Pomelo vs. Figs — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Figs are higher in carbohydrates, calories, fats, fiber, and vitamin A. They also provide more calcium, magnesium, and potassium. Figs provide 31mg more calcium.
In contrast, pomelo contains higher amounts of vitamin C and phosphorus, it is lower in oxalates. Pomelo is 30 times higher in vitamin C compared to figs.
Introduction
In this article, we will compare figs and pomelos regarding their nutritional values and health impacts.
Nutrition
This section compares the nutritional composition and shows the differences between 100g servings of raw figs and raw pomelo.
Recommended serving sizes for these fruits are one cup (190g) for pomelo and one medium (50g) for figs.
Macronutrients
Pomelo has a higher water content compared to figs. Pomelo provides 89% water, while figs have 79% water. Figs are significantly higher in carbs and fats, and slightly lower in proteins.
Macronutrient Comparison
Contains
more
WaterWater
+12.6%
Contains
more
FatsFats
+650%
Contains
more
CarbsCarbs
+99.4%
Contains
more
OtherOther
+37.5%
Calories
Figs contain almost two times more calories per 100g. This serving of fings contains 74 kcal, whereas the same amount of pomelo provides 38 kcal.
Protein
Pomelo has slightly more protein than pomelo. However, the protein amounts in these plants are less than one gram, so they can be ignored.
Fats
Being plant food products, figs and pomelo are bad sources of fats and contain less than 1g of fat. However, figs provide 7.5 times more fat compared to pomelo.
Cholesterol
Pomelo and figs are cholesterol-free.
Carbohydrates
Figs have a higher carbohydrate content. 100g of figs contain 19.18g of carbs, of which 2.9g is dietary fiber and 16.28g are net carbs. Most of the net carbs of figs are sugars. 00g serving of pomelo contains 9.62g of carbohydrates, of which 1g is dietary fiber and 8.62g are net carbs.
Vitamins
Figs are the winners in this category. They are richer in all vitamins, except vitamin C. Figs are almost 18 times higher in vitamin A compared to pomelo. They contain folate and vitamin K, which are absent in pomelo. Also, figs are higher in B-complex vitamins.
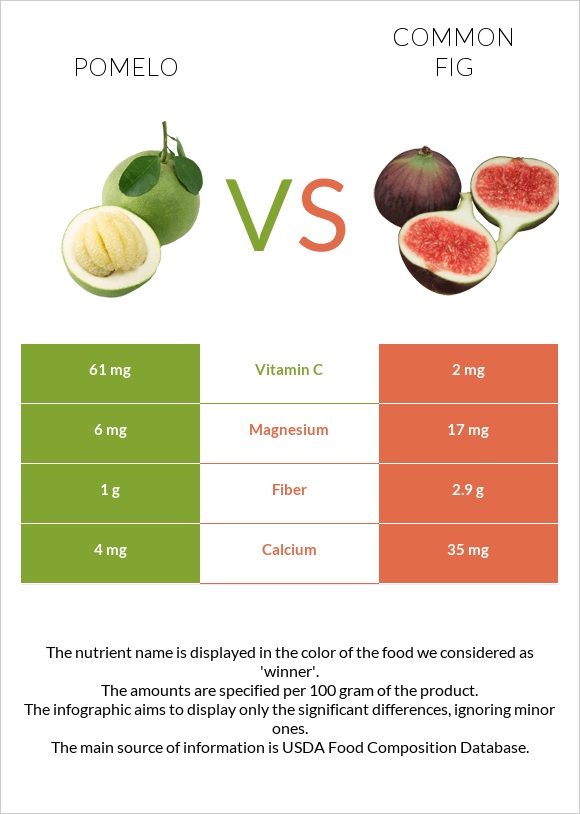
In contrast, pomelo is richer in vitamin C than figs. It contains 30.5 times more vitamin C, providing 61mg in a 100g serving, compared to 2mg in the same serving of figs.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+2950%
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+76.5%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+85.2%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+81.8%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+213.9%
Minerals
Figs are higher in most minerals than pomelo. They are richer in iron, copper, magnesium, zinc, and manganese. Figs are around 9 times richer in calcium.
