Rabbit meat vs Goat meat — Nutrition and Health Impact Comparison

Summary
Compared to goat meat, rabbit meat contains more calories. Goat meat and rabbit meat contain no carbs, so they have glycemic indices equal to 0. Their calories are mainly based on fats and proteins.
Rabbit meat has higher protein than goat meat, with 33.02g and 27.1g per 100g, respectively. Both are high in essential amino acids, which are important for a lot of physiological functions. Rabbit meat and goat meat have almost equal overall fat content.
Rabbit meat has more iron and less sodium compared to goat meat. Rabbit meat is also high in vitamin B12, unlike goat meat.
Introduction
Rabbit meat and goat meat are not part of most people’s everyday diets, and consumption of both is not as typical as other types of meat consumption.
Goats and rabbits are mammals, but rabbit meat falls under the proper and ground game categories. Farm-raised rabbits are raised optimally for human consumption in terms of nutrient content.
Today, we will compare rabbit meat and goat meat, highlighting the main differences and health impacts.
What’s The Actual Difference?
Classification
Rabbit meat is generally classified as poultry meat. Nonetheless, due to its slightly higher myoglobin content and the fact that it is a mammal, some sources classify rabbit meat as red meat.
In the culinary world, rabbit meat is classified as white meat due to its similarity to chicken meat.
Goat meat is classified as red meat, but it is leaner and contains less cholesterol and fat than beef; thus, it necessitates low-heat, slow cooking to retain tenderness and moisture.
Taste and Culinary
Besides the fact that goat meat is packed with nutrients and has many health benefits, it is also delicious. It is sweet and slightly gamy. You can use goat meat in different dishes, such as Mexican and Jamaican dishes, curries, and so on.
Rabbit meat tastes like chicken meat, but rabbit meat is gamier and dryer. In comparison to red meat, rabbit meat has a lighter taste.
You can cook rabbit meat in the same way as chicken meat. When baking rabbit meat, it is recommended to keep the oven temperature at least 163 °C.
Price
In general, rabbit meat and goat are equal in price.
However, depending on the quality, rabbit meat may cost $5 to $7 per pound, whereas prices for goat meat range from $13.63 to 18.24 per pound.
Nutrition
The nutritional values are described for 100-gram servings of rabbit meat (wild, cooked, stewed) and goat meat (cooked, roasted).
Both rabbit meat and goat meat have an average serving size of 85g.
At the bottom of this page, you can find nutritional infographics that visually show the differences between rabbit meat and goat.
Calories
Compared to goat meat, rabbit meat contains more calories. Goat meat contains 143 calories per 100g, compared to 173 in rabbit meat.
Protein
Rabbit meat has higher protein than goat meat, with 33.02g and 27.1g per 100g, respectively. Both are high in essential amino acids such as methionine, isoleucine, phenylalanine, tryptophan, threonine, leucine, lysine, valine, and histidine, which are not synthesized in the human body but are crucial for numerous physiological functions.
Fats
Rabbit meat and goat meat have almost equal overall fat content. In particular, goats contain less saturated fat and more monounsaturated fat. However, rabbit meat has more polyunsaturated fat than goat meat.
Rabbit meat has 1.6 times higher cholesterol than goat meat. Rabbit meat contains 123 mg of cholesterol, while goat meat has 75mg.
Carbs
Goat meat and rabbit meat contain no carbs, so they have glycemic indices equal to 0. Their calories are mainly based on fats and proteins.
Minerals
Now, let’s discuss the mineral content of these two products. Both are rich in minerals. Rabbit meat has more magnesium, iron, phosphorus, and selenium and less sodium than goat meat. On the other hand, goats contain more potassium, manganese, copper, and zinc.
