Big Mac vs. Quarter Pounder — Nutrition Facts, Calories, Carbs & More


Summary
Quarter pounder provides more carbs and protein. It contains 1.5 times more vitamins B2 and B12 and is a better source of minerals, including iron, potassium, and zinc. At the same time, Big Mac has higher amounts of vitamin A and calcium.
Introduction
Two of the most famous burgers around the world are Big Mac and Quarter Pounder, belonging to the fast food chain McDonald’s. They are just as popular as McDonald's Double Cheeseburger, Happy Meal, Egg McMuffin, french fries, and premium salads.
People often ask which is better according to nutrition composition and health impact. This article will discuss the differences between these two popular items on McDonald’s menu.
What Are The Actual Differences?
First of all, Big Mac and Quarter Pounder differ in the ingredients they are made of.
Big Mac is the biggest hamburger on the McDonald’s menu, containing two beef patties and a slice of American cheese sandwiched between three slices of sesame seed bun. It also has shredded lettuce, chopped onions, sliced pickles, and a Big Mac special sauce. On the other hand, Quarter Pounder has only one patty with Cheddar cheese packed in a sesame seed bun. It usually lacks Big Mac sauce and a third slice of bread, containing ketchup and mustard sauce instead. Thus, Quarter Pounder is smaller in size than Big Mac.
According to statistics, Big Mac is more popular worldwide than Quarter Pounder. Quarter Pounder is cheaper than Big Mac.
Nutrition
In the infographics below, you can see the information about the nutritional content of 100g servings of Big Mac and Quarter Pounder.
Usually, these fast foods are served as one item, equalling 219g for Big Mac and 171g for Quarter Pounder.
Macronutrients
Both of these fast foods contain 50% of water.
However, Big Mac provides 20% of carbs, 15% of fats, and 12% of proteins, while Quarter Pounder contains 22% of carbs, 12% of fats, and 14% of proteins. You can see the distribution of the other nutrients in the infographic below.
Macronutrient Comparison
Contains
more
ProteinProtein
+19.3%
Contains
more
FatsFats
+29.5%
Calories
Big Mac and Quarter Pounder are highly processed fast foods; thus, they are high in calories.
Big Mac is higher in calories, containing 13 more calories per every 100g. In each 100g, Quarter Pounder contains 244 calories /417 calories per item/, while Big Mac provides 257 calories /563 calories per item/.
Carbohydrates
Quarter Pounder is 2.1g higher in net carbs than Big Mac in every 100g serving. 100g serving size of Big Mac contains 20.1g of total carbs, 92% of which are net carbs and 8% - dietary fiber, while the same serving of Quarter Pounder provides 22.2g of total carbs, 93% of which are net carbs and 7% - dietary fiber.
Quarter Pounder is richer in sugars, particularly in glucose and fructose. Thus, it may taste slightly sweeter than Big Mac.
Big Macs and Quarter Pounders contain 1.6g of dietary fiber.
Carbohydrate type comparison
Contains
more
GlucoseGlucose
+83.7%
Contains
more
FructoseFructose
+30.2%
Contains
more
MaltoseMaltose
+49%
Contains
more
SucroseSucrose
+109.1%
Contains
more
LactoseLactose
+357.1%
Protein
Quarter Pounder is higher in protein, containing 14.1g per 100g, while Big Mac has 11.9g.
Fats
Being well-known fast food products, Big Mac and Quarter Pounder are both high in fats. However, Big Mac contains 3.4g more fats compared to the Quarter Pounder.
Quarter Pounder is higher in monounsaturated, saturated, and trans fats. Big Mac is relatively lower in cholesterol than Quarter Pounder.
Fat Type Comparison
Contains
more
Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat
+21%
Vitamins
Quarter Pounder is higher in most vitamins, containing 1.5 times more vitamin B2 and vitamin B12 and overall more vitamins B1, B3, and B9 (folate).
Big Mac has over 3 times more vitamin A than Quarter Pounder.
One Quarter Pounder covers the recommended daily value (RDV) of vitamin B12 by 91%, while Bic Mac covers the RDV of vitamin B12 by 80%.
