomes clear that halibut is higher in minerals.
The amount of potassium is very similar in these two types of fish. However, halibut contains more iron, whereas haddock contains more sodium than halibut.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+250%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+32.4%
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+26.9%
Contains
more
IronIron
+304.8%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+46.2%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+27.5%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-60.5%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+15.4%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+47.6%
Vitamins
When speaking about vitamins, the comparison charts tell us that haddock is the winner with a score of 8:3. It is an excellent source of folate, containing 13 times more than halibut. Haddock is also higher in vitamin B12 and B3.
On the other hand, halibut is richer in vitamins B2 and B6.
They contain equal amounts of vitamin A.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+16.7%
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin DVitamin D
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+114.2%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+71.5%
Contains
more
Vitamin B12Vitamin B12
+121.9%
Contains
more
Vitamin KVitamin K
+∞%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+1200%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+217.4%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+49.3%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+48.3%
Health Impact
Thanks to its high omega-3 fatty acid content, halibut has a protective effect on the cardiovascular system. It also prevents heart ailments like atherosclerosis, artery clotting, inflammation, stroke and controls high blood pressure (1). Other health benefits of this fish are:
- Maintainance of cells
They contribute to maintaining cells thanks to considerably high levels of vitamin B12. Its role in repairing, formatting, and maintaining red blood cells is of vital importance. It is beneficial for nervous health as well (2). - Reduction of fatigue
Vitamin B12 also enhances stamina in the body and relieves weakness and fatigue. - Supports digestion
The functions of the digestive system are supported by vitamin B3. It also stimulates appetite, nerve function, and healthy skin (3). The intake of this vitamin is also useful for lowering cholesterol and preventing atherosclerosis (4). - Regeneration of tissues and cells
The consumption of this fish helps to restore and renew cells and tissues thanks to amino acids. It is crucial for nails, hair, and skin. - Muscle problems
Health ailments like numbness, muscle weakness, and fatigue are possible to prevent due to the phosphorus levels in halibut (5). - Brain health
This fish is rich in potassium, which plays a significant role in maintaining proper nerve transmission, muscle contraction, and kidney function (6).
The health benefits of haddock fish are numerous. Some of these health benefits include:
- Maintenance of cells
This seafood is high in vitamin B12, which is responsible for maintaining, repairing, and forming red blood cells and nerve health (2). - Strengthening immunity
It is a great source of protein, which is essential for stronger immunity. It is essential for the proper work of the body’s self-defense mechanism to struggle against diseases and infections. - Supporting digestion
For effective digestion, our organism requires riboflavin and niacin, which are also important for emotional and neurological response systems (7). - Function of brain
Cognitive development and growth require considerable amounts of vitamin B6. Brain function can diminish because of the lack of this mineral (8). - Lowers bad cholesterol
We can keep away diseases like artery thickening and atherosclerosis by consuming this fish. The reason is that its high intake lowers LDL cholesterol (“bad” cholesterol) and increases HDL cholesterol (“good” cholesterol) (1). - Sugar level
A proper level of potassium and sodium is necessary to avoid headaches, weakness, trembling, and nervousness. The intake of this fish relatively lowers that risk and is helpful for diabetic patients, as it may lower sugar levels (6). - Relax muscles
For the contraction and relaxation of muscles, our body requires potassium. It also keeps the function of nerves and optimal muscles at the right level (6). - Bone health
For the maintenance of teeth and bone health, we can thank the calcium, magnesium, and phosphorus contents found in this fish (5).
