Orange Chicken vs. Sesame Chicken — What’s the Difference?


Summary
The nutritional differences between orange and sesame chicken are mainly due to the sauces used when coating the chicken.
Sesame chicken is somewhat higher in calories and carbohydrates due to net carbs. This dish also contains more fats due to a higher unsaturated fat content.
Sesame chicken is a better source of most B-complex vitamins, iron, and copper, while orange chicken is richer in folate, calcium, and zinc.
Introduction
Chinese orange chicken and sesame chicken are two of the most popular options ordered at Chinese restaurants. Naturally, people have their preferences based on taste, but how different are these two dishes regarding nutrition and health impact? In this article, we will find an answer to this question.
Appearance, Taste, & Use
Sesame and orange chicken are commonly found in North American Chinese restaurants. While these dishes find their roots in China, they are now much more popular in the US and Canada than in Asia.
Orange and sesame chicken are dishes typically made by deep-frying chicken and coating it in different sauces.
Orange chicken is coated in a sweet and tangy orange sauce. The sauce is usually made with orange juice, soy sauce, brown sugar, vinegar, garlic, ginger, and sometimes chili flakes or hot sauce for a bit of heat. The crispy chicken is then tossed in the sauce, making for a sweet and savory flavor profile.
Sesame chicken sauce is usually made with soy sauce, honey, garlic, ginger, and sesame oil and then garnished with toasted sesame seeds. The resulting dish is sweet, savory, and nutty.
Both dishes are similar in that they are sweet and savory, but orange chicken has a more pronounced citrus flavor, while sesame chicken has a nuttier flavor from the toasted sesame seeds.
Nutrition
The nutritional infographics below are presented for 100g servings of orange and sesame chicken from Chinese restaurants. The nutrition information does not include rice or broccoli contained in the dishes.
However, one order of orange chicken usually weighs 648g, while an average order of sesame chicken equals around 547g.
Macronutrients And Calories
Naturally, these dishes have similar macronutrient compositions, as the main ingredient of both is the chicken, and the coating makes up for the difference in nutrition.
Sesame chicken is only a little denser in nutrients, consisting of 43% water and 57% nutrients, while orange chicken contains 48% water and 52% nutrients.
The primary macronutrient in both dishes is carbs, followed by fat and protein.
Macronutrient Comparison
Contains
more
FatsFats
+12.4%
Contains
more
CarbsCarbs
+19.7%
Contains
more
WaterWater
+13.2%
Contains
more
OtherOther
+13.2%
Calories
Orange and sesame chicken are both high-calorie foods. A 100g serving of each dish provides around 15% of the recommended daily calorie intake.
Sesame chicken is somewhat higher in calories, providing 293 calories per 100g serving, while orange chicken provides 262 calories in an equal serving.
Carbohydrates
Sesame chicken is also higher in carbohydrates, by about 4.5g per every 100g serving, due to net carbs, such as starch and sucrose. While both these dishes are insufficient sources of dietary fiber, orange chicken is slightly richer in fiber.
Sesame chicken and orange chicken provide 26.9g and 22.5g of carbohydrates per 100g, respectively.
The predominant carbohydrates found in these dishes are starch and sucrose. Sesame chicken also contains glucose and fructose, while orange chicken lacks these.
Carbohydrate type comparison
Contains
more
GlucoseGlucose
+246%
Contains
more
FructoseFructose
+200%
Protein
Sesame and orange chicken are great sources of protein. These dishes provide equal amounts of protein - about 14.5g per 100g serving, which covers 34% of the daily needed value.
Orange chicken is ever so slightly higher in protein, containing 0.1g more.
Fats
Sesame chicken is higher in fats by about 1.5g per every 100g serving, containing 14.25g, while orange chicken has 12.7g of fats.
However, while sesame chicken is higher in unsaturated fats, both chicken dishes contain nearly equal amounts of saturated fats.
These two dishes have similar fat compositions. The fat content of both sesame and orange chicken is made up of over 50% polyunsaturated fats, followed by monounsaturated fats, leaving saturated fats in the last place. Despite this, they are still high in saturated fats, with a 100g serving covering over 12% of the recommended daily value.
