Black Pepper vs. Cayenne Pepper — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Black and cayenne peppers are nutrient-dense spices with various health-promoting phytochemicals.
Cayenne pepper is relatively higher in fats, protein, and dietary fiber, whereas black pepper is higher in net carbs. However, both spices are very high in dietary fiber.
From notable micronutrient differences, black pepper is richer in vitamin K, calcium, and copper, whereas cayenne pepper is richer in vitamins A, E, B6, B9, and zinc.
Introduction
This article will compare two of the most common and widely consumed spices: black pepper and cayenne pepper (moderately hot chili pepper). Comparison topics are focused on their nutritional differences and health benefits.
Classification
Black pepper (Piper nigrum) belongs to the Piper genus and Piperaceae family. Black pepper is made from dried peppercorns that grow on Piper nigrum.
Cayenne pepper (Capsicum annuum) belongs to the Capsicum genus and Solanaceae or nightshade family.
Taste and Use
Black pepper is a milder spice with a versatile flavor that is commonly used in a wide range of dishes. Cayenne pepper, on the other hand, is significantly hotter and is primarily used for adding spice and heat to recipes, particularly in spicy cuisines.
Nutrition
The nutritional infographics in this article are presented for 100g servings of black pepper and cayenne pepper. However, spices are naturally not consumed in such large quantities, so we will also discuss these spices in 0.5g servings.
The average serving size of spices is ¼ tsp or 0.5g.
Macronutrients
Black and cayenne peppers are rich in nutrients, making them nutrient-dense spices.
Cayenne pepper is higher in fats, protein, and dietary fiber than black pepper.
Black pepper consists of 12.5% water, and cayenne pepper consists of 8.05% water, making cayenne pepper nutritionally denser.
Macronutrient Comparison
Contains
more
ProteinProtein
+15.6%
Contains
more
FatsFats
+429.8%
Contains
more
CarbsCarbs
+12.9%
Contains
more
WaterWater
+54.8%
Contains
more
OtherOther
+64.6%
Calories
Due to having a 0.5g of serving size, spices are very low in calories. One serving of black pepper provides 1.255 calories, while one serving of cayenne pepper provides 1.59 calories.
When comparing 100g of each spice, black pepper provides 251 calories, whereas cayenne pepper provides 318 calories.
Carbohydrates
Carbs are the main macronutrients in black and cayenne peppers, making up over 50% of the nutrients. Black pepper is somewhat higher in total and net carbs.
Black pepper contains 39% net carbs, while this percentage is 29% for cayenne pepper.
Both spices are rich in dietary fiber: 40% of black pepper carbs and 48% of cayenne pepper carbs are dietary fiber.
Protein
These peppers have similar amounts of protein. Cayenne pepper is only 1.15 times richer in proteins.
Fats
Cayenne pepper is 5.3 times richer in fats.
The predominant fats in black pepper are saturated fatty acids, whereas the predominant fats in cayenne pepper are polyunsaturated fatty acids.
Fat Type Comparison
Contains
more
Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat
+272.1%
Contains
more
Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat
+738.7%
Contains
less
Sat. FatSaturated fat
-57.3%
Both spices are naturally absent in trans fats and cholesterol.
Vitamins
Spices can be a great way to add some beneficial nutrients, such as vitamins and minerals, to the dish.
Cayenne pepper is the absolute winner in this category, as it is richer in almost all vitamins except for vitamin K.
Black pepper is two times richer in vitamin K.
Cayenne pepper is 76 times richer in vitamin A, 29 times richer in vitamin E, 8.4 times richer in vitamin B6, and six times richer in vitamin B9 or folate. Cayenne pepper is richer in all B complex vitamins.
Both spices are naturally absent in vitamin B12 and vitamin D. Black pepper is absent in vitamin C.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+7607.4%
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+2768.3%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+203.7%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+410.6%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+661.2%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+741.9%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+523.5%
Contains
more
Vitamin KVitamin K
+103.9%
Minerals
These spices are rich in various minerals.
Black pepper is 3 times richer in calcium and 3.5 times richer in copper. Black pepper is also somewhat richer in iron and magnesium and contains less sodium.
Cayenne pepper is from 1.5 to 2 times richer in phosphorus, potassium, zinc, and selenium.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+51.5%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+108.4%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+85.4%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+79.6%
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+12.5%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+199.3%
Contains
more
IronIron
+24.5%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+256.6%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-33.3%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+537.7%
Glycemic Index
The glycemic index values of black pepper and cayenne pepper have not been calculated.