References
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3705336/
- https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/VitaminB12-HealthProfessional/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30097857/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12873710/
- https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Phosphorus-HealthProfessional/
- https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Potassium-HealthProfessional/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4772032/
- https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/VitaminB6-HealthProfessional/
Infographic
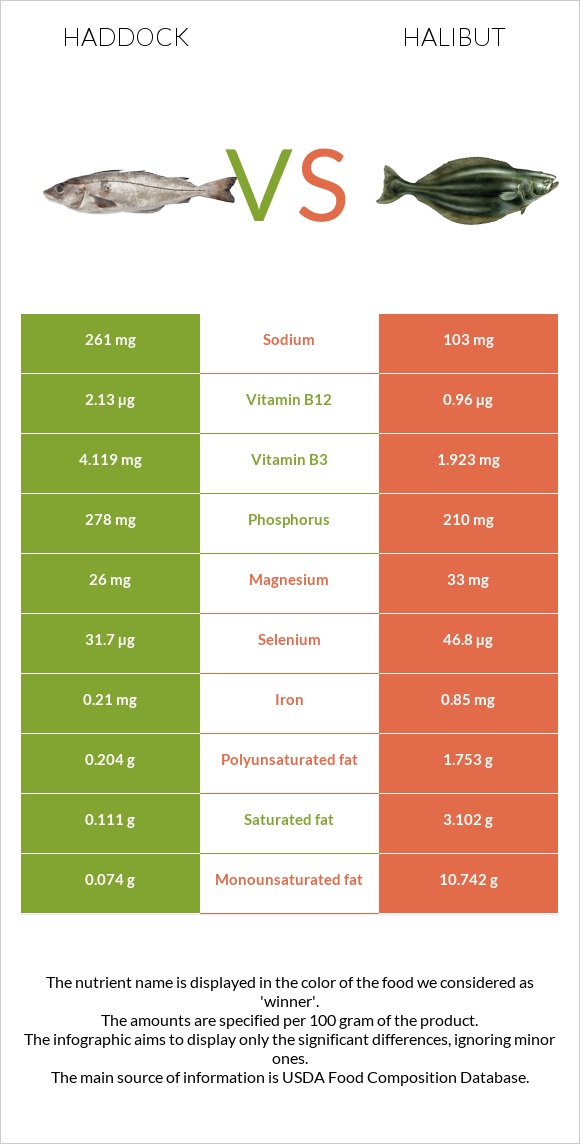
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Vitamin B12 | 2.13µg | 0.96µg | 49% |
| Selenium | 31.7µg | 46.8µg | 27% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 0.074g | 10.742g | 27% |
| Fats | 0.55g | 17.74g | 26% |
| Vitamin B3 | 4.119mg | 1.923mg | 14% |
| Choline | 79.6mg | 14% | |
| Saturated fat | 0.111g | 3.102g | 14% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.327mg | 0.485mg | 12% |
| Phosphorus | 278mg | 210mg | 10% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.204g | 1.753g | 10% |
| Iron | 0.21mg | 0.85mg | 8% |
| Calories | 90kcal | 239kcal | 7% |
| Sodium | 261mg | 103mg | 7% |
| Vitamin E | 0.55mg | 4% | |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.023mg | 0.073mg | 4% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.494mg | 0.288mg | 4% |
| Protein | 19.99g | 18.42g | 3% |
| Vitamin D | 23 IU | 3% | |
| Vitamin D | 0.6µg | 3% | |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.069mg | 0.103mg | 3% |
| Folate | 13µg | 1µg | 3% |
| Cholesterol | 66mg | 59mg | 2% |
| Magnesium | 26mg | 33mg | 2% |
| Calcium | 14mg | 4mg | 1% |
| Copper | 0.026mg | 0.038mg | 1% |
| Zinc | 0.4mg | 0.51mg | 1% |
| Potassium | 351mg | 344mg | 0% |
| Vitamin A | 21µg | 18µg | 0% |
| Manganese | 0.013mg | 0.015mg | 0% |
| Vitamin K | 0.1µg | 0% | |
| Trans fat | 0.005g | N/A | |
| Tryptophan | 0.26mg | 0.206mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 1.015mg | 0.808mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 1.067mg | 0.849mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 1.882mg | 1.497mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 2.126mg | 1.692mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.686mg | 0.545mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 0.904mg | 0.719mg | 0% |
| Valine | 1.193mg | 0.949mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.682mg | 0.542mg | 0% |
| Omega-3 - EPA | 0.051g | 0.674g | N/A |
| Omega-3 - DHA | 0.109g | 0.504g | N/A |
| Omega-3 - DPA | 0.006g | 0.114g | N/A |
| Omega-6 - Eicosadienoic acid | 0.001g | N/A |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Haddock - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/174198/nutrients
- Halibut - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/174232/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.




