Hummus vs. Peanut butter — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Peanut butter is relatively richer in vitamins, healthy fats, and minerals, such as magnesium, calcium, and zinc. Peanut butter is higher in calories, and it is also 22 times lower in sodium.
Peanut butter provides 5 times more fats, 3 times more protein, and 1.5 times more carbohydrates.
On the other hand, hummus is lower in calories and saturated fats.
Introduction
Peanut butter and hummus are one of the most popular choices for snacks. In this article, we will talk about the differences between these foods.
Peanut butter consists of roasted peanuts, sugar, and salt. It is made by blending roasted peanuts into a smooth mixture with no added oil or fats.
Traditional hummus is a nutrient-dense snack. It comprises chickpeas, garlic, lemon juice, olive oil, salt, and tahini.
Appearance
Peanut butter comes in several textures, such as creamy or crunchy, but it's almost always the same shade of brown. Unlike peanut butter, hummus has a pale yellow color.
Taste and Use
Peanut butter is salty, sweet, and nutty. Natural or unsweetened peanut butter has a less sweet taste as it does not contain sweeteners or flavorings. Processed peanut butter, on the other hand, is sweeter and has a slight saltiness.
There are many ways to use peanut butter. It goes well with pancakes, waffles, and crepes. You can use it instead of butter and make some desserts, such as pizza and muffins.
The perfect hummus is smooth and has a creamy texture. Hummus is delicious and healthy. Vegans can eat it because it doesn't contain any animal products. There are different uses for hummus. Hummus is a nutritious dip for bell peppers, fresh cucumbers, and carrots. Hummus can be used as a pasta sauce or a salad dressing.
Nutrition
The nutritional values are presented for peanut butter (smooth, without salt) and hummus (commercial). In this article, we used FDA's database for the information.
Macronutrients and Calories
Nutrient density is higher in peanut butter than in hummus. Peanut butter contains only 2% water, while hummus contains 66.6%.
Peanut butter includes five times more fats, three times more protein, and 50 percent more carbohydrates.
Macronutrient Comparison
Contains
more
WaterWater
+5313.8%
Contains
more
ProteinProtein
+181.1%
Contains
more
FatsFats
+435%
Contains
more
CarbsCarbs
+56.1%
Contains
more
OtherOther
+78.4%
Calories
Peanut butter is significantly more in calories. Peanut butter has 598 calories per 100 grams, compared to hummus, which has only 166.
Protein
Peanut butter contains more proteins and almost all essential amino acids than hummus. Peanut butter has 22.2 g of protein, while hummus has 7.78 g.
Peanut butter is richer in tryptophan, histidine, phenylalanine, and leucine. Hummus is richer in threonine, isoleucine, and lysine compared with peanut butter.
Fats
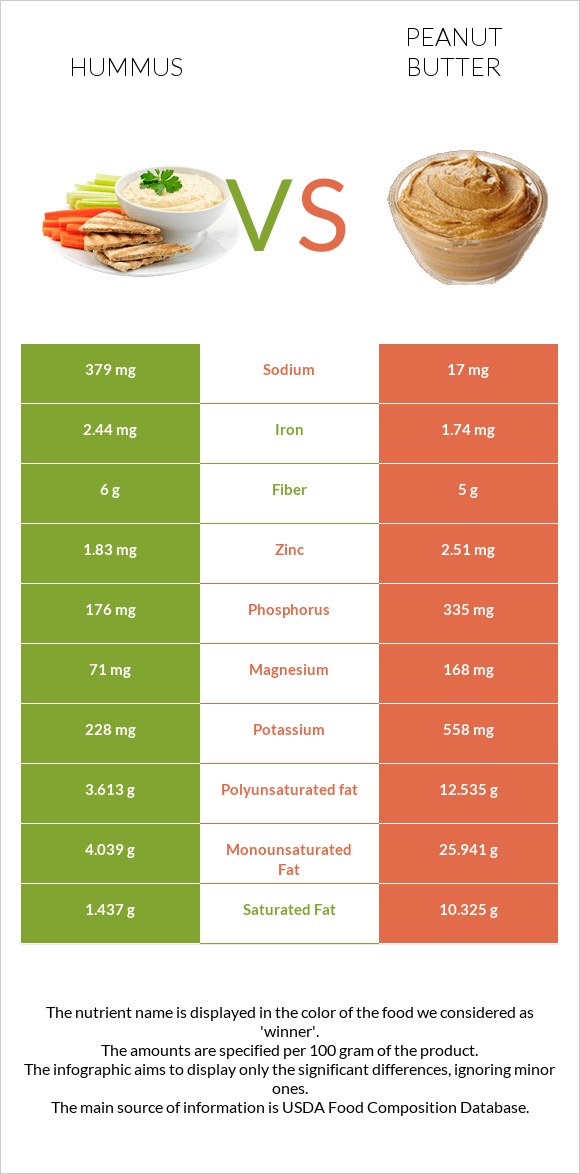
Peanut butter contains more fats than hummus. Compared to hummus, peanut butter contains eight times more saturated fat, six times more monounsaturated fat, and three times more polyunsaturated fat.
