Cayenne pepper vs. Chili powder spice — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Chili powder spice and cayenne pepper, both popular spices, offer different nutritional profiles. Chili powder spice is higher in iron, copper, vitamin E, fiber, vitamin K, and selenium. On the other hand, cayenne pepper stands out with more vitamin C, vitamin A, and vitamin B6. Notably, chili powder spice covers daily sodium needs significantly more than cayenne pepper, with a 123% difference, while cayenne pepper contains less sodium. Additionally, chili powder spice has three times more copper.
Table of contents
Introduction
This article contrasts and compares two of the most popular and extensively used spices: chili powder spice and cayenne pepper (a reasonably spicy chili pepper). Topics for comparison are based on dietary differences and health advantages.
What’s The Actual Differences?
Chili powder spice is a complex blend featuring ground-dried chili peppers, herbs like cumin, garlic powder, Mexican oregano, and salt, while cayenne pepper consists solely of ground-dried chili peppers, providing a more concentrated and intense spiciness.
Chili powder blend incorporates diverse elements like cumin, paprika, garlic powder, onion powder, and salt, contributing to its popularity. The blend of spices delivers a well-rounded flavor with moderate heat. Additionally, pure chili powder is made exclusively from dried, finely ground chili peppers, varying in flavor and heat levels depending on the pepper types used.
Classification
Cayenne pepper is a specific chili pepper belonging to the Capsicum genus and the Solanaceae, or nightshade family. On the other hand, chili powder spice is a blend of ground chili peppers and various other spices, and it doesn't belong to a specific botanical genus or family.
Taste and Uses
Ground cayenne pepper and chili powder have distinctive culinary uses in various cuisines and dishes. Cayenne pepper, known for its fiery kick, is versatile, enhancing various recipes, from sauces and soups to seasoning blends. It is a popular ingredient in Mexican, Indian, and Thai cuisine, and it is also used in many American dishes, such as chili and hot sauces. On the other hand, chili powder is a spice blend typical in Latin American dishes such as enchiladas, tacos, stews, and sauces like Chili Con Carne. Whether a subtle kick for Cheesy Zucchini and Chicken "Enchiladas" or a Tex-Mex flair in Instant Pot Tex-Mex Beef Stew, chili powder adds complexity to earthy, savory flavors. While they share some uses, their distinct flavor profiles make them less interchangeable, especially in sweet or milder dishes.
Nutrition
The nutritional infographics in this article are presented for 100g servings of chili powder spice and cayenne pepper. However, spices are not naturally consumed in such large quantities. The average serving size of cayenne is ¼ tsp or 0.5g, and the chili powder spice is 1 tsp or 2.7 g.
Macronutrients and Calories
Chili powder spice and cayenne peppers are nutrient-rich, making them nutrient-dense spices.
Chili powder spice consists of 11% water, and cayenne pepper consists of 8.05% water, making cayenne pepper nutritionally denser.
Macronutrient Comparison
Contains
more
FatsFats
+20.9%
Contains
more
CarbsCarbs
+13.9%
Contains
more
ProteinProtein
+12.1%
Contains
more
WaterWater
+33.5%
Contains
more
OtherOther
+95.5%
Calories
Due to having a 0.5g (cayenne pepper) and 2.7g (chili powder spice) serving size, spices are very low in calories. One serving of chili powder spice provides eight calories, while one serving of cayenne pepper provides two calories.
100g of each spice, chili powder spice provides 282 calories, whereas cayenne pepper provides 318 calories.
Protein
Both spices have almost similar amounts of protein. Chili powder spice contains 1.45 g more protein.
Fats
Cayenne pepper has 3 g more fat than chili powder spice.
The predominant fats in chili powder spice and cayenne pepper are polyunsaturated fatty acids. Trans fats and cholesterol are naturally absent in both spices.
Fat Type Comparison
Contains
less
Sat. FatSaturated fat
-24.5%
Contains
more
Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat
+16.8%
Carbohydrates
Carbs are the main macronutrients in chili powder spice and cayenne peppers, making up over 50% and 57% of the nutrients.
Cayenne spice is somewhat higher in total and net carbs. Chili powder spice contains 14.9g net carbs and 49.7g total carbs, while cayenne pepper contains 29.43g net carbs and 56.63g total carbs.
Fiber
Both spices are rich in dietary fiber. Chili powder spice has more fiber, with 34.8 grams, compared to 27.2 grams in cayenne pepper.
Vitamins
Cayenne pepper is richer in vitamin A, providing 41,610 IU, compared to chili powder spice, with 29,650 IU. Additionally, cayenne pepper has more vitamin C and folate content than chili powder spice. On the other hand, chili powder spice has higher levels of vitamin E (38.14mg), vitamin B3 (11.6mg), vitamin B5 (0.888mg), and vitamin K (105.7 mg) compared to cayenne pepper. Chili powder spice and cayenne pepper have comparable vitamins B1, B2, and B6.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+10814.3%
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+40.3%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+31.2%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+17%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+278.6%
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+27.9%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+33.3%
Contains
more
Vitamin KVitamin K
+31.6%
Minerals
Chili powder spice provides more sodium (2867mg), calcium (330mg), iron (17.3mg), zinc (4.3mg), copper (1mg), and selenium (20.4 mg). On the other hand, cayenne pepper is more abundant in potassium (2014mg).
