Sunflower seeds vs. Cashew — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Both sunflower seeds and cashews are packed with compounds beneficial for health. However, they differ in the density of nutrients they provide. Sunflower seeds are richer in fats, proteins, and vitamins. Cashews provide 10.2g of carbs and are richer in vitamin K and iron.
Introduction
Cashew is a kidney-shaped seed of the cashew tree - a tropical tree growing in warm climates across the world. Sunflower seeds are a very popular nutrient-dense snack. This article compares the nutritional values and health impacts of raw cashews (1) and dried sunflower seeds (2).
Nutrition
Fats
Both cashew and sunflower seeds are rich in fats. However, sunflower seeds are higher in fats, than cashews: 100g serving of them provides 51.5g of fats compared to 43.9g in the same amount of cashews. These foods are rich in unsaturated fats. Sunflower seeds are especially high in linoleic acid, which is linked with reducing LDL cholesterol (3).
Protein
Sunflower seeds are higher in proteins than cashews. 100g of sunflower seeds contains 20.8g of proteins compared to 17.2g in the same serving of cashews.
One of the main proteins provided by cashews is glutelin (4), which is a common storage protein in plant seeds.
Carbs
Cashews are richer in carbs than sunflower seeds. A 100g serving of cashews provides 30.2g of carbs, while the same amount of sunflower seeds contains 20g.
Sunflower seeds are nearly three times rich in fiber. They provide 9g of fiber compared to 3g in cashews. Therefore, the net carb content in cashews is higher.
It is important to mention that cashews contain 23.5g of starch, while sunflower seeds do not contain any.
Calories
Both cashews and sunflower seeds are considered to be high-calorie foods. However, in terms of calories, sunflower seeds (584calories per 100g) are a little bit higher than cashews (553calories per 100g).
Minerals
Cashews and sunflower seeds are extremely rich in minerals. They cover the daily needs for nearly all the minerals, except sodium and calcium.
Sunflower seeds contain more calcium, magnesium, and phosphorus. They have nearly two times more calcium than cashews.
Cashews provide more zinc, copper, and iron.
Mineral Comparison
| Contains more MagnesiumMagnesium | +11.3% |
| Contains more CalciumCalcium | +110.8% |
| Contains more PhosphorusPhosphorus | +11.3% |
| Contains less SodiumSodium | -25% |
| Contains more ManganeseManganese | +17.8% |
| Contains more SeleniumSelenium | +166.3% |
| Contains more IronIron | +27.2% |
| Contains more CopperCopper | +21.9% |
| Contains more ZincZinc | +15.6% |
Vitamins
The winner in this section is sunflower seeds. They provide more amounts of all the vitamins than cashews. They are richer in vitamins C, E, and A. They contain more B complex vitamins.
Cashews are richer only in vitamin K. They contain 34 micrograms of vitamin K, while sunflower seeds do not have any.
Vitamin Comparison
| Contains more Vitamin CVitamin C | +180% |
| Contains more Vitamin AVitamin A | +∞% |
| Contains more Vitamin EVitamin E | +3807.8% |
| Contains more Vitamin B1Vitamin B1 | +249.9% |
| Contains more Vitamin B2Vitamin B2 | +512.1% |
| Contains more Vitamin B3Vitamin B3 | +684.8% |
| Contains more Vitamin B5Vitamin B5 | +30.8% |
| Contains more Vitamin B6Vitamin B6 | +222.5% |
| Contains more FolateFolate | +808% |
| Contains more Vitamin KVitamin K | +∞% |
Health impact
Benefits
Cardiovascular health
Nuts, such as cashews, promote cardiovascular health (5). Sunflower seeds also provide a lot of chemicals that are good for the heart. However, these foods differ in the compounds they provide for cardiovascular health.
A study (6) shows that people who get 10% of the daily calories from cashews had lower LDL cholesterol to HDL cholesterol ratio than those who did not eat cashews. Lower this ratio less risk of the development of cardiovascular disease.
Sunflower seeds are rich in magnesium and linoleic acid (7) (8). Both are used in your organism to relax blood vessels and lower blood pressure (9).
Diabetes
Both sunflower seeds and cashews are suitable for people with diabetes, but they contain different chemicals which help control blood sugar levels.
Sunflower seeds provide an antioxidant linked with glucose metabolism (10). That chemical is chlorogenic acid. One of the studies shows that people who consume sunflower seeds regularly may reduce blood sugar levels by 10% in six months (9).
Studies show that consuming cashews helps control insulin levels (6). Also, cashews contain a notable amount of fiber that protects the organism against type 2 diabetes (11).
Downsides
Despite all the benefits they provide, cashews and sunflower seeds can be harmful too.
Roasted or salted cashews may contain high amounts of salt and oils. Also, cashews contain phytates which make absorption of vitamins and minerals difficult. They can be allergic to people who are sensitive to tree nuts.
Sunflower seeds contain high levels of cadmium, a metal that can harm kidneys. They are prepared with the sprouting method, which is a good living condition for harmful bacteria, such as Salmonella (12). There are reports of fever, skin rashes, and anaphylactic reactions linked with the consumption of sunflower seeds too.
References
- https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/170162/nutrients
- https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/170562/nutrients
- https://www.hsph.harvard.edu/nutritionsource/2014/11/05/dietary-linoleic-acid-and-risk-of-coronary-heart-disease/#:~:text=Instead%2C%20linoleic%20acid%20itself%20plays,insulin%20sensitivity%20and%20blood%20pressure.