On the other hand, pomelo provides 3mg more phosphorus than figs.
Both contain equal amounts of sodium and potassium.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+21.4%
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+183.3%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+775%
Contains
more
IronIron
+236.4%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+45.8%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+87.5%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+652.9%
Oxalates
Although figs and pomelo are classified as low-oxalate foods, figs are higher in oxalates compared to pomelo.
The oxalate content of figs is equal to 21mg, while the oxalate content of pomelo is 0mg.
Glycemic Index
Pomelo has a higher glycemic index (GI) than figs. Figs have a GI of 61. The glycemic index of pomelo equals 78. The glycemic index of figs falls in the medium category, while the GI of pomelo falls in the high category.
Glycemic Load
The glycemic load (GL) of figs is 5, while pomelo has a GL level of 13. The glycemic load of figs falls in the low category, while the GL of pomelo falls in the medium category.
Acidity
Figs have a PRAL value of -4.9, while pomelo has a PRAL value of -3.7, both being alkaline-forming fruits.
Health Impact
Diabetes
Figs and pomelo both offer potential benefits for individuals managing diabetes. Figs, known for their natural sweetness, are rich in dietary fiber, which helps regulate blood sugar levels by slowing down the absorption of sugars in the bloodstream. Moreover, fig fruit extract containing abscisic acid showed beneficial effects on insulin resistance and blood glucose level management (1). Additionally, figs contain compounds like chlorogenic acid and quercetin, which have been studied for their potential anti-diabetic effects by improving insulin sensitivity and reducing inflammation (2) (3).
On the other hand, pomelo is low in glycemic index and rich in vitamin C and antioxidants. Studies suggest that consuming pomelo may help lower blood sugar levels and improve insulin resistance, potentially reducing the risk of developing type 2 diabetes (4) (5).
Digestive Health
Figs and pomelo both offer potential benefits for digestive health. The soluble and insoluble fiber content of figs aids in digestion by promoting regular bowel movements and preventing constipation along with bowel inflammation (6) (7). Additionally, figs contain natural enzymes that help break down food more efficiently in the digestive tract. Research suggests that figs may possess prebiotic properties, promoting the growth of beneficial bacteria in the gut, which can further support digestive health (8) (9).
Pomelo, being rich in fiber and water, can also aid in digestion by adding bulk to stools and preventing constipation. Moreover, the presence of enzymes like bromelain in pomelo may assist in the breakdown of proteins, facilitating easier digestion (10).
Cardiovascular Health
Both fruits promote heart health with the different chemicals they provide. Figs contain antioxidants such as phenols and flavonoids, which have been shown to reduce inflammation and oxidative stress, thus lowering the risk of cardiovascular diseases (11). Furthermore, fig leaf extract can help lower cholesterol levels by binding to cholesterol in the digestive tract and aiding in its excretion from the body (12). However, dried fig consumption has not shown lowering effects on LDL cholesterol in a human study (13).
Pomelo, being a citrus fruit, is also rich in antioxidants like vitamin C and flavonoids, which can help reduce inflammation and improve blood vessel function. Studies have indicated that regular consumption of citrus fruits like pomelo may be associated with a reduced risk of cardiovascular diseases such as heart attacks and strokes (14).
Classification
Pomelo, scientifically known as Citrus maxima or Citrus grandis, belongs to the Rutaceae family, which includes many citrus fruits such as oranges, lemons, and grapefruits. Figs are classified under the genus Ficus and belong to the Moraceae family. The common fig species cultivated for its fruit has a scientific name - Ficus carica.
Appearance
Pomelos are native to Southeast Asia but are now cultivated in various tropical and subtropical regions worldwide. Figs are deciduous trees or shrubs native to the Mediterranean region and Western Asia but are now cultivated in various parts of the world with suitable climates.