Both contain almost similar amounts of magnesium, phosphorus, and manganese.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-99%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+17.6%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+123%
Contains
more
IronIron
+121.8%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+168.1%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+73.4%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+131.8%
Oxalates
The oxalate content of chili powder spice is 274mg per 100 grams. Chili powder spice is considered to be high in oxalates. There is currently no available information regarding the oxalate content of cayenne pepper.
Glycemic Index
The glycemic index value of cayenne pepper is 32, and the glycemic index of chili powder spice has not been calculated.
Acidity
Both chili powder spice and cayenne pepper have similar acidity levels, with a PRAL (potential renal acid load) of -31.4, indicating an alkaline nature.
Weight Loss and Diets
Due to their small serving sizes, both spices are considered keto-friendly despite their high carb content.
During the Atkins diet, cayenne pepper can be consumed in moderation. Mediterranean, Dukan, and Paleo diets also allow the consumption of chili powder spice and cayenne peppers. Chili powder spice and cayenne peppers are great for anti-inflammatory diets.
The spices help with weight-loss diets through exact mechanisms. Both spices are rich in capsaicin, which increases satiety, stimulates thermogenesis, and regulates fat metabolism (1,2,3).
Health Benefits
Pain Relief
Although capsaicinoids are found in cayenne pepper and chili powder spice, capsaicin is found most in peppers (4). It attaches itself to pain receptors, rendering them impervious to all types of pain (5). It is essential to remember that the desensitization effect is temporary, as evidenced by a study that found that pain receptors returned three days after stopping capsaicin intake (6).
Cardiovascular Health and Diabetes
Both chili powder spice and cayenne pepper, rich in capsaicin, have been associated with health benefits, particularly in reducing the risk of total and heart disease-related death (7,8). The phytochemicals in chili peppers, including capsaicin, may positively impact metabolic syndrome and atherosclerosis by enhancing insulin sensitivity, reducing body fat, and improving liver and heart functions (9,10,11). Both spices have shown potential for improving insulin sensitivity, managing blood glucose levels, and promoting weight loss, with studies indicating lower blood glucose and insulin levels in individuals consuming cayenne-rich diets (12,13).
Digestive Health
Cayenne peppers and chili powder spice derived from chili peppers offer distinct characteristics and potential health effects. They are recognized for their gastroprotective effects, enhancing antioxidant enzyme activity in the mucosal layer of the stomach and intestines, thereby reducing mucosal injury (14). In animal studies, capsaicin from chili peppers, the substance responsible for their hot flavor, has been shown to stimulate alkali and mucus secretions and inhibit gastric acid secretion, providing benefits against gastric ulcers (15,16). However, individuals with peptic ulcers should exercise caution and avoid cayenne peppers if they experience dyspepsia or discomfort (17). On the other hand, chili peppers, known for their fiery taste due to capsaicin, can cause gastrointestinal distress, including abdominal pain, cramps, and diarrhea. Due to its intense burning sensation, the compound oleoresin capsicum extracted from chili peppers is a crucial ingredient in pepper sprays. While regular exposure to capsaicin may desensitize specific pain neurons over time, individuals with irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) may experience exacerbated symptoms, necessitating moderation in the consumption of chili and other spicy foods (18,19,20).
Cancer
Studies suggest that cayenne or chili peppers may decrease the risk of various cancers, including liver, lung, colorectal, cervix, and prostate, owing to their antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and immunomodulatory effects (21). The active components in peppers have demonstrated the ability to induce programmed cell death, inhibit cancer cellular proliferation and migration, and increase radiotherapy and chemotherapy sensitivity (22). However, caution is warranted as test-tube and animal studies and some human observational studies present conflicting findings. While capsaicin, a plant compound in chili peppers, has shown potential in both increasing and decreasing cancer risk in various studies, observational research has linked chili pepper consumption to an elevated risk of gallbladder and stomach cancers, particularly in some regions like India, where red chili powder is identified as a risk factor for oral and throat cancer (23,24,25,26). Observational studies cannot establish causation, and further research is needed to determine the long-term safety of heavy chili intake or capsaicin supplements.