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29439533/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5762129/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6408729/
- https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11032-016-0527-2
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30218979/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24959542/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30249058/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29378044/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29513105/
Infographic
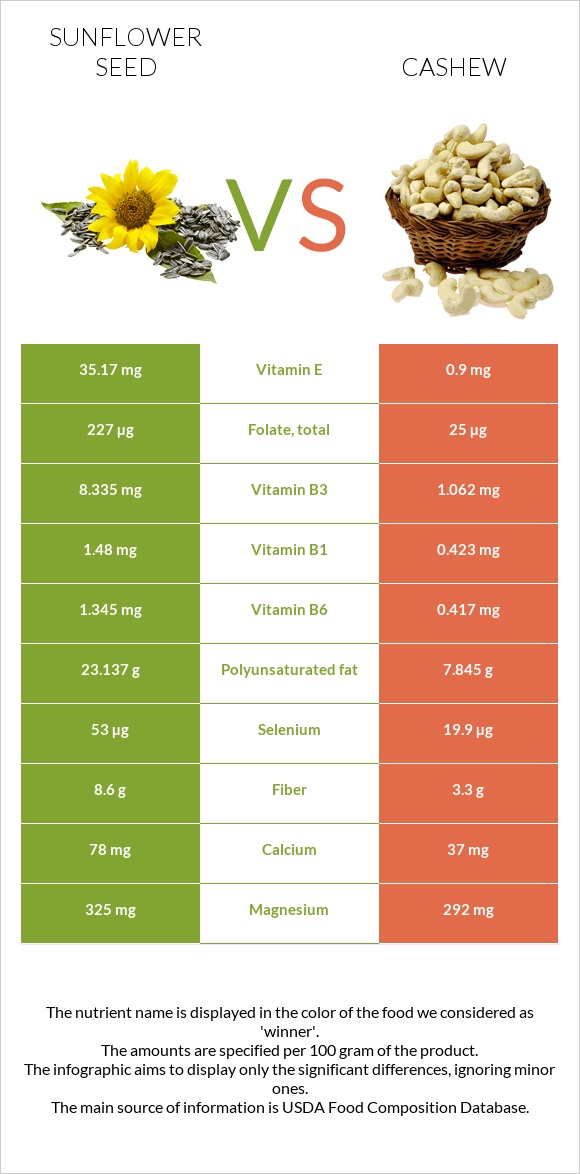
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Vitamin E | 35.17mg | 0.9mg | 228% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 23.137g | 7.845g | 102% |
| Vitamin B1 | 1.48mg | 0.423mg | 88% |
| Vitamin B6 | 1.345mg | 0.417mg | 71% |
| Selenium | 53µg | 19.9µg | 60% |
| Folate | 227µg | 25µg | 51% |
| Vitamin B3 | 8.335mg | 1.062mg | 45% |
| Copper | 1.8mg | 2.195mg | 44% |
| Vitamin K | 0µg | 34.1µg | 28% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.355mg | 0.058mg | 23% |
| Fiber | 8.6g | 3.3g | 21% |
| Iron | 5.25mg | 6.68mg | 18% |
| Saturated fat | 4.455g | 7.783g | 15% |
| Manganese | 1.95mg | 1.655mg | 13% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 18.528g | 23.797g | 13% |
| Fats | 51.46g | 43.85g | 12% |
| Starch | 23.49g | 10% | |
| Phosphorus | 660mg | 593mg | 10% |
| Choline | 55.1mg | 10% | |
| Magnesium | 325mg | 292mg | 8% |
| Zinc | 5mg | 5.78mg | 7% |
| Protein | 20.78g | 18.22g | 5% |
| Vitamin B5 | 1.13mg | 0.864mg | 5% |
| Calcium | 78mg | 37mg | 4% |
| Carbs | 20g | 30.19g | 3% |
| Calories | 584kcal | 553kcal | 2% |
| Vitamin C | 1.4mg | 0.5mg | 1% |
| Net carbs | 11.4g | 26.89g | N/A |
| Potassium | 645mg | 660mg | 0% |
| Sugar | 2.62g | 5.91g | N/A |
| Sodium | 9mg | 12mg | 0% |
| Vitamin A | 3µg | 0µg | 0% |
| Tryptophan | 0.348mg | 0.287mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 0.928mg | 0.688mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 1.139mg | 0.789mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 1.659mg | 1.472mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 0.937mg | 0.928mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.494mg | 0.362mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 1.169mg | 0.951mg | 0% |
| Valine | 1.315mg | 1.094mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.632mg | 0.456mg | 0% |
| Fructose | 0.05g | 0% | |
| Omega-3 - EPA | 0.014g | 0g | N/A |
Macronutrient Comparison
| Contains more ProteinProtein | +14.1% |
| Contains more FatsFats | +17.4% |
| Contains more OtherOther | +19.3% |
| Contains more CarbsCarbs | +51% |
Fat Type Comparison
| Contains less Sat. FatSaturated fat | -42.8% |
| Contains more Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat | +194.9% |
| Contains more Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat | +28.4% |
Carbohydrate type comparison
| Contains more StarchStarch | +∞% |
| Contains more SucroseSucrose | +132.4% |
| Contains more GlucoseGlucose | +∞% |
| Contains more FructoseFructose | +∞% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Sunflower seeds - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/170562/nutrients
- Cashew - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/170162/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.