Pomelos are large citrus fruits, typically much larger than common oranges and similar in size to small melons. They have a thick, green, or yellowish-green rind. Pomelo peel is quite tough and can be difficult to remove compared to other citrus fruits. The flesh of the pomelo is typically pale yellow to pinkish, depending on the variety, and is divided into segments like other citrus fruits. Inside, pomelos have a spongy pith surrounding the segments, which is usually discarded before eating.
On the other hand, figs are unique fruits with a distinctive appearance. They grow on small trees or shrubs and are characterized by their pear-shaped or bell-shaped structure. The exterior of a fig is typically smooth and varies in color depending on the variety, ranging from green to purple or black when ripe. The surface may also have a slightly grainy texture due to tiny surface pores. When ripe, figs become soft to the touch and may develop wrinkles or cracks, indicating their readiness for harvest.
The interior of figs is filled with soft, sweet, and juicy flesh, often tinged with shades of pink, red, or amber. Within this flesh, there are many small, edible seeds that add a slight crunch to the fruit's texture.
Taste and Use
Figs have a sweet taste with hints of honey, making them a versatile fruit for various dishes. Fresh figs can be enjoyed on their own or paired with cheese, nuts, and meats for appetizers or salads. They are also perfect for desserts like cakes and tarts. Dried figs, with their chewy texture and intensified sweetness, are excellent for baking, snacking, or adding to breakfast bowls and trail mixes.
Pomelos have a mild and refreshing flavor, somewhat like a sweeter, less acidic grapefruit. They are great as a snack on their own or for adding to receipts of fruit salads. You can also use pomelo segments in green salads or pair them with seafood or poultry dishes.
References
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6722713/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7275206/
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0753332221013470
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29058284/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24147098/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22232635/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29870788/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28165863/
- https://www.researchgate.net/figure/n-vitro-prebiotic-potential-of-formulations-mean-SD_fig5_266741409
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1878535221001295
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10490098/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28193094/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21811062/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21389640/
Infographic
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Vitamin C | 61mg | 2mg | 66% |
| Fiber | 1g | 2.9g | 8% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.3mg | 6% | |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.036mg | 0.113mg | 6% |
| Manganese | 0.017mg | 0.128mg | 5% |
| Vitamin K | 4.7µg | 4% | |
| Carbs | 9.62g | 19.18g | 3% |
| Magnesium | 6mg | 17mg | 3% |
| Calcium | 4mg | 35mg | 3% |
| Iron | 0.11mg | 0.37mg | 3% |
| Calories | 38kcal | 74kcal | 2% |
| Copper | 0.048mg | 0.07mg | 2% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.034mg | 0.06mg | 2% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.027mg | 0.05mg | 2% |
| Folate | 6µg | 2% | |
| Zinc | 0.08mg | 0.15mg | 1% |
| Vitamin A | 0µg | 7µg | 1% |
| Vitamin E | 0.11mg | 1% | |
| Vitamin B3 | 0.22mg | 0.4mg | 1% |
| Choline | 4.7mg | 1% | |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.144g | 1% | |
| Protein | 0.76g | 0.75g | 0% |
| Fats | 0.04g | 0.3g | 0% |
| Net carbs | 8.62g | 16.28g | N/A |
| Potassium | 216mg | 232mg | 0% |
| Sugar | 16.26g | N/A | |
| Phosphorus | 17mg | 14mg | 0% |
| Sodium | 1mg | 1mg | 0% |
| Selenium | 0.2µg | 0% | |
| Saturated fat | 0.06g | 0% | |
| Monounsaturated fat | 0.066g | 0% | |
| Tryptophan | 0.006mg | 0% | |
| Threonine | 0.024mg | 0% | |
| Isoleucine | 0.023mg | 0% | |
| Leucine | 0.033mg | 0% | |
| Lysine | 0.03mg | 0% | |
| Methionine | 0.006mg | 0% | |
| Phenylalanine | 0.018mg | 0% | |
| Valine | 0.028mg | 0% | |
| Histidine | 0.011mg | 0% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Pomelo - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/167754/nutrients
- Figs - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/173021/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.





