Tomato vs. Persimmon — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
While tomatoes are higher in copper, magnesium, and zinc, persimmons are a good source of calcium, iron, potassium, and vitamin C. Tomatoes are relatively richer in vitamins.
Tomatoes also are slightly higher in protein, while persimmons are richer in carbs and fats. Persimmons also contain more calories, less sodium, and less sugar.
Introduction
Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) is a flowering plant of the nightshade family. Tomatoes and persimmons are technically berries. The commercial persimmon fruit comes from the Ebenaceae family plant Diospyros kaki L.
Varieties
There are around 7,500 different tomato varieties grown for various uses.
The main categories for categorizing tomato varieties are based on shape and size.
Unlike tomatoes, there are two main types of persimmons - astringent and non-astringent. Astringent varieties contain more tannin content in comparison to non-astringent.
Flavor
The flavor of tomatoes is juicy and refreshing, with a hint of sweetness and tang.
Overall, persimmons have a sweet, rich taste with a slight hint of spiciness and a subtle astringency. Astringent persimmons have a sweeter, richer flavor, while non-astringent persimmons have a slightly more tart taste.
Nutrition
In this part of the article, we will compare the nutritional information of tomatoes and persimmons, focusing on the differences.
Macronutrients and Calories
Tomato contains slightly more proteins. Tomato has about 94.5% water, whereas persimmon contains 64.5% water. On the other hand, persimmons contain more carbs and fats.
Macronutrient Comparison
Contains
more
WaterWater
+46.8%
Contains
more
FatsFats
+100%
Contains
more
CarbsCarbs
+761.2%
Contains
more
OtherOther
+76.5%
Calories
A hundred grams of tomato contains 18 calories, whereas the same amount of persimmon contains 127 calories.
Protein
The amount of protein in both is low. 100g of tomatoes contains 0.88g of protein, and the same amount of persimmons contains 0.8g.
Fats
A 100g tomato contains 0.2g of fat, while a 100g of persimmon contains 0.4g. Both do not contain trans fats.
Tomatoes and persimmons naturally contain no cholesterol.
Carbohydrates
Persimmons contain a significantly higher level of carbohydrates due to their net carbs content. Persimmon contains 33.5g net carbs, while tomato contains only 2.69g.
Aside from net carbs, the main carbohydrates found in tomatoes are dietary fiber, fructose, and glucose.
Vitamins
Tomatoes are relatively richer in vitamins. Tomatoes include several B-group vitamins, including vitamins B1, B3, B5, and B6, and folate.
Tomatoes also contain small amounts of vitamin A and vitamin K.
Persimmons, on the other hand, are a significant source of vitamin C. They have five times more vitamin C content than tomