General Tso vs Orange Chicken - Nutrition & Health impact comparison


Summary
General Tso’s and Chinese orange chicken are popular Chinese American dishes with high amounts of carbs and sodium. However, they are rich in vitamins, minerals, and protein. Consuming these foods in moderation is essential since they increase metabolic and cardiovascular disease mortality risks.
Introduction
This article is a comparison between 2 American Chinese dishes, General Tso's chicken and Chinese orange chicken.
General Tso’s chicken is a dish that originated in Taiwan and was later brought to the US. In comparison, Chinese orange chicken is also an American Chinese dish, which is claimed to be a variation of General Tso’s chicken recipe.
Ingredient Differences
It is essential to understand the main ingredients in each dish. The base is chicken. However, there exists a difference in the preparation of the chicken.
General Tso’s chicken is made from chicken thigh cuts, breaded, and fried. In comparison, orange chicken is chicken breast fried till golden crispy.
The other main difference is the sauce in that the chicken gets drizzled.
General Tso’s chicken tangy sauce contains rice vinegar, soy sauce, hoisin sauce, chili flakes, pepper, and cornstarch. It is usually served with rice, vegetables, Chinese noodles, and salads.
In comparison, orange chicken contains orange juice, sugar, orange peel, cornstarch, soy sauce, spices, garlic, and ginger. It is best served with rice, egg, egg noodles, and steamed broccoli.
From the ingredients of the sauce, we can differentiate the taste also. The orange chicken will have a sweet and savory flavor, whereas General Tso’s chicken will give a milder, spicier, and more savory flavor.
Nutrition
In this section, we will be considering 100g servings of each. In the infographic below, you can see that both of them contain nearly the same amounts of water. However, General Tso's chicken is slightly higher in carbs and fats.
Macronutrient Comparison
Contains
more
ProteinProtein
+12.1%
Contains
more
OtherOther
+23.1%
Contains
more
FatsFats
+29%
Carbs
They contain high amounts of carbs. Their carb content is nearly similar, 24g for General Tso’s chicken and 23g for orange chicken. Both contain nearly the same amount of dietary fiber.
General Tso's chicken is higher in starch due to additional cornstarch used in its preparation. Orange chicken is richer in sucrose.
Carbohydrate type comparison
Contains
more
SucroseSucrose
+17.6%
Contains
more
FructoseFructose
+31.4%
Contains
more
StarchStarch
+12.7%
Calories
General Tso's chicken and Orange chicken are high in calories. General Tso’s chicken contains nearly 300 calories. In comparison, orange chicken is lower in calories: it contains about 260 calories.
Protein
Orange chicken contains higher amounts of proteins than General Tso’s chicken, at 15g for orange chicken and 13g for General Tso’s chicken. Orange chicken has a leaner cut, which is chicken breast.
Fat
General Tso’s chicken contains higher amounts of fats compared to orange chicken. General Tso’s chicken contains 16g of fat, whereas orange chicken has 12g.
General Tso's chicken is comparably richer in unsaturated fats. Orange chicken contains 8mg more cholesterol.
Fat Type Comparison
Contains
less
Sat. FatSaturated fat
-12.2%
Contains
more
Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat
+11.7%
Contains
more
Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat
+23.3%
Minerals
Both these dishes are very high in sodium. In comparison, orange chicken contains higher amounts of sodium than general Tso’s chicken.
General Tso’s chicken is richer in iron. In contrast, Chinese orange chicken is richer in selenium and phosphorus.
Below we can visualize their mineral profiles.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+16.7%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+16%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+18.8%
Contains
more
IronIron
+23.4%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+15%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-21.3%
Vitamins
General Tso’s chicken is richer in vitamins K and E. Chinese orange chicken is richer in vitamins B2, B3, B5, and B6.
Below, we can visualize their vitamin profiles.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+581.8%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+59.3%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+86.4%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+25.8%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+62.1%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+13.9%
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+77.8%
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+13.1%
Contains
more
Vitamin DVitamin D
+100%
Contains
more
Vitamin KVitamin K
+56.6%
Health impacts
Cardiovascular Health
General Tso's Chicken and Orange Chicken are fried dishes that are high in calories and may have negative effects on cardiovascular health.
Both dishes typically contain high levels of saturated fats and sodium, which can raise blood pressure and LDL (bad cholesterol) levels, increasing the risk of cardiovascular disease (1).
To promote heart health, it is advisable to consume these dishes in moderation. Healthier alternatives, such as grilled or baked versions, along with low-sodium and low-sugar sauces, are recommended to help reduce cardiovascular risk.