Acidity
PRAL or potential renal acid load value calculates how much acid or base is produced in the organism from the given food.
The PRAL value of black pepper is -27.2, whereas the PRAL value of cayenne pepper is -31.4, making cayenne pepper more alkaline or base-producing.
Weight Loss & Diets
Despite their high carb content, both spices are considered keto-friendly and can be consumed during the keto diet due to their small serving sizes.
Cayenne pepper can be consumed in moderation during the Atkins diet.
Black and cayenne peppers can be consumed during the Mediterranean, Dukan, and Paleo diets as well.
Black and cayenne peppers are great for anti-inflammatory diets.
The spices help in weight loss diets through various mechanisms. Black pepper, rich in piperine, enhances intestinal barrier function and inhibits fatty acid absorption from the intestines (1). Cayenne pepper, rich in capsaicin, regulates fat metabolism, stimulates energy expenditure due to increased thermogenesis, and increases the feeling of satiety (2).
Health Impact
Spices have been used for medicinal purposes for centuries for their antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-cancer, as well as glucose, and cholesterol-lowering effects.
Higher consumption of spices has been linked to decreased risk of death from various chronic diseases (3).
Cardiovascular Health
Piperine is an alkaloid found in black pepper, which has been shown to have various heart-protecting effects. Animal studies have shown that piperine attenuates drug-induced (isoproterenol) myocardial ischemia and reduces the death of heart muscle cells after reperfusion injury (4, 5).
Active components, mainly piperine, have been shown to reduce “bad” cholesterol (triglyceride, total cholesterol or TC, and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol or LDL-C) levels in animal studies. High “bad” cholesterol levels are a major risk factor for atherosclerosis (6, 7). However, more research on humans is still needed.
Regular consumption of cayenne pepper is associated with a lower risk of total and heart disease-related death (8, 9).
Capsaicin and other chili pepper phytochemicals may positively affect metabolic syndrome and atherosclerosis by improving insulin sensitivity, decreasing body fat, and improving liver and heart functions (10, 11, 12).
Diabetes
Animal studies have shown that black pepper can lower blood glucose and fat levels.
Black pepper has also been shown to protect against diabetes-induced oxidative stress and have a somewhat protective effect against diabetes complications (13, 14).
Cayenne and other chili peppers may improve insulin sensitivity, regulate blood glucose levels, and aid in weight loss (10).
Neurological Health & Pain
Animal studies demonstrate that piperine may show neuroprotective effects and modulate the activity of epilepsy, Parkinson’s, and Alzheimer’s disease, depression, as well as improve cognitive functions and relieve pain (3, 15).
Capsaicin from red peppers has also been shown to have pain-relieving properties (16, 17).
Digestive Health
Both black and cayenne peppers are considered to have gastroprotective effects. They enhance the activity of antioxidant enzymes in the mucosal layer of the stomach and intestines and lower mucosal injury (18).
Black pepper has been shown to reduce food transit time and stimulate pancreatic digestive enzymes and bile acids (19, 20). Black pepper has been shown to have hepatoprotective or liver-protective and anti-allergic effects (21).
In animal studies, capsaicin from chili peppers has been shown to inhibit gastric acid secretion and stimulate alkali and mucus secretions, which are beneficial against gastric ulcers (22, 23). However, people with peptic ulcers should avoid consuming black and cayenne peppers if the spices cause dyspepsia or discomfort (24).
Cancer
According to several studies, black and cayenne or chili peppers decrease the risk of lung, liver, colorectal, cervix, and prostate cancers due to their antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and immunomodulatory effects (24). Active components from peppers induce programmed cell death, inhibit the proliferation and migration of cancer cells, as well as sensitize cancers to radio and chemotherapy (25).
