Kumquat vs. Loquat — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Kumquat has more Vitamin C, fiber, iron, and Vitamin B2. It is also lower in net carbs. On the other hand, loquat has more Vitamin A, less sodium, saturated fat, and fewer sugars.
Introduction
We will discuss loquat and kumquat similarities and differences, focusing on nutrition and health impact.
What's The Actual Difference?
Loquat belongs to the Eriobotrya genus, a large evergreen shrub or tree grown for its orange fruit and leaves, which are used to make herbal tea. It is also grown as an ornamental plant.
Kumquats are a genus of small fruit-bearing trees in the Rutaceae and Citrus families. Kumquat means "golden orange" in Chinese. A kumquat is about the size of a grape and has a sweet-tart citrus flavor. Loquats are oval, with smooth or downy skin that is yellow or orange and sometimes red-blushed. The flavor of loquats is sweet and tropical, with a citrusy, slightly tangy undertone. It is a hybrid of apricot, a pineapple, and an apple.
Nutrition
Calories
Kumquat has almost two times more calories than loquat. It contains 71 calories per 100g, while loquat contains only 47 calories per 100g.
Vitamins
Kumquat contains more Vitamin B21, Vitamin B2, Vitamin B3, Vitamin C, and Folate.
The amount of Vitamin C is 42 times higher in kumquat.
Also, it falls in the range of the top 13% of food as a source of Vitamin C.
On the other hand, loquat has higher Vitamin A and Vitamin B6.
Both have no Vitamin D, Vitamin K, and Vitamin B12.
Vitamin Comparison
| Contains more Vitamin CVitamin C | +4290% |
| Contains more Vitamin EVitamin E | +∞% |
| Contains more Vitamin B1Vitamin B1 | +94.7% |
| Contains more Vitamin B2Vitamin B2 | +275% |
| Contains more Vitamin B3Vitamin B3 | +138.3% |
| Contains more Vitamin B5Vitamin B5 | +∞% |
| Contains more FolateFolate | +21.4% |
| Contains more Vitamin AVitamin A | +406.7% |
| Contains more Vitamin B6Vitamin B6 | +177.8% |
Minerals
Kumquat has a relatively higher amount of minerals than loquat. It has more magnesium, calcium, zinc, and iron.
On the other hand, a loquat has less sodium, also more phosphorus and potassium than a kumquat.
Mineral Comparison
| Contains more MagnesiumMagnesium | +53.8% |
| Contains more CalciumCalcium | +287.5% |
| Contains more IronIron | +207.1% |
| Contains more CopperCopper | +137.5% |
| Contains more ZincZinc | +240% |
| Contains more PotassiumPotassium | +43% |
| Contains more PhosphorusPhosphorus | +42.1% |
| Contains less SodiumSodium | -90% |
| Contains more SeleniumSelenium | +∞% |
Glycemic Index
The GI of kumquats is 0, and the glycemic index of loquat is unknown.
Fats
Both have fats of less than 1g.
Carbs
They both have low and high net carbs: 9.4 g of net carbs in kumquat and 10.44g in loquat.
Fiber
Kumquat has more fiber: 6.5g. Kumquat falls in the range of the top 15% of foods as a fiber source, containing 6.5g of fiber per 100g. Loquat has only 1.5g of fiber.
Cholesterol
Both loquat and loquat have no cholesterol.
Health Impact
Cancer
Some research suggests that extracts of loquat skin, leaves, and seeds have anticancer properties. One test-tube study [1] found that extract from loquat fruit skins significantly inhibited the growth and spread of human bladder cancer cells.
Kumquats contain many plant compounds like flavonoids, phytosterols, and essential oils. According to research, phloretin and acacetin, both found in kumquats, have anti-inflammatory and anticancer properties [2].
Diabetes
According to research, loquat has significant anti-diabetes potential. Recent research has shown that loquat leaf or seed extracts can help prevent and control type 1 and type 2 diabetes [3].
According to one animal study [4], kumquat extract may lower fasting blood sugar, total cholesterol, LDL (bad) cholesterol, and triglycerides. However, more research is required.
One study [5] indicates that pectin, another antioxidant found in citrus fruits, has anti-diabetic effects, including improved glucose tolerance and blood lipid levels and reduced insulin resistance.
Side Effects
People can experience intense tingling and itching of the lips, tongue, and throat [6]. Those who are allergic to citrus fruits may also be sensitive to loquat and kumquat. Allergies to citrus fruit peels are frequently caused by limonene, a chemical found in citrus fruit peels.