Fat Type Comparison
Contains
less
Sat. FatSaturated fat
-86.1%
Contains
more
Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat
+542.3%
Contains
more
Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat
+246.9%
Cholesterol
Peanut butter and hummus are cholesterol-free.
Omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids
Omega-3 and omega-6 are essential fatty acids (EFA) the body cannot produce, so the only way to obtain them is through foods and supplements. Peanut butter has a significant amount of omega-6, which helps lower bad cholesterol while increasing good cholesterol levels. A high intake of omega-6 may cause an increase in omega-3.
Peanut butter has 2.27 g of omega-6, whereas hummus has only 0.54 g.
Carbohydrates
Both have about the same amount of carbohydrates.
100g of peanut butter contains 22g of carbohydrates, of which 5g are dietary fiber and 17g are net carbs.
100g of hummus contains 15g of carbohydrates, of which 6g are dietary fiber and 8g are net carbs.
Peanut butter contains more sucrose, whereas hummus is higher in starch and amylose. Furthermore, hummus does not contain any sugar.
Vitamins
Peanut butter is a good source of most B-group vitamins. It also contains vitamin E (9mg).
Peanut butter contains 13.11 mg of vitamin B3, 1.14mg of vitamin B5, and 0.44mg of vitamin B6.
Hummus, at the same time, has a higher vitamin B1 level (0.48 mg). It also contains low amounts of vitamin A, while peanut butter does not contain it.
Hummus contains more folate (vitamin B9). It has 557 µg, whereas peanut butter only has 87µg.
Both of them do not contain vitamin C, vitamin D, and vitamin B12.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+20%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+200%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+2152.9%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+761.4%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+120.5%
Minerals
Peanut butter has two times more magnesium, potassium, and phosphorus.
Moreover, peanut butter is also a good source of zinc and calcium.
Hummus contains more copper and iron.
Sodium levels are 22 times higher in hummus (379 mg).
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
IronIron
+40.2%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+24.9%
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+136.6%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+28.9%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+144.7%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+37.2%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+90.3%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-95.5%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+115.4%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+57.7%
Glycemic Index
Both foods have a low glycemic index (GI<55). The glycemic index of peanut butter is 14, and for hummus, the glycemic index is 6 (1, 2).
Glycemic Load
The glycemic load of peanut butter is equal to 1. The GL of hummus is equal to 3,5. Both classify as low-GL foods.
Insulin Index
Peanut butter's insulin index (II) is 15, whereas the insulin index of hummus is 52 (3, 4).
Acidity
Peanut butter has a pH level of 6,3. Hummus has a pH level of 4,5-5.
The potential renal acid load value (PRAL) shows how much acid is produced in the organism from the given food. The PRAL value of peanut butter is 6,6 (acidic).
The PRAL value of hummus is 3,3 (acidic).
Weight Loss & Diets
Hummus and peanut butter are nutrient-dense foods high in calories.
Peanut butter is higher in calories; therefore, it's important to limit your portions when eating peanut butter on low-calorie diets, even though it may help curb your appetite due to being high in proteins and fats.
Peanut butter may be used in small amounts on low-carb diets such as the keto diet, although hummus is better for low-fat, low-calorie, and high-fiber diets.
Both of them can be allowed during vegan, vegetarian, and DASH diets.
Health Benefits
Aside from the healthy fat composition, peanuts, and their skin contain several antioxidative compounds, such as p-coumarin and resveratrol (RES). RES is well known for its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties and the ability to stimulate endothelial NO synthase. It can decrease the endothelial dysfunction observed in diabetes (5).
Furthermore, peanut skins are rich sources of phenolics. They increased the antioxidant activity of peanut butter (6).
Moreover, natural antioxidants are important in preventing and lowering the risk of noncommunicable diseases, in which oxidative stress is a primary causative agent.
In contrast, hummus has minerals like iron, folate, zinc, and calcium, which are important for good metabolism, muscles, and bones.
Furthermore, hummus contains 30 IU of vitamin A, which is necessary for maintaining vision and encouraging growth and development. Because of its importance in improving immune function, vitamin A is also classified as an anti-inflammation vitamin(7).
Cardiovascular Health
Micronutrients in peanut butter have a cardioprotective effect, which is associated with a lower risk of coronary heart disease (CHD). Moreover, one tablespoon (16 grams) of peanut butter daily was associated with a significantly lower risk of coronary heart disease (8).
Hummus, as mentioned above, has 379 mg of sodium. Consuming too much sodium increases the risk of hypertension. High blood pressure is a significant risk factor for heart disease and stroke (9). Whereas peanut butter, being much lower in sodium than hummus, can be a better choice for people with high blood pressure.
Digestive Health
According to human studies of chickpeas, comparing a chickpea diet with a habitual diet resulted in increased frequency of defecation, easier defecation, and softer stool consistency.
Conversely, if you do not consume too much water during the day, peanut butter might cause constipation.