Fat Type Comparison
Contains
more
Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat
+13.1%
These dishes are high in cholesterol. Even though sesame chicken contains more fats overall, it is slightly lower in cholesterol, providing 59mg per 100g serving, while orange chicken has 61mg.
Vitamins
Orange and sesame chicken are excellent sources of B-complex vitamins, containing nearly equal amounts. However, sesame chicken is slightly higher in almost all of them, including vitamins A, E, C, and K, and vitamins B3 (niacin), B6, and B12.
Orange chicken is only somewhat higher in vitamin B9 or folate.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+22.4%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+16.1%
Contains
more
Vitamin B12Vitamin B12
+25%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+25%
Minerals
These two chicken dishes are also overall similar in their mineral compositions. Nonetheless, sesame chicken is slightly richer in iron and copper, while orange chicken is higher in calcium and zinc.
While both dishes are high in salt, sesame chicken contains slightly less sodium. The sodium content per 100g servings of sesame and orange chicken is 482mg and 553mg, respectively.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
IronIron
+16%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+21.4%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-12.8%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+16.7%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+24.2%
Glycemic Index
Boiled chicken contains almost no carbohydrates and, therefore, has a glycemic index of 0. However, the coating and the deep-frying notably increase this value.
The glycemic indices of Chinese orange and sesame chicken have not yet been calculated. We can assume them to be close to the value of chicken nuggets, which have a glycemic index of 46 (1).
Insulin Index
The insulin index values of foods demonstrate how the consumption of the given food increases insulin levels in the blood.
Similarly, no studies have been carried out on the insulin index values of orange and sesame chicken.
It can be said that while roasted chicken has an insulin index of 23, this value for chicken nuggets has been studied to be 41 (2, 3). This value falls in the low insulin index category.
Health Impact
Orange and sesame chicken can be good sources of protein, healthy fats, and various minerals and vitamins.
At the same time, the consumption of deep-fried food overall has been researched to have negative health impacts, increasing the risk of heart disease and type 2 diabetes (4, 5). However, eating sesame and orange chicken alongside vegetables, such as broccoli and carrots, can be slightly healthier as they provide additional nutrients like fiber, vitamins, and minerals.
Cardiovascular Health
Frequent fried food consumption has been demonstrated to have a linear correlation with increased risk of hypertension or high blood pressure, stroke, coronary heart disease, heart failure, and coronary mortality by several mechanisms, one of which is elevating “bad” cholesterol levels in the blood. (4, 6).
Sesame and orange chicken are also high in sodium. A high-sodium diet has also been proven to increase the risk of high blood pressure (7).
Diabetes
Despite potentially low glycemic and insulin index values, sesame and orange chicken should be consumed in strict moderation for people at risk of diabetes.
The cooking method may be as significant as the meal's ingredients when discussing diabetes risk. Cooking meat at high temperatures, such as deep-frying, grilling, and barbecuing, increases the risk of type 2 diabetes compared to cooking at moderate temperatures, such as boiling, steaming, and stir-frying (8).