Both products are equal in calcium.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+∞%
Contains
more
IronIron
+30%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+19.4%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-47.7%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+28.8%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+18.1%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+72.2%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+121.4%
Vitamins
Overall, rabbit meat is relatively richer in vitamins. It contains more water-soluble vitamins, such as vitamins B3, B6, B9, and B12, and fat-soluble vitamins, like vitamin E and vitamin K, than goat meat, which is higher in vitamins B1 and B2. It should be noted that rabbit meat contains 5.4 times more vitamin B12 compared to goat meat.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+20.6%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+62%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin B12Vitamin B12
+447.1%
Contains
more
Vitamin KVitamin K
+25%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+60%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+350%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+771.4%
Health Benefits
Weight Loss and Diets
Goat and rabbit meat are good choices for some diets, but it's important to note how you prepare both of these foods.
Keto Diet
Since the Keto diet requires low-carb and high-fat foods, rabbit and goat meat are excellent choices in the case of Keto diet (including Atkins and other types) because both have zero carbs and are high in proteins (1).
It should be emphasized that high-protein diets may be associated with a variety of metabolic problems that may be dangerous to kidney function (2).
The Mediterranean Diet
Whole grains, healthy fats (fish, olive oil, nuts, etc.), vegetables, fruits, fish, and very little non-fish meat consumption are all part of the Mediterranean diet profile. As a result, goat and rabbit meats can be ingested in moderation throughout this diet.
DASH (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension)
The DASH diet includes potassium, calcium, and magnesium-rich foods. These nutrients aid in blood pressure regulation. The diet restricts sodium, saturated fat, and added sugars. Based on this, rabbit and goat meats are allowed in moderation during this diet.
Cardiovascular Health
Because rabbit and goat meats include proteins that may block angiotensin-converting enzymes (ACE), they play an essential function in lowering arterial blood pressure and avoiding artery and myocardial remodeling. These effects are important for patients with arterial hypertension, coronary heart disease, heart failure, and people who have had a myocardial infarction (3.4.5).
Both of these products are low in fat, which is important for preventing metabolic syndrome, which in turn is essential for reducing CVD (cardiovascular disease) risk (6.7).
For a long time, red meat (in this context, goat meat) has been linked to an elevated risk of CVDs. Recent research, however, has shown that, despite the presence of heme iron and carnitine, red meat does not significantly raise cardiovascular risk when consumed in moderation (8). It should be mentioned that curing, salting, smoking, drying, or canning processed meat may raise the risk of CVD (9).
This study found a strong and inverse relationship between eating unprocessed white meat and all-cause mortality, as well as a neutral relationship between cardiovascular mortality and morbidity (10).
In conclusion, white meat consumption may be a more 'healthy' and environmentally sustainable alternative to red and processed meat consumption (10).
Diabetes
Rabbit and goat meats have 0g of carbs, so their glycemic indices are equal to 0. Based on this, rabbit meat can be eaten in diets modified for diabetic patients to control blood glucose and insulin levels (11).
As for goat meat, it is red meat and contains nitrites and nitrates, which may lead to increased insulin resistance, dysregulated blood glucose levels, and elevated oxidative stress, all of which lead to chronic diseases. The causal links show that even the occasional use of red meat raises the risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus (12).
Anemia
Anaemia is described as a hemoglobin (Hb) level that is lower than the reference value, which varies depending on gender, age, and pregnancy status. Symptoms include fatigue, weakness, lightheadedness, shortness of breath, etc. There are many reasons for anemia, but in this section, we are going to talk about iron deficiency anemia, which is the most frequent cause of anemia worldwide. It affects 3% of individuals and is slightly more prevalent in women under the age of 50 (13.14).
In addition to the symptoms described above, iron deficiency anemia is characterized by pica (an abnormal craving to consume nonfood substances such as clay or mud, paper goods, or cornstarch) and pagophagia (an excessive craving to eat ice) (15).
If iron deficiency anemia is caused by a lack of iron intake, eating iron-rich foods (keep in mind that rabbit meat has 4.85mg per 100g and goat meat contains 3.73mg) may be beneficial. It should be mentioned that there are other causes of iron deficiency anemia, and you should visit a doctor for a proper diagnosis.
It should be noted that both of these are high in vitamin B12, so that they may be beneficial for people with vitamin B12 deficiency anemia.
Cancer
According to studies, white meat (in this context, rabbit meat) consumption is negatively associated with a high risk of stomach cancer, in contrast to red meat (in this context, goat meat), whose increased consumption may be a risk factor for stomach cancer. Larger prospective studies are needed to confirm this connection (16.17).