Sources
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24246368/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8926537/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34383610/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459168/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/7753877/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31856971/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33657876/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29772784/
- https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/8/5/174/htm
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33783751/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29772784/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20383223/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9403789/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16621751/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/2072799/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12809862/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18647268/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24867591/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/2072799/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27529277/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21487045/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12402311/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8116601/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/3112746/
Infographic
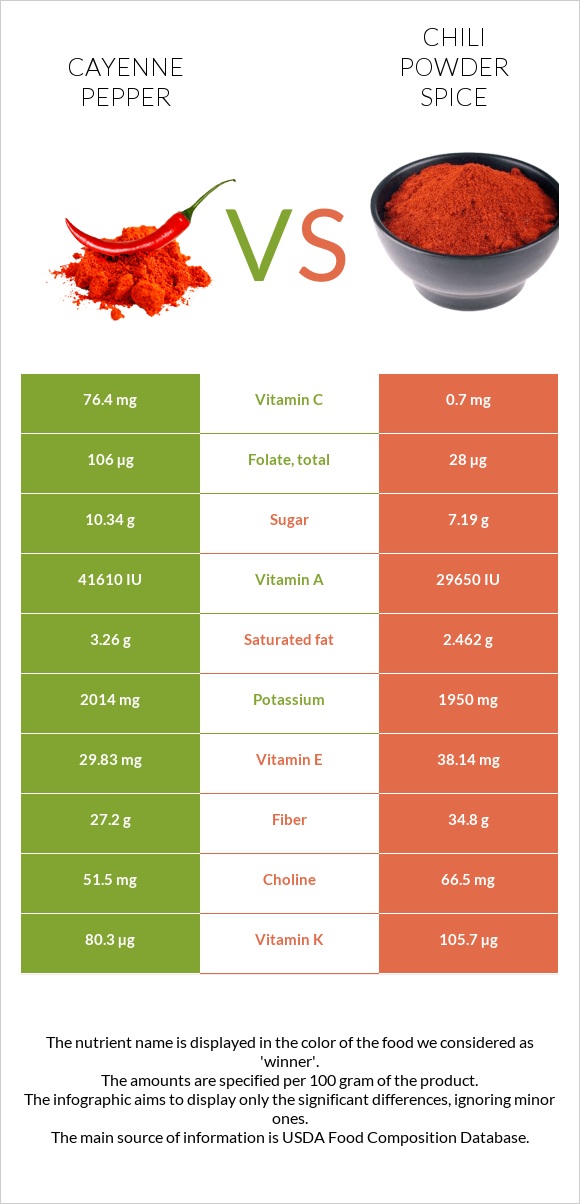
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Sodium | 30mg | 2867mg | 123% |
| Iron | 7.8mg | 17.3mg | 119% |
| Vitamin C | 76.4mg | 0.7mg | 84% |
| Copper | 0.373mg | 1mg | 70% |
| Vitamin A | 2081µg | 1483µg | 66% |
| Vitamin E | 29.83mg | 38.14mg | 55% |
| Fiber | 27.2g | 34.8g | 30% |
| Vitamin B6 | 2.45mg | 2.094mg | 27% |
| Selenium | 8.8µg | 20.4µg | 21% |
| Vitamin K | 80.3µg | 105.7µg | 21% |
| Folate | 106µg | 28µg | 20% |
| Calcium | 148mg | 330mg | 18% |
| Vitamin B3 | 8.701mg | 11.6mg | 18% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.888mg | 18% | |
| Zinc | 2.48mg | 4.3mg | 17% |
| Manganese | 2mg | 1.7mg | 13% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.328mg | 0.25mg | 7% |
| Fats | 17.27g | 14.28g | 5% |
| Fructose | 4.29g | 5% | |
| Saturated fat | 3.26g | 2.462g | 4% |
| Protein | 12.01g | 13.46g | 3% |
| Choline | 51.5mg | 66.5mg | 3% |
| Calories | 318kcal | 282kcal | 2% |
| Carbs | 56.63g | 49.7g | 2% |
| Potassium | 2014mg | 1950mg | 2% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.919mg | 0.94mg | 2% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 8.37g | 8.006g | 2% |
| Magnesium | 152mg | 149mg | 1% |
| Phosphorus | 293mg | 300mg | 1% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 2.75g | 3.211g | 1% |
| Protein per 100 calories | 3.7767295597484276g | 4.773049645390071g | N/A |
| Calories per 10 g protein | 264.77935054121565kcal | 209.50965824665676kcal | N/A |
| Net carbs | 29.43g | 14.9g | N/A |
| Sugar | 10.34g | 7.19g | N/A |
| Tryptophan | 0.07mg | 0% | |
| Threonine | 0.27mg | 0% | |
| Isoleucine | 0.39mg | 0% | |
| Leucine | 0.63mg | 0% | |
| Lysine | 0.36mg | 0% | |
| Methionine | 0.13mg | 0% | |
| Phenylalanine | 0.37mg | 0% | |
| Valine | 0.54mg | 0% | |
| Histidine | 0.18mg | 0% | |
| Omega-3 - ALA | 0.519g | N/A | |
| Omega-6 - Gamma-linoleic acid | 0.014g | N/A |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Cayenne pepper - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/170932/nutrients
- Chili powder spice - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/171319/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.