Cayenne pepper vs. Chili pepper — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Cayenne pepper provides more vitamin A, vitamin B1, fiber, vitamin B3, iron, and zinc.
On the other hand, chili pepper contains more vitamin C and less sodium.
Introduction
This article will show the main differences in the nutrition and health impact of cayenne pepper (1) and chili pepper (2).
Actual differences
Cayenne pepper is chili pepper with a moderate hot flavor. Chili pepper is a variety of pepper from the Capsicum family. Chili pepper is usually hotter than cayenne pepper. They also differ in flavor: cayenne pepper is earthy and spicy, while chili pepper is milder. Chili pepper can have green varieties, while cayenne pepper is only red.
Nutrition
Calories
Cayenne pepper is nearly eight times higher in calories than chili pepper. Cayenne pepper contains 318 calories, while chili pepper provides 40 calories per 100g. Cayenne pepper is considered a high-calorie food, but because people consume it in a tiny amount, calories can be neglected.
Fats
Cayenne pepper has 17.3g of fats per 100g, while the same amount of chili pepper provides less than one gram.
Both cayenne pepper and chili pepper do not provide cholesterol.
Carbs
Cayenne pepper contains 56.6g of carbs per 100g, whereas chili pepper provides only 8.8g of carbs. Once consumed in small amounts, cayenne pepper and chili pepper are not considered foods with high carbohydrate amounts.
Fiber
Cayenne pepper is richer in fiber: 100g contains 27.2g of fiber, while the same amount of chili pepper has only 1.5g of fiber.
Minerals
Cayenne pepper contains more calcium, phosphorus, iron, magnesium, potassium, zinc, and copper.
Chili pepper contains less sodium.
You can check the mineral comparison chart below.
Mineral Comparison
| Contains more MagnesiumMagnesium | +560.9% |
| Contains more CalciumCalcium | +957.1% |
| Contains more PotassiumPotassium | +525.5% |
| Contains more IronIron | +657.3% |
| Contains more CopperCopper | +189.1% |
| Contains more ZincZinc | +853.8% |
| Contains more PhosphorusPhosphorus | +581.4% |
| Contains more ManganeseManganese | +969.5% |
| Contains more SeleniumSelenium | +1660% |
| Contains less SodiumSodium | -70% |
Vitamins
Cayenne pepper is significantly higher in vitamins A, E, K, B1, B2, B3, and B6.
Chili pepper is higher in vitamin C. It provides two times more vitamin C than cayenne pepper.
Vitamin Comparison
| Contains more Vitamin AVitamin A | +4235.4% |
| Contains more Vitamin EVitamin E | +4223.2% |
| Contains more Vitamin B1Vitamin B1 | +355.6% |
| Contains more Vitamin B2Vitamin B2 | +968.6% |
| Contains more Vitamin B3Vitamin B3 | +599.4% |
| Contains more Vitamin B6Vitamin B6 | +384.2% |
| Contains more Vitamin KVitamin K | +473.6% |
| Contains more FolateFolate | +360.9% |
| Contains more Vitamin CVitamin C | +88.1% |
Health impact
Pain relief
Cayenne pepper and chili pepper contain capsaicinoids, but capsaicin is the most abundant in peppers (3). It binds with pain receptors making them insensitive to any form of pain (4). You should consider that the desensitization effect is not permanent: according to a study, pain receptors were reversed three days after capsaicin consumption stopped (5).
Antioxidants
Both cayenne pepper and chili pepper are rich in antioxidants. These are compounds fighting against oxidative stress, cancer, and inflammation.
Cayenne pepper is rich in flavonoids, antioxidants that may have anticancer effects and promote heart health (6) (7).
Chili pepper contains capsanthin - the primary carotenoid in them. It has powerful anti-cancer properties. It also provides ferulic acid, which may help protect against various diseases.