Metabolic Diseases
Since these foods are high in carbs, consuming high-carb foods increases the risks of several metabolic diseases, including obesity and diabetes. It is also important to remember that these foods are primarily associated with white rice, which increases carbohydrate intake. (2)
Infographic
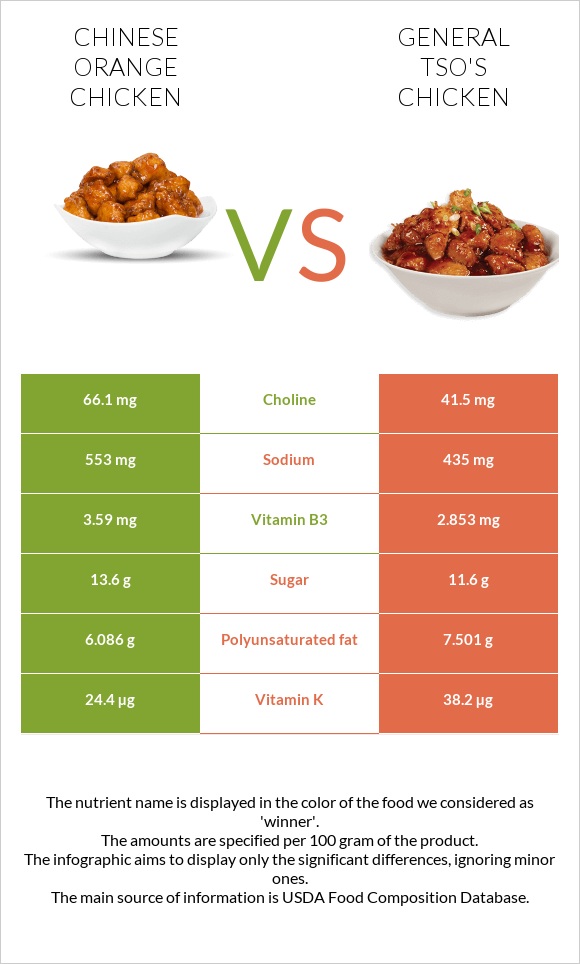
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Vitamin K | 24.4µg | 38.2µg | 12% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 6.086g | 7.501g | 9% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.22mg | 0.118mg | 8% |
| Vitamin B5 | 1mg | 0.617mg | 8% |
| Vitamin A | 75µg | 11µg | 7% |
| Fats | 12.68g | 16.36g | 6% |
| Sodium | 553mg | 435mg | 5% |
| Selenium | 17.1µg | 14.4µg | 5% |
| Vitamin B3 | 3.59mg | 2.853mg | 5% |
| Choline | 66.1mg | 41.5mg | 4% |
| Protein | 14.46g | 12.9g | 3% |
| Cholesterol | 61mg | 53mg | 3% |
| Iron | 0.94mg | 1.16mg | 3% |
| Calories | 262kcal | 295kcal | 2% |
| Zinc | 1.13mg | 1.3mg | 2% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.23mg | 0.202mg | 2% |
| Saturated fat | 2.422g | 2.76g | 2% |
| Vitamin C | 0.9mg | 1.6mg | 1% |
| Carbs | 22.46g | 23.99g | 1% |
| Starch | 10.5g | 11.83g | 1% |
| Vitamin E | 1.07mg | 1.21mg | 1% |
| Vitamin D | 0.1µg | 0.2µg | 1% |
| Manganese | 0.087mg | 0.075mg | 1% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.043mg | 0.027mg | 1% |
| Vitamin B12 | 0.2µg | 0.22µg | 1% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 3.474g | 3.879g | 1% |
| Net carbs | 21.66g | 23.09g | N/A |
| Vitamin D | 5 IU | 6 IU | 0% |
| Magnesium | 20mg | 18mg | 0% |
| Calcium | 14mg | 12mg | 0% |
| Potassium | 209mg | 201mg | 0% |
| Sugar | 13.6g | 11.6g | N/A |
| Fiber | 0.8g | 0.9g | 0% |
| Copper | 0.042mg | 0.046mg | 0% |
| Phosphorus | 130mg | 127mg | 0% |
| Folate | 10µg | 11µg | 0% |
| Trans fat | 0.053g | 0.09g | N/A |
| Tryptophan | 0.113mg | 0.142mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 0.576mg | 0.552mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 0.576mg | 0.564mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 1.001mg | 1.026mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 1.058mg | 1.089mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.34mg | 0.332mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 0.51mg | 0.563mg | 0% |
| Valine | 0.614mg | 0.607mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.359mg | 0.333mg | 0% |
| Fructose | 0.67g | 0.51g | 0% |
| Omega-3 - EPA | 0.001g | 0.005g | N/A |
| Omega-3 - DHA | 0.005g | 0.005g | N/A |
| Omega-3 - ALA | 0.619g | 0.84g | N/A |
| Omega-3 - DPA | 0.003g | 0.006g | N/A |
| Omega-3 - Eicosatrienoic acid | 0g | 0.001g | N/A |
| Omega-6 - Gamma-linoleic acid | 0.028g | 0.005g | N/A |
| Omega-6 - Dihomo-gamma-linoleic acid | 0.01g | 0.01g | N/A |
| Omega-6 - Eicosadienoic acid | 0.008g | 0.011g | N/A |
| Omega-6 - Linoleic acid | 5.284g | 6.47g | N/A |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Orange chicken - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/167679/nutrients
- General tso's chicken - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/167675/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.


