Sunflower oil vs. Mustard oil — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Sunflower oil has a higher polyunsaturated fat content, but mustard oil has a lower saturated fat content and a higher monounsaturated fat content. Sunflower oil is higher in vitamins E and K than mustard oil.
Introduction
The seeds of the Helianthus annuus plant are pressed to produce sunflower oil.
Mustard oil is made from the seeds of the mustard plant, whereas mustard essential oil is obtained by grinding the seeds, blending them with water, and then steam distilling them. The difference between them will be discussed in this article.
Taste, Use, and Cooking
Mustard oil is typically yellow to dark brown with an intense aroma and a robust and spicy flavor. It may appear cloudy or opaque due to natural compounds called glucosinolates, which can settle to the bottom of the bottle. On the other hand, sunflower oil is pale yellow and has a mild, neutral flavor. It is typically straightforward and transparent, although some varieties may have a slightly golden hue. These oils can be used in the kitchen, skin, hair products, perfumes, candles, paint, lubricants, biofuels, and detergents.
Most of the fats in pure mustard oil are monounsaturated, which are more heat-resistant than polyunsaturated fats and have a high smoke point. Sunflower oil also has a high smoke point—the temperature at which it begins to smoke and degrade—it is frequently used in high-heat cooking. According to research, compared to other oils, sunflower oil releases the highest amounts of harmful aldehyde fumes when heated to a high temperature for an extended length of time.
Varieties
Mustard essential oil, also known as volatile mustard oil, is safe to use in food or as a flavoring. Although pure mustard oil is not permitted as a vegetable oil in the United States, Canada, or Europe, it is frequently used topically as a massage oil, skin serum, and hair treatment. Sunflower oil varieties are high-oleic, mid-oleic (NuSun), and linoleic.
Nutrition
As vegetable oils are fats derived from seeds or plants, mustard and sunflower oils naturally have the same nutritional profile as other oils. The nutritional values of sunflower oil and mustard oil are presented in this article.
Macronutrients and Calories
Both oils have no protein or carbohydrates and are composed entirely of fat. They also have no water or other macronutrients.
Macronutrient Comparison
Calories
Both mustard oil and sunflower oil have the same calories, 884 kcal per 100 g.
Fats
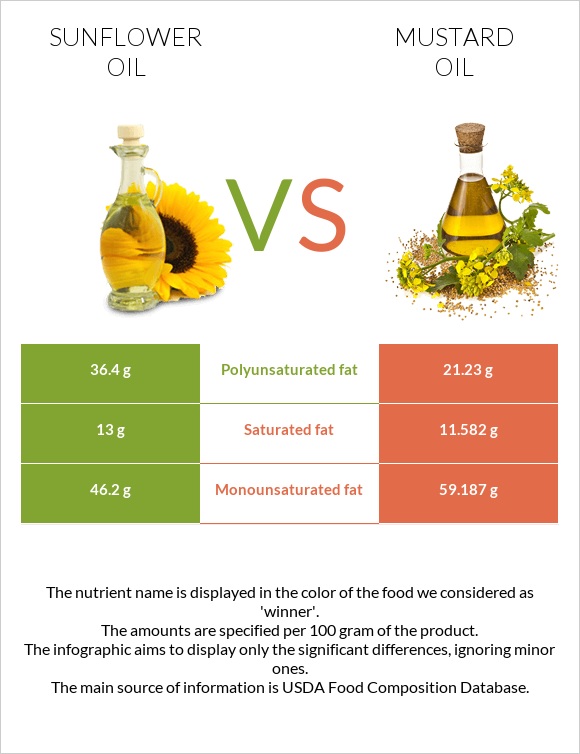
Mustard oil has a lower proportion of saturated fat (by 10.9%) and a higher proportion of monounsaturated fat (by 28.1%) compared to sunflower oil.
On the other hand, sunflower oil has a higher proportion of polyunsaturated fat (71%) than mustard oil. It's worth noting that the type of fat present in each oil may have different health implications, and a balanced intake of different kinds of fat is recommended for overall health.
Sunflower oil that has been partially hydrogenated has 13% saturated fat, 36.4% polyunsaturated fat, and 46.2% monounsaturated fat. In comparison, 83.7% of the fatty acids in high-oleic sunflower oil are monounsaturated.
Fat Type Comparison
Contains
more
Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat
+71.5%
Contains
less
Sat. FatSaturated fat
-10.9%
Contains
more
Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat
+28.1%
Vitamins
Sunflower oil is richer in vitamin E (822%) and vitamin K (14%), compared to mustard oil, which has vitamin E in the form of α-tocopherols(1).