References
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34591253/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34383610/
- https://academic.oup.com/jaoac/article/102/2/395/5658185
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32912121/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33732347/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33492139/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22463744/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31856971/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33657876/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29772784/
- https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/8/5/174/htm
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33783751/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4961342/
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S2221169112605243
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26560940/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33276488/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6273518/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20383223/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17987447/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15218978/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32929825/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9403789/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16621751/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/2072799/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27529277/
Infographic
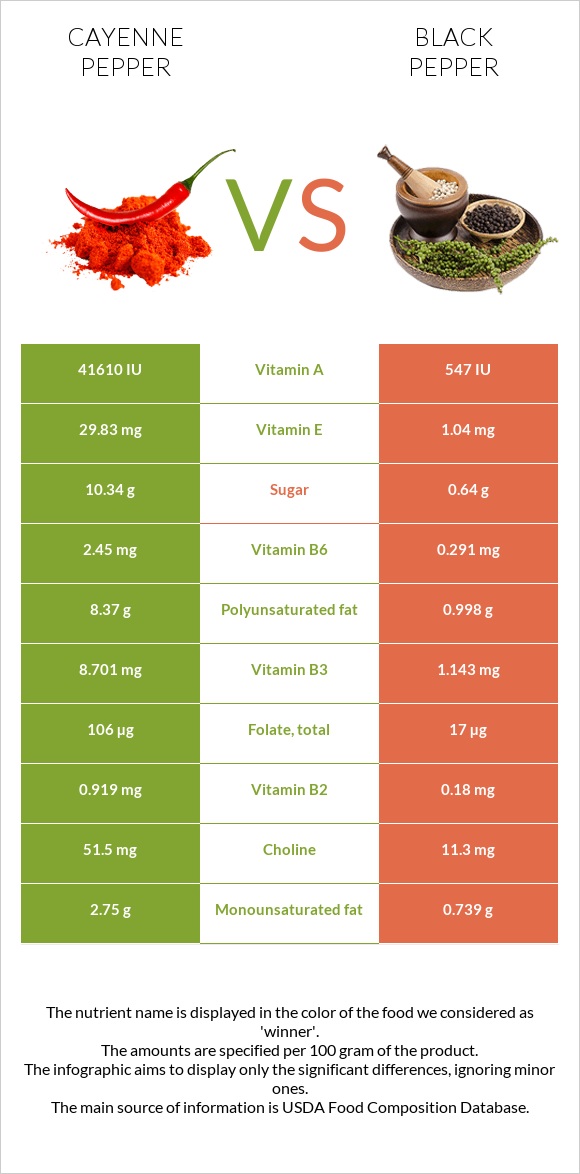
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Manganese | 2mg | 12.753mg | 468% |
| Vitamin A | 2081µg | 27µg | 228% |
| Vitamin E | 29.83mg | 1.04mg | 192% |
| Vitamin B6 | 2.45mg | 0.291mg | 166% |
| Copper | 0.373mg | 1.33mg | 106% |
| Vitamin C | 76.4mg | 0mg | 85% |
| Vitamin K | 80.3µg | 163.7µg | 70% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.919mg | 0.18mg | 57% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 8.37g | 0.998g | 49% |
| Vitamin B3 | 8.701mg | 1.143mg | 47% |
| Calcium | 148mg | 443mg | 30% |
| Vitamin B5 | 1.399mg | 28% | |
| Iron | 7.8mg | 9.71mg | 24% |
| Fats | 17.27g | 3.26g | 22% |
| Folate | 106µg | 17µg | 22% |
| Potassium | 2014mg | 1329mg | 20% |
| Phosphorus | 293mg | 158mg | 19% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.328mg | 0.108mg | 18% |
| Zinc | 2.48mg | 1.19mg | 12% |
| Fiber | 27.2g | 25.3g | 8% |
| Saturated fat | 3.26g | 1.392g | 8% |
| Selenium | 8.8µg | 4.9µg | 7% |
| Choline | 51.5mg | 11.3mg | 7% |
| Magnesium | 152mg | 171mg | 5% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 2.75g | 0.739g | 5% |
| Calories | 318kcal | 251kcal | 3% |
| Protein | 12.01g | 10.39g | 3% |
| Carbs | 56.63g | 63.95g | 2% |
| Net carbs | 29.43g | 38.65g | N/A |
| Sugar | 10.34g | 0.64g | N/A |
| Sodium | 30mg | 20mg | 0% |
| Tryptophan | 0.058mg | 0% | |
| Threonine | 0.244mg | 0% | |
| Isoleucine | 0.366mg | 0% | |
| Leucine | 1.014mg | 0% | |
| Lysine | 0.244mg | 0% | |
| Methionine | 0.096mg | 0% | |
| Phenylalanine | 0.446mg | 0% | |
| Valine | 0.547mg | 0% | |
| Histidine | 0.159mg | 0% | |
| Fructose | 0.23g | 0% | |
| Omega-3 - ALA | 0.152g | N/A |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Cayenne pepper - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/170932/nutrients
- Black pepper - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/170931/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.