References
- https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/19768354.2017.1358665
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28911534/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5187783/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24705395/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6401843/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25831042/
Infographic
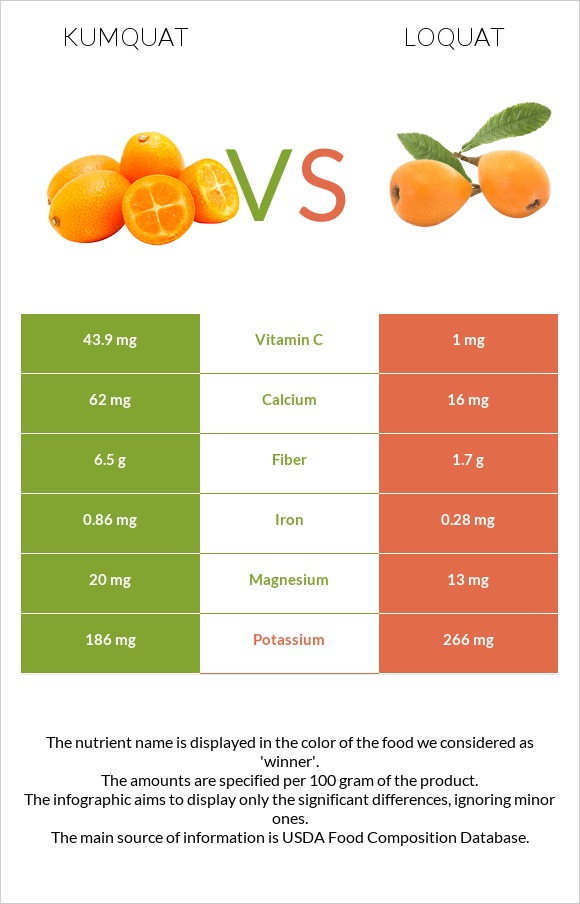
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Vitamin C | 43.9mg | 1mg | 48% |
| Fiber | 6.5g | 1.7g | 19% |
| Iron | 0.86mg | 0.28mg | 7% |
| Vitamin A | 15µg | 76µg | 7% |
| Copper | 0.095mg | 0.04mg | 6% |
| Calcium | 62mg | 16mg | 5% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.09mg | 0.024mg | 5% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.036mg | 0.1mg | 5% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.208mg | 4% | |
| Protein | 1.88g | 0.43g | 3% |
| Magnesium | 20mg | 13mg | 2% |
| Potassium | 186mg | 266mg | 2% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.037mg | 0.019mg | 2% |
| Vitamin B3 | 0.429mg | 0.18mg | 2% |
| Choline | 8.4mg | 2% | |
| Calories | 71kcal | 47kcal | 1% |
| Fats | 0.86g | 0.2g | 1% |
| Carbs | 15.9g | 12.14g | 1% |
| Zinc | 0.17mg | 0.05mg | 1% |
| Phosphorus | 19mg | 27mg | 1% |
| Vitamin E | 0.15mg | 1% | |
| Manganese | 0.135mg | 0.148mg | 1% |
| Selenium | 0µg | 0.6µg | 1% |
| Folate | 17µg | 14µg | 1% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.171g | 0.091g | 1% |
| Net carbs | 9.4g | 10.44g | N/A |
| Sugar | 9.36g | N/A | |
| Sodium | 10mg | 1mg | 0% |
| Saturated fat | 0.103g | 0.04g | 0% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 0.154g | 0.008g | 0% |
| Tryptophan | 0.005mg | 0% | |
| Threonine | 0.015mg | 0% | |
| Isoleucine | 0.015mg | 0% | |
| Leucine | 0.026mg | 0% | |
| Lysine | 0.023mg | 0% | |
| Methionine | 0.004mg | 0% | |
| Phenylalanine | 0.014mg | 0% | |
| Valine | 0.021mg | 0% | |
| Histidine | 0.007mg | 0% |
Macronutrient Comparison
| Contains more ProteinProtein | +337.2% |
| Contains more FatsFats | +330% |
| Contains more CarbsCarbs | +31% |
Fat Type Comparison
| Contains more Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat | +1825% |
| Contains more Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat | +87.9% |
| Contains less Sat. FatSaturated fat | -61.2% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Kumquat - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/168154/nutrients
- Loquat - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/169908/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.