Diabetes
Peanut butter is a good addition to a diabetic diet. Peanut butter has a low glycemic index, which doesn’t cause blood sugar to rise sharply. However, as it is high in calories, it should be consumed in moderation. People with type 2 diabetes must avoid peanut butter with added sugars or hydrogenated oils.
Hummus has a higher amount of starch and amylose, which results in lower availability of glucose, thus reducing the slower entry of glucose into the bloodstream. It leads to a lowering of the GI (10).
Low GI plays a significant role in lowering both type 2 diabetes incidence and severity.
They are both high in dietary fiber (each contains 5g). The minimum amount of fiber per 1,000 calories recommended by the Dietary Guidelines is 14g. Eating more fiber-rich foods can also help with blood sugar control, digestion, and lowering your risk of heart disease (11).
Downsides and Risks
- As peanut butter contains a high concentration of omega-6, it may cause an increase in omega-3, so the acid ratio will be out of balance, which can increase the risk of insulin and leptin resistance (12).
Unlike it, hummus does not increase the risk of insulin resistance.
- Peanut butter is higher in calories, and overusing peanut butter increases the risk of obesity. Unlike it, long-term consumption of hummus can lead to a lower body mass index (13).
- Many store-bought kinds of peanut butter have added sugar. People with type 2 Diabetes should choose all-natural peanut butter containing only peanuts and possibly some salt. At the same time, hummus can help to enhance diet quality by replacing foods high in added sugars or saturated fats (14).
- Some people are allergic to peanuts. Peanut allergy is a reaction that involves your body’s immune system, which interprets the proteins in peanuts as toxic. When foods contain peanuts, an allergic reaction to peanuts might occur immediately or up to several hours later. Allergic reactions to peanuts can cause mild, moderate, or severe signs and symptoms, even signs of anaphylaxis.
Although chickpeas come from the same family as peanuts, peanut-allergic people can eat hummus safely (15).
Sources
- https://academic.oup.com/ajcn/article/93/5/984/4597984
- https://academic.oup.com/ajcn/article/114/5/1625/6320814
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/26770180
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4730744/
- https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/8/5/250
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/agricultural-and-biological-sciences/peanut-butter
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6162863/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18716180/
- https://www.cdc.gov/heartdisease/sodium.htm
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7760696/
- https://diabetes.org/healthy-living/recipes-nutrition/understanding-carbs/get-to-know-carbs
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4808858/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7760696/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33260594/
- https://www.rch.org.au/uploadedFiles/Main/Content/allergy/Avoiding%20Peanuts%20and%20Treenuts(1).pdf
Infographic
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Vitamin B3 | 0.582mg | 13.112mg | 78% |
| Fats | 9.6g | 51.36g | 64% |
| Vitamin E | 9.1mg | 61% | |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 3.613g | 12.535g | 59% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 4.039g | 25.941g | 55% |
| Saturated fat | 1.437g | 10.325g | 40% |
| Manganese | 0.773mg | 1.665mg | 39% |
| Protein | 7.9g | 22.21g | 29% |
| Magnesium | 71mg | 168mg | 23% |
| Phosphorus | 176mg | 335mg | 23% |
| Calories | 166kcal | 598kcal | 22% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.132mg | 1.137mg | 20% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.2mg | 0.441mg | 19% |
| Sodium | 379mg | 17mg | 16% |
| Copper | 0.527mg | 0.422mg | 12% |
| Choline | 63mg | 11% | |
| Potassium | 228mg | 558mg | 10% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.064mg | 0.192mg | 10% |
| Iron | 2.44mg | 1.74mg | 9% |
| Zinc | 1.83mg | 2.51mg | 6% |
| Fiber | 6g | 5g | 4% |
| Carbs | 14.29g | 22.31g | 3% |
| Selenium | 2.6µg | 4.1µg | 3% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.18mg | 0.15mg | 3% |
| Calcium | 38mg | 49mg | 1% |
| Starch | 3.56g | 1% | |
| Folate | 83µg | 87µg | 1% |
| Net carbs | 8.29g | 17.31g | N/A |
| Sugar | 10.49g | N/A | |
| Vitamin K | 0.3µg | 0% | |
| Trans fat | 0.075g | N/A | |
| Tryptophan | 0.231mg | 0% | |
| Threonine | 0.525mg | 0% | |
| Isoleucine | 0.616mg | 0% | |
| Leucine | 1.546mg | 0% | |
| Lysine | 0.681mg | 0% | |
| Methionine | 0.265mg | 0% | |
| Phenylalanine | 1.202mg | 0% | |
| Valine | 0.782mg | 0% | |
| Histidine | 0.557mg | 0% | |
| Fructose | 0.12g | 0% | |
| Omega-3 - ALA | 0.027g | N/A | |
| Omega-3 - Eicosatrienoic acid | 0.01g | N/A | |
| Omega-6 - Gamma-linoleic acid | 0.001g | N/A | |
| Omega-6 - Eicosadienoic acid | 0.008g | N/A | |
| Omega-6 - Linoleic acid | 12.215g | N/A |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Hummus - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/174289/nutrients
- Peanut butter - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/172470/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.