In comparison to white meat, there is a link between red meat consumption and colorectal, lung, prostate, and pancreatic cancer, according to studies (18.19).
Downsides and Risks
Kidney Health
A high-protein consumption, defined as more than 1.2 grams of dietary protein per kilogram of body weight per day (g/kg/day), has been shown to cause significant changes in renal function and kidney health (20).
Increased protein consumption may result in increased intraglomerular pressure and glomerular hyperfiltration. This can damage the glomerular structure, causing or exacerbating chronic kidney disease (CKD). As a result, a low-protein diet of 0.6–0.8 g/kg/day is frequently advised for CKD therapy (20).
To avoid those mentioned above, eat high-protein foods (including these) in moderation.
Meat Allergy
Meat allergies are uncommon, but they are more common in children with atopic dermatitis than in others. According to studies, red meat allergies are more common than white meat allergies.
Difficulty breathing, hives, vomiting, stomach cramps, and, in rare cases, anaphylaxis are all symptoms of a red meat allergy.
Avoiding the offending meat(s) is the most prevalent method of controlling food allergies. If the patient experiences an allergic response to raw meat, determining if the meat is tolerated in a well-cooked form may be important since the patient may be able to keep the meal in his or her diet in cooked form. Patients with immunoglobulin E-mediated meat allergies should be provided with an epinephrine autoinjector and shown how to use it (21.22).
Gout
Higher meat consumption is linked to an increased risk of gout (23). A gout diet may aid in lowering uric acid levels in the blood. It may reduce the risk of future gout attacks as well as decrease the progression of joint damage (24).
People with gout who follow a gout diet still require medication to manage pain and lower uric acid levels (24).
In conclusion, lean meat consumption, such as rabbit and goat meat, is allowed in moderation during the gout diet.
Tularemia
Tularemia is a zoonotic infection caused by bacteria (Francisella tularensis) frequently associated with rabbit hunters and consumers of rabbit meat. Infection can occur due to contact with infected tissue during rabbit skinning or eating infected meat. Transmission can also happen due to a tick bite on the animal's skin (25).
References
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3945587/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32669325/
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0308814621020768
- https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/jsfa.7538
- https://www.escardio.org/Guidelines/Clinical-Practice-Guidelines/Angiotensin-Converting-Enzyme-Inhibitors-in-Cardiovascular-Disease-Expert-Conse
- https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Ayodeji-Olarinmoye/publication/236878099_Goat_Products_Meeting_the_Challenges_of_Human_Health_and_Nutrition/links/59443e080f7e9b6910ee2deb/Goat-Products-Meeting-the-Challenges-of-Human-Health-and-Nutrition.pdf
- http://www.cuniculture.info/Docs/Magazine/Magazine2008/FiguresMag2008/Congres-2008-Verone/Papers/Q0-Hernandez.pdf
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5474906/
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0899900715004098
- https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/13/2/676