However, both oils do not contain significant amounts of other vitamins. It's important to note that oils are not a primary source of vitamins, and a balanced diet consisting of various nutrient-dense foods is recommended for meeting daily vitamin requirements.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin KVitamin K
+∞%
Minerals
Minerals are not found primarily in oils.
Mineral Comparison
Glycemic Index
Neither oil contains carbohydrates, so it has no glycemic index.
Acidity
Based on the potential renal acid load (PRAL), both oils' acidity equals 0.
Weight Loss and Diets
Although they have a lot of calories, mustard oil and sunflower oil can still be used in some diets. Sunflower oil is a popular choice for cooking and is suitable for many diets, such as keto, DASH, Mediterranean, vegan, vegetarian, pescatarian, and low-carb diets, like mustard oil. However, it is not recommended for diets that restrict fat intake, such as the Dukan diet or low-fat, low-calorie diets. Additionally, unlike mustard oil, sunflower oil is not known for its anti-inflammatory properties (2).
Health Impact
Both oils have health benefits and risks. It's important to consume both oils in moderation as part of a balanced diet and to consider individual health factors and nutritional needs when choosing which oil to use.
Cardiovascular Health
Mustard oil has been shown to have cardiovascular benefits due to its high content of monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fatty acids, including omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids (3).
These fatty acids can help lower LDL, or "bad" cholesterol levels, reduce inflammation, and decrease the risk of heart disease (4). However, it also contains erucic acid, which, in high doses, has been linked to heart problems, so it's essential to consume mustard oil in moderation (5).
On the other hand, sunflower oil is rich in polyunsaturated fatty acids, including omega-6 fatty acids (6). While omega-6 fatty acids are essential to health, excessive intake can lead to inflammation and increase the risk of chronic diseases, including cardiovascular disease (7).
It's essential to consider individual health factors and nutritional needs when choosing which oil to use.
Diabetes
Mustard and sunflower oils have been studied for their potential impact on diabetes. Some studies have suggested that consuming mustard oil may improve blood sugar control and insulin sensitivity in people with type 2 diabetes (8). This may be due to compounds in mustard oil, such as alpha-linolenic acid, which have been shown to have beneficial effects on blood sugar levels (9). Erucic acid-rich yellow mustard oil may have the potential as a dietary supplement for people with type 2 diabetes. However, more research is needed to confirm these findings and determine the optimal dosage and duration of supplementation (10).
Similarly, sunflower oil may improve insulin sensitivity and blood sugar control in people with type 2 diabetes. This may be due to compounds in sunflower oil, such as polyunsaturated fatty acids and vitamin E, which have been shown to benefit blood sugar levels (11).
Cancer
Studies suggest that high consumption of omega-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) found in sunflower oil may be associated with increased cancer risk. Still, a direct causal relationship has not been established (12). Heating sunflower oil to high temperatures can produce toxic compounds called aldehydes, which are linked to cancer and other health problems. Still, the effects of consuming unheated sunflower oil have not been investigated (13). In contrast to sunflower oil, some studies have suggested that mustard oil may have a health advantage by lowering cancer risk. However, it is crucial to emphasize that the evidence is still limited and not conclusive. According to certain studies, mustard oil includes chemicals such as allyl isothiocyanate, which has been demonstrated in laboratory trials to have anti-cancer potential (14).
Sources
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/336118318_Medicinal_Qualities_of_Mustard_Oil_and_Its_Role_in_Human_Health_against_Chronic_Diseases_A_Review.
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28900017/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34820730/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31979308/
- https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/cms_ia/importalert_89.htm
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32623461/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12442909/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33013020/
- https://www.sjkdt.org/article.asp?issn=1319-2442;year=2012;volume=23;issue=3;spage=500;epage=506;aulast=Tayyebi-Khosroshahi
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33494317/
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0899900700004688 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10220204/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25908304/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4106693/
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-018-19353-7#Sec22
Infographic
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Vitamin E | 41.08mg | 274% | |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 36.4g | 21.23g | 101% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 46.2g | 59.187g | 32% |
| Saturated fat | 13g | 11.582g | 6% |
| Vitamin K | 5.4µg | 5% | |
| Calories | 884kcal | 884kcal | 0% |
| Fats | 100g | 100g | 0% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Sunflower oil - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/172328/nutrients
- Mustard oil - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/172337/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.



