Pigeon pea vs. Pea — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Pigeon pea has more magnesium, potassium, calcium, selenium, sodium, folate, and calories. Moreover, pigeon peas have higher protein, net carbs, dietary fiber, and polyunsaturated fats. In contrast, peas contain more monounsaturated fats, manganese, iron, zinc, choline, and vitamins A, C, B1, B2, B3, B6, K, and E. Peas have less saturated fats, whereas pigeon peas have fewer GI.
Table of contents
Introduction
Cooked peas and cooked pigeon peas are the types used in this article. We will compare their health benefits and nutritional content.
Pigeon pea is also known as no-eye pea, toor dal, gungo pea, or congo pea. Peas are also known as garden peas or field peas.
Nutrition
Here, you can find nutritional information for 100g of peas and pigeon peas.
Macronutrients and Calories
Pigeon peas are high in all macronutrients. Pigeon pea is denser compared to pea. Pea contains 78% water, whereas pigeon pea has 68.5% water.
Macronutrient Comparison
Contains
more
ProteinProtein
+26.1%
Contains
more
FatsFats
+72.7%
Contains
more
CarbsCarbs
+48.8%
Contains
more
OtherOther
+15.2%
Contains
more
WaterWater
+13.6%
Calories
Pigeon peas have more calories than green peas. A hundred grams of pea provides 84 calories, whereas a pigeon pea has 121 calories.
One serving of peas (1 cup or 160g) has 134 kcal, whereas one serving of pigeon peas (1 cup or 168g) provides 203 kcal.
Protein
Compared to green peas, pigeon peas have more protein. A hundred grams of peas have 5.36g of protein, whereas pigeon peas provide 6.76g.
Pea and pigeon peas contain all essential amino acids. Pigeon pea is higher in all of them except for methionine.
Fats
Pea and pigeon peas contain less than 0.5g of fat per 100 grams. Pea provides only 0.22g of fats, whereas pigeon pea provides 0.38g. Moreover, pigeon peas contain more polyunsaturated fats, whereas peas provide more monounsaturated and less saturated fats.
Fat Type Comparison
Contains
more
Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat
+101%
Contains
less
Sat. FatSaturated Fat
-53%
Contains
more
Mono. FatMonounsaturated Fat
+533.3%
Carbohydrates
Pigeon pea is the winner in carb content.
100g of pigeon pea contains 23.25g of carbohydrates, of which 6.7g are dietary fiber and 16.55g are net carbs.
100g of pea contains 15.63g of carbohydrates, of which 5.5g are dietary fiber and 10.13g are net carbs.
Carbohydrate type comparison
Vitamins
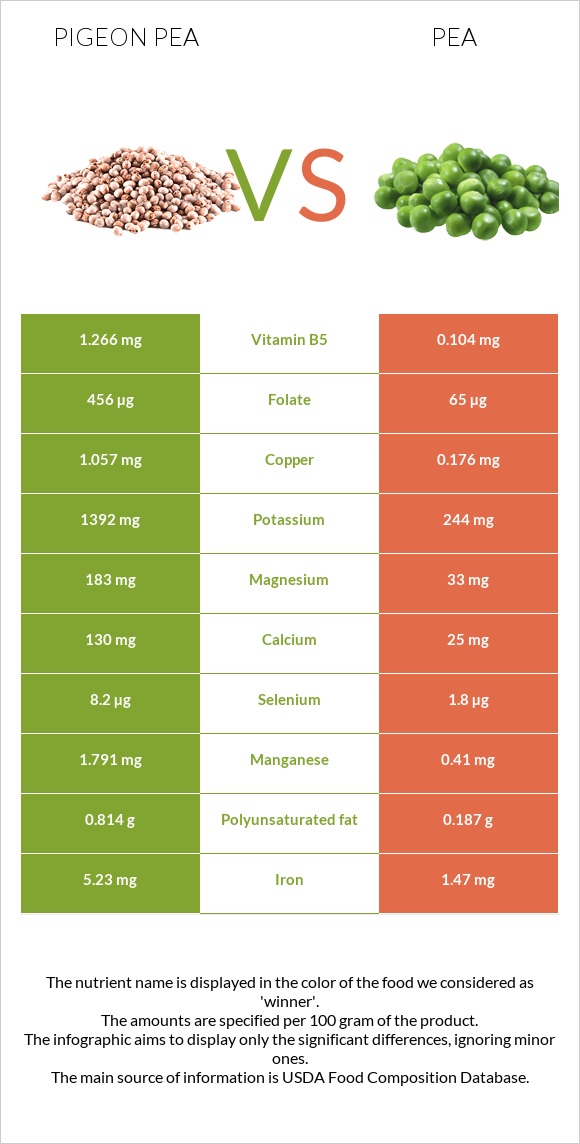
Pea has significantly more vitamin A (over 267 times more) and vitamin B5 (over 480 times more). A hundred grams of pea provides 801IU of vitamin A, whereas pigeon pea has only 3IU. In a 100g serving, peas and pigeon peas have 153mg and 0.319mg of vitamin B5, respectively.
Pea also provides over four times more vitamin B6, 2.5 times more B2 (riboflavin), and 2.8 times more B3 (niacin). In addition, peas are high in vitamins B1 (thiamine), E, and K. Peas provide 14.2 mg of vitamin C, whereas pigeon peas lack vitamin C. In contrast, pigeon pea has over 1.7 times more folate. In a 100g serving, peas and pigeon peas have 63µg and 111µg of folate, respectively.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+76.2%
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+26600%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+77.4%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+152.5%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+158.8%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+47862.4%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+332%
Minerals
Pigeon pea has more magnesium, copper, potassium, calcium, phosphorus, and selenium. On the other hand, pea has higher choline, manganese, iron, and zinc. Moreover, pea has less sodium content.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+17.9%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+59.3%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+41.7%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+55.5%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+52.6%
Contains
more
IronIron
+38.7%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+32.2%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-40%
Glycemic Index
The glycemic index of peas is equal to 54. Pigeon pea has a glycemic index of 22.
As we can see, peas tend to have a higher glycemic index than pigeon peas. However, the glycemic index of both falls in the low category.
Insulin Index
While there is no specific insulin index value for pigeon peas, pea has an insulin index of 37.
Acidity
The potential renal acid load (PRAL) is an approach to assess the acidity of a food. The PRAL number indicates the food's capacity to degrade into acids or bases within the body. The PRAL value of a pea is -0.1, while the pigeon pea has a PRAL level of -2.1. Both are considered alkaline-forming.
Weight Loss & Diets
Vegan: Peas and pigeon peas are vegan because they are made entirely of plants and do not contain any animal ingredients.
Vegetarian: Vegetarians avoid all animal products. Peas and pigeon peas are vegetarian foods.
Paleo: Eating natural, unprocessed foods and staying away from processed foods are the main goals of the paleo diet. Peas and pigeon peas are considered legumes. Because legumes were not an essential component of the hunter-gatherer diet and because of their possible antinutrient content, peas and pigeon peas are not paleo-friendly.
Keto: The keto diet includes low-carb, high-fat, and high-protein foods.
Peas and pigeon peas have a comparatively high carbohydrate content. Because of this, they are often not advised for the more stringent variations of the ketogenic diet.
Mediterranean: The Mediterranean diet places a strong emphasis on eating lots of fruits, vegetables, legumes, whole grains, and healthy fats. It also calls for eating little to no red meat and only modest amounts of fish and chicken. Peas and pigeon peas can be part of this diet.
DASH: The DASH diet emphasizes nutrient-dense foods such as legumes, vegetables, whole grains, lean meats, and fruits. The nutritious content of peas and pigeon peas makes them excellent complements to this diet plan.
Health Benefits
Antiinflammatory Properties
Peas and pigeon peas provide bioactive compounds with antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities (1).
According to the study, ethanol extract and cyanidin-3-monoglucoside of pigeon peas may inhibit the production of inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-, IL-1, and IL-6 (2).
Neuroprotective Properties
Pea provide 480 times more vitamin B5. According to the study, cerebral vitamin B5 deficiency may produce neurodegeneration and dementia in Alzheimer's disease, which may be prevented or even reversible in its early stages by therapy with oral dosages of vitamin B5 adequate to restore brain levels (3).
On the other hand, pigeon peas are high in folate. The nutritional status of a mother's folate is linked to the occurrence of neural tube abnormalities (NTDs) in her children. It is essential to include folate in the diet. To lower the incidence of NTDs during the periconceptional stage, you may take folic acid (a synthetic version of folate) as a supplement (4).
Anticancer Properties
Cajanol, an isoflavone found in pigeon peas, is being studied for its possible anticancer activities against MCF-7 human breast cancer cells.
The results showed that Cajanol was effective in inhibiting the growth of MCF-7 cells, and this effect was dependent on both the dosage and the duration of exposure. Moreover, the study suggests that Cajanol may induce apoptosis in cancer cells by targeting several key signaling pathways involved in this process (5).
Peas contain some active phytochemical substances (lectins, flavonoids), which may have anticancer properties.
Several investigations have shown that lectins have cytotoxic or tumor-inhibitory effects in several tumor cell lines, including skin, liver, bile duct, and bone cell lines (6).
Downsides and Risks
Peas and pigeon peas contain antinutritive agents that may hinder nutrient absorption. Pea provides antinutrient agents like phytic acid, lectins, and trypsin inhibitors (1,7).
Pigeon peas include antinutritional agents such as protease and amylase inhibitors, phytoalexins, polyphenols, and oligosaccharides (8).
Classification
Peas and pigeon peas are legumes, although they come from different genera and species.
Peas and pigeon peas belong to the family Fabaceae. Pea(Pisum sativum) belongs to the genus Pisum and the species sativum. The pigeon pea (Cajanus Cajan) belongs to the genus Cajanus and Cajan species.
Peas originated in Central Asia, the Near East, Ethiopia, and the Mediterranean region. Pigeon peas come from South Asia, most precisely in eastern India.
Appearance
Peas are small, smooth, and round. Usually, they can be found canned, frozen, or in their fresh form in the pod. Peas are generally similar in size, ranging from 0.25 to 0.5 inches (0.6 to 1.3 cm) in diameter. Fresh peas are usually green, but there are also yellow and purple kinds. Dried or processed peas retain their unique green hue.
Pigeon peas are larger, elongated, and more oval-shaped than green peas. They might be pale yellow to dark brown in hue. Their hue varies depending on the variety and stage of maturity. They are typically available dry or canned. Pigeon peas can range in length from 0.25 to 0.5 inches (0.6 to 1.3 cm).
Taste and Use
Peas have a sweet and somewhat starchy flavor. Fresh peas have a delicate sweetness with a crisp, juicy texture. Cooked peas are a flexible complement to a broad range of meals since they soften and keep some of their natural sweetness. Peas have a moderate flavor and are excellent for salads, soups, stir-fries, and casseroles.
The flavor of pigeon peas is slightly earthy and nutty. Cooked pigeon peas retain their firm structure and nutty flavor, giving meals a robust depth. Since pigeon peas have a unique taste and texture, they are frequently used to make hearty and filling dishes. Pigeon peas are a popular choice for soups, stews, and rice dishes across many cultures because of their taste profile, which goes well with a wide range of savory components.
Sources
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37444265/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22914868/
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28603928/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20638373/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5414455/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22916813/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/2467276/
Infographic
Comparison summary table
 |
 |
||
| Lower in Sugar |
|
||
| Lower in Glycemic Index |
|
||
| Rich in minerals |
|
||
| Lower in Sodium |
|
||
| Lower in Saturated Fat |
|
||
| Lower in price |
|
||
| Rich in vitamins |
|
||
| Lower in Cholesterol | Equal | ||
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
Opinion |
| Calories | 121kcal | 84kcal |
 |
| Protein | 6.76g | 5.36g |
 |
| Fats | 0.38g | 0.22g |
 |
| Vitamin C | 0mg | 14.2mg |
 |
| Net carbs | 16.55g | 10.13g |
 |
| Carbs | 23.25g | 15.63g |
 |
| Magnesium | 46mg | 39mg |
 |
| Calcium | 43mg | 27mg |
 |
| Potassium | 384mg | 271mg |
 |
| Iron | 1.11mg | 1.54mg |
 |
| Sugar | 5.93g |
 |
|
| Fiber | 6.7g | 5.5g |
 |
| Copper | 0.269mg | 0.173mg |
 |
| Zinc | 0.9mg | 1.19mg |
 |
| Phosphorus | 119mg | 117mg |
 |
| Sodium | 5mg | 3mg |
 |
| Vitamin A | 3IU | 801IU |
 |
| Vitamin A | 0µg | 40µg |
 |
| Vitamin E | 0.14mg |
 |
|
| Manganese | 0.501mg | 0.525mg |
 |
| Selenium | 2.9µg | 1.9µg |
 |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.146mg | 0.259mg |
 |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.059mg | 0.149mg |
 |
| Vitamin B3 | 0.781mg | 2.021mg |
 |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.319mg | 153mg |
 |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.05mg | 0.216mg |
 |
| Vitamin K | 25.9µg |
 |
|
| Folate | 111µg | 63µg |
 |
| Choline | 29.7mg |
 |
|
| Saturated Fat | 0.083g | 0.039g |
 |
| Monounsaturated Fat | 0.003g | 0.019g |
 |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.205g | 0.102g |
 |
| Tryptophan | 0.066mg | 0.037mg |
 |
| Threonine | 0.239mg | 0.201mg |
 |
| Isoleucine | 0.245mg | 0.193mg |
 |
| Leucine | 0.483mg | 0.32mg |
 |
| Lysine | 0.474mg | 0.314mg |
 |
| Methionine | 0.076mg | 0.081mg |
 |
| Phenylalanine | 0.579mg | 0.198mg |
 |
| Valine | 0.292mg | 0.232mg |
 |
| Histidine | 0.241mg | 0.105mg |
 |
| Fructose | 0.41g |
 |
Which food is preferable for your diet?
 |
 |
|
| Low Calories diet |
|
|
| Low Fats diet |
|
|
| Low Carbs diet |
|
|
| Low Glycemic Index diet |
|
People also compare
Vitamins & Minerals Daily Need Coverage Score
Comparison summary
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Pigeon pea - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/172437/nutrients
- Pea - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/170420/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.