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/289674478_Rabbit_Meat_has_the_Potential_of_Being_a_Possible_Alternative_to_Other_Meats_as_a_Protein_Source_A_Brief_Review
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30229313/
- https://www.who.int/health-topics/anaemia#tab=tab_1
- https://www.aafp.org/pubs/afp/issues/2021/0800/p211.html
- https://pro.uptodatefree.ir/show/695
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6520977/
- https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00432-014-1637-z
- https://www.who.int/news-room/questions-and-answers/item/cancer-carcinogenicity-of-the-consumption-of-red-meat-and-processed-meat
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7139399/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5962279/
- https://pro.uptodatefree.ir/show/2393
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6488443/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15014182/
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/nutrition-and-healthy-eating/in-depth/gout-diet/art-20048524
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK430905/
Infographic
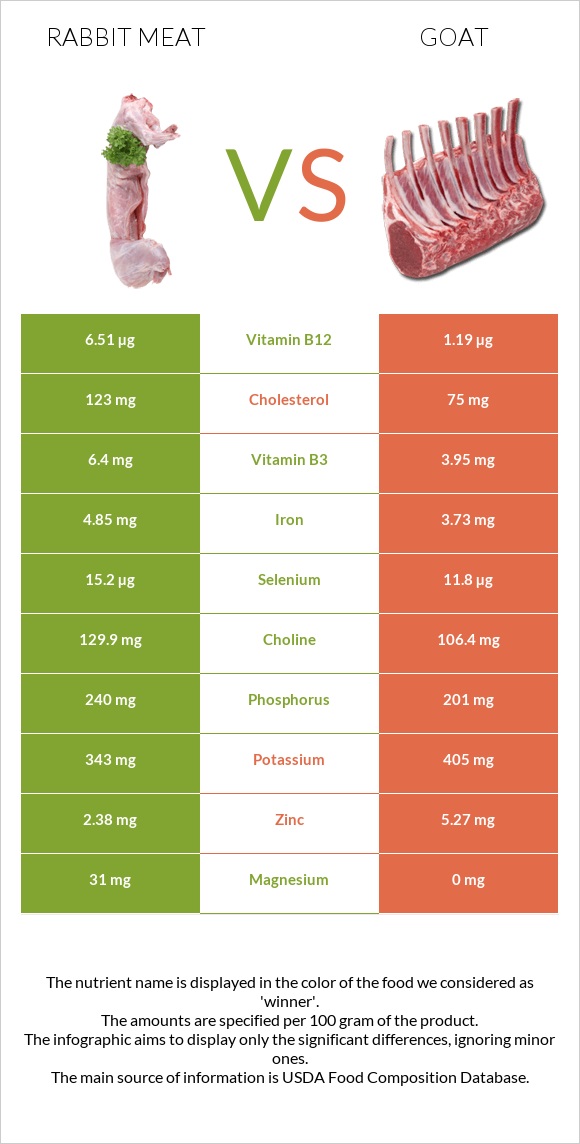
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Vitamin B12 | 6.51µg | 1.19µg | 222% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.07mg | 0.61mg | 42% |
| Zinc | 2.38mg | 5.27mg | 26% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.34mg | 0mg | 26% |
| Cholesterol | 123mg | 75mg | 16% |
| Vitamin B3 | 6.4mg | 3.95mg | 15% |
| Iron | 4.85mg | 3.73mg | 14% |
| Copper | 0.176mg | 0.303mg | 14% |
| Protein | 33.02g | 27.1g | 12% |
| Magnesium | 31mg | 0mg | 7% |
| Phosphorus | 240mg | 201mg | 6% |
| Selenium | 15.2µg | 11.8µg | 6% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.02mg | 0.09mg | 6% |
| Choline | 129.9mg | 106.4mg | 4% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.68g | 0.23g | 3% |
| Calories | 173kcal | 143kcal | 2% |
| Potassium | 343mg | 405mg | 2% |
| Sodium | 45mg | 86mg | 2% |
| Manganese | 0.042mg | 2% | |
| Fats | 3.51g | 3.03g | 1% |
| Folate | 8µg | 5µg | 1% |
| Saturated fat | 1.05g | 0.93g | 1% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 0.95g | 1.36g | 1% |
| Calcium | 18mg | 17mg | 0% |
| Vitamin E | 0.41mg | 0.34mg | 0% |
| Vitamin K | 1.5µg | 1.2µg | 0% |
| Tryptophan | 0.436mg | 0.403mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 1.477mg | 1.29mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 1.567mg | 1.371mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 2.573mg | 2.258mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 2.891mg | 2.016mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.826mg | 0.726mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 1.355mg | 0.941mg | 0% |
| Valine | 1.678mg | 1.452mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.926mg | 0.565mg | 0% |
Macronutrient Comparison
| Contains more ProteinProtein | +21.8% |
| Contains more FatsFats | +15.8% |
| Contains more OtherOther | +26.5% |
| Contains more WaterWater | +11.1% |
Fat Type Comparison
| Contains more Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat | +195.7% |
| Contains less Sat. FatSaturated fat | -11.4% |
| Contains more Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat | +43.2% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Rabbit Meat - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/174348/nutrients
- Goat - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/175304/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.