Sources
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5852758/
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/26770180
- https://ses.library.usyd.edu.au/handle/2123/11945
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33468573
- https://www.hsph.harvard.edu/news/hsph-in-the-news/eating-fried-foods-tied-to-increased-risk-of-diabetes-and-heart-disease/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4632424/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6770596/
- https://www.hsph.harvard.edu/nutritionsource/2018/03/23/how-meat-is-cooked-may-affect-risk-of-type-2-diabetes/
Infographic
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Vitamin B5 | 1mg | 20% | |
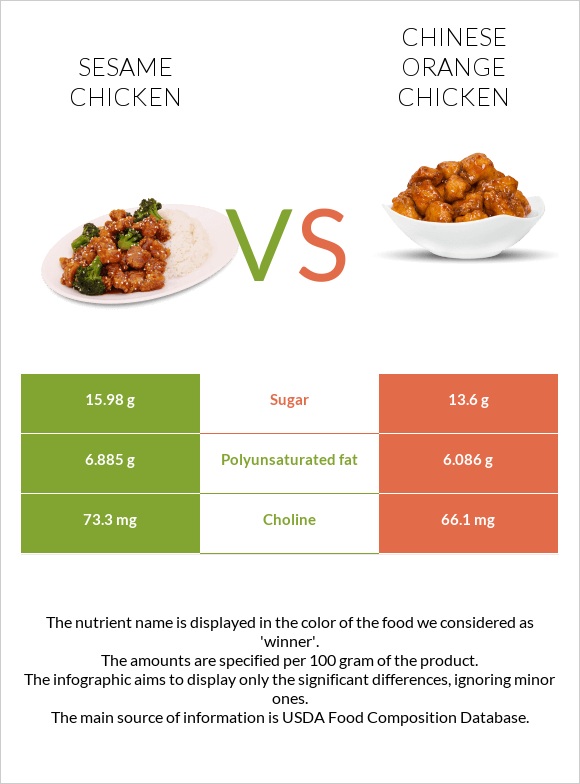
| Polyunsaturated fat | 6.885g | 6.086g | 5% |
| Sodium | 482mg | 553mg | 3% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.267mg | 0.23mg | 3% |
| Calories | 293kcal | 262kcal | 2% |
| Fats | 14.25g | 12.68g | 2% |
| Iron | 1.09mg | 0.94mg | 2% |
| Zinc | 0.91mg | 1.13mg | 2% |
| Vitamin E | 1.31mg | 1.07mg | 2% |
| Vitamin B3 | 3.96mg | 3.59mg | 2% |
| Vitamin B12 | 0.25µg | 0.2µg | 2% |
| Vitamin K | 27.1µg | 24.4µg | 2% |
| Fructose | 2.01g | 0.67g | 2% |
| Carbs | 26.88g | 22.46g | 1% |
| Cholesterol | 59mg | 61mg | 1% |
| Copper | 0.051mg | 0.042mg | 1% |
| Vitamin A | 83µg | 75µg | 1% |
| Selenium | 16.7µg | 17.1µg | 1% |
| Folate | 8µg | 10µg | 1% |
| Choline | 73.3mg | 66.1mg | 1% |
| Protein | 14.33g | 14.46g | 0% |
| Vitamin C | 1mg | 0.9mg | 0% |
| Net carbs | 26.18g | 21.66g | N/A |
| Vitamin D | 5 IU | 5 IU | 0% |
| Magnesium | 22mg | 20mg | 0% |
| Calcium | 12mg | 14mg | 0% |
| Potassium | 204mg | 209mg | 0% |
| Sugar | 15.98g | 13.6g | N/A |
| Fiber | 0.7g | 0.8g | 0% |
| Starch | 10.7g | 10.5g | 0% |
| Phosphorus | 130mg | 130mg | 0% |
| Vitamin D | 0.1µg | 0.1µg | 0% |
| Manganese | 0.083mg | 0.087mg | 0% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.04mg | 0.043mg | 0% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.225mg | 0.22mg | 0% |
| Trans fat | 0.045g | 0.053g | N/A |
| Saturated fat | 2.41g | 2.422g | 0% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 3.546g | 3.474g | 0% |
| Tryptophan | 0.113mg | 0% | |
| Threonine | 0.576mg | 0% | |
| Isoleucine | 0.576mg | 0% | |
| Leucine | 1.001mg | 0% | |
| Lysine | 1.058mg | 0% | |
| Methionine | 0.34mg | 0% | |
| Phenylalanine | 0.51mg | 0% | |
| Valine | 0.614mg | 0% | |
| Histidine | 0.359mg | 0% | |
| Omega-3 - EPA | 0.003g | 0.001g | N/A |
| Omega-3 - DHA | 0.005g | 0.005g | N/A |
| Omega-3 - ALA | 0.774g | 0.619g | N/A |
| Omega-3 - DPA | 0.006g | 0.003g | N/A |
| Omega-3 - Eicosatrienoic acid | 0.001g | 0g | N/A |
| Omega-6 - Gamma-linoleic acid | 0.039g | 0.028g | N/A |
| Omega-6 - Dihomo-gamma-linoleic acid | 0.009g | 0.01g | N/A |
| Omega-6 - Eicosadienoic acid | 0.009g | 0.008g | N/A |
| Omega-6 - Linoleic acid | 5.925g | 5.284g | N/A |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Sesame chicken - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/168087/nutrients
- Orange chicken - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/167679/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.