They are absent in vitamins D, E, K, B5, and B6 and contain insignificant amounts of vitamin C.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+125%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+64.6%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+31.6%
Contains
more
Vitamin B12Vitamin B12
+45.5%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+21.7%
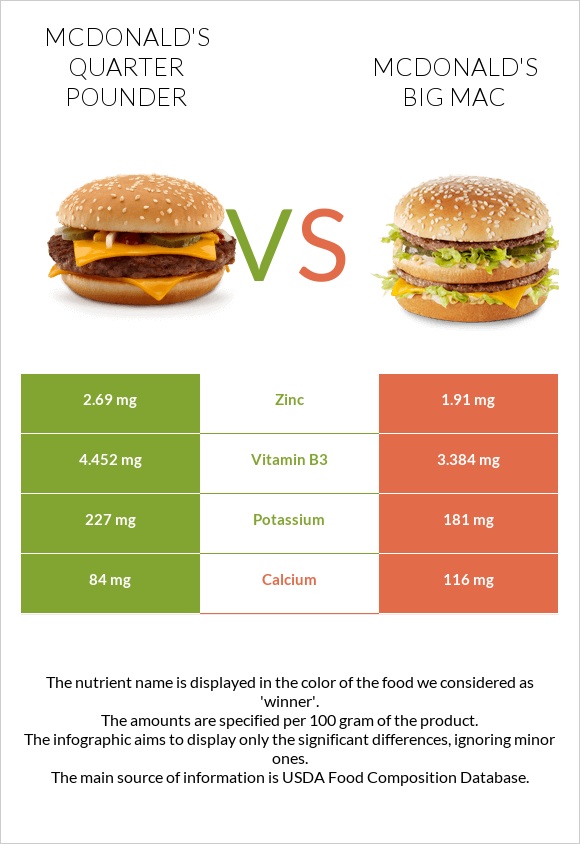
Minerals
Quarter Pounder is the winner in this section as well. Quarter Pounder is higher in iron, potassium, and zinc, whereas Big Mac contains more calcium.
One Big Mac and Quarter Pounder cover the RDV or recommended daily value of calcium by 25.4% and 11.4%, respectively.
One Big Mac covers the RDV of iron by 54% for men and 24% for women, whereas Quarter Pounder covers the RDV of iron by 51% for men and 23% for women.
A 100g Quarter Pounder and Big Mac have similar amounts of magnesium, phosphorus, copper, and manganese.
Both Quarter Pounder and Big Mac are very high in sodium.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+25.4%
Contains
more
IronIron
+20.5%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+40.8%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+38.1%
Glycemic Index
Big Mac has an average GI of 66, belonging to the group of medium-glycemic index foods. Quarter Pounder’s average glycemic index is not calculated yet.
You can also check our glycemic index chart page for more information about other foods' glycemic indexes.
Health Impact
Big Mac and Quarter Pounder are well-known burgers - a typical highly processed fast food high in calories and low in nutrients. They show similar effects on different organ systems.
Frequent consumption of such food products results in repetitive blood sugar spikes, leading to insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes, fatty liver, and weight gain (1).
Other sources of calories are added sugars and trans fats. Trans fat consumption is associated with a high risk of many diseases and conditions; for example, they increase blood LDL cholesterol levels and, therefore, increase the risk of developing cardiovascular disease. Besides, burgers are very high in sodium, a mineral linked to high blood pressure, which may lead to heart disease and stroke. Thus, people with high blood pressure should consider eating foods lower in sodium (3).
Infographic
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Vitamin B12 | 1.28µg | 0.88µg | 17% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.344mg | 0.209mg | 10% |
| Zinc | 2.69mg | 1.91mg | 7% |
| Vitamin B3 | 4.452mg | 3.384mg | 7% |
| Protein | 14.1g | 11.82g | 5% |
| Fats | 11.55g | 14.96g | 5% |
| Iron | 2.41mg | 2mg | 5% |
| Calcium | 84mg | 116mg | 3% |
| Folate | 56µg | 46µg | 3% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 4.202g | 3.474g | 2% |
| Calories | 244kcal | 257kcal | 1% |
| Vitamin C | 0.9mg | 0.4mg | 1% |
| Carbs | 22.17g | 20.08g | 1% |
| Cholesterol | 39mg | 36mg | 1% |
| Potassium | 227mg | 181mg | 1% |
| Copper | 0.107mg | 0.098mg | 1% |
| Sodium | 427mg | 460mg | 1% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.183mg | 0.176mg | 1% |
| Saturated fat | 4.008g | 3.803g | 1% |
| Fructose | 2.2g | 1.69g | 1% |
| Net carbs | 20.57g | 18.48g | N/A |
| Magnesium | 22mg | 20mg | 0% |
| Sugar | 5.13g | 3.97g | N/A |
| Fiber | 1.6g | 1.6g | 0% |
| Phosphorus | 124mg | 122mg | 0% |
| Manganese | 0.199mg | 0.206mg | 0% |
| Trans fat | 0.724g | 0.588g | N/A |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.283g | 0.306g | 0% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- McDonald's Quarter Pounder - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/170321/nutrients
- McDonald's Big Mac - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/170720/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.