References
- https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/170932/nutrients
- https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/170106/nutrients
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459168/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5326624/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/7753877/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7602036/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6250988/
Infographic
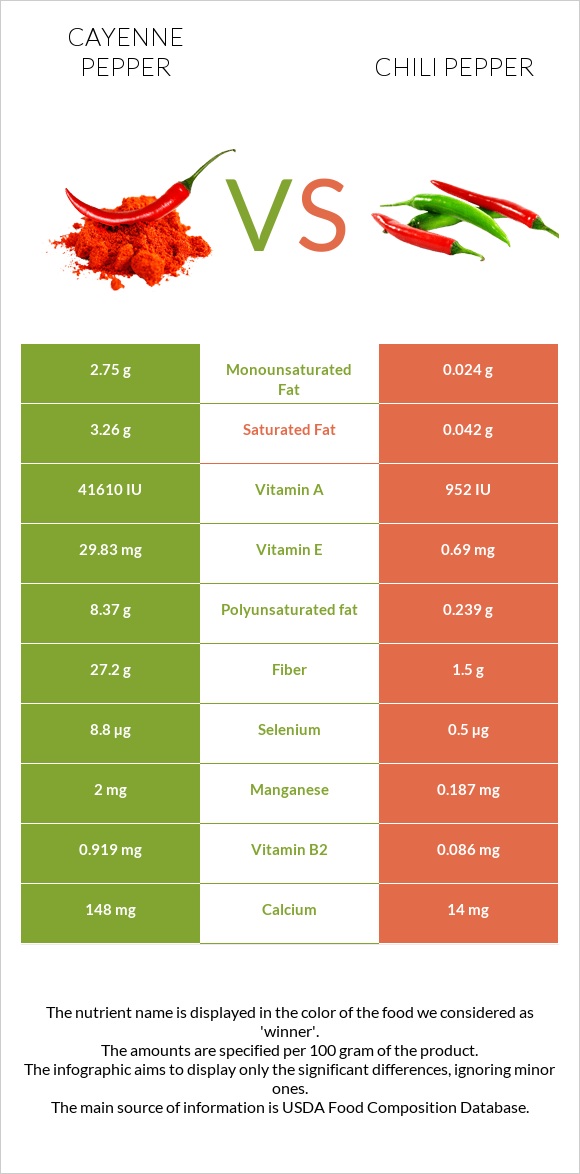
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Vitamin A | 2081µg | 48µg | 226% |
| Vitamin E | 29.83mg | 0.69mg | 194% |
| Vitamin B6 | 2.45mg | 0.506mg | 150% |
| Fiber | 27.2g | 1.5g | 103% |
| Iron | 7.8mg | 1.03mg | 85% |
| Manganese | 2mg | 0.187mg | 79% |
| Vitamin C | 76.4mg | 143.7mg | 75% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.919mg | 0.086mg | 64% |
| Vitamin K | 80.3µg | 14µg | 55% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 8.37g | 0.239g | 54% |
| Potassium | 2014mg | 322mg | 50% |
| Vitamin B3 | 8.701mg | 1.244mg | 47% |
| Phosphorus | 293mg | 43mg | 36% |
| Magnesium | 152mg | 23mg | 31% |
| Copper | 0.373mg | 0.129mg | 27% |
| Fats | 17.27g | 0.44g | 26% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.328mg | 0.072mg | 21% |
| Folate | 106µg | 23µg | 21% |
| Protein | 12.01g | 1.87g | 20% |
| Zinc | 2.48mg | 0.26mg | 20% |
| Carbs | 56.63g | 8.81g | 16% |
| Selenium | 8.8µg | 0.5µg | 15% |
| Saturated fat | 3.26g | 0.042g | 15% |
| Calories | 318kcal | 40kcal | 14% |
| Calcium | 148mg | 14mg | 13% |
| Choline | 51.5mg | 10.9mg | 7% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 2.75g | 0.024g | 7% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.201mg | 4% | |
| Sodium | 30mg | 9mg | 1% |
| Net carbs | 29.43g | 7.31g | N/A |
| Sugar | 10.34g | 5.3g | N/A |
| Tryptophan | 0.026mg | 0% | |
| Threonine | 0.074mg | 0% | |
| Isoleucine | 0.065mg | 0% | |
| Leucine | 0.105mg | 0% | |
| Lysine | 0.089mg | 0% | |
| Methionine | 0.024mg | 0% | |
| Phenylalanine | 0.062mg | 0% | |
| Valine | 0.084mg | 0% | |
| Histidine | 0.041mg | 0% |
Macronutrient Comparison
| Contains more ProteinProtein | +542.2% |
| Contains more FatsFats | +3825% |
| Contains more CarbsCarbs | +542.8% |
| Contains more OtherOther | +602.3% |
| Contains more WaterWater | +993.4% |
Fat Type Comparison
| Contains more Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat | +11358.3% |
| Contains more Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat | +3402.1% |
| Contains less Sat. FatSaturated fat | -98.7% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Cayenne pepper - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/170932/nutrients
- Chili pepper - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/170106/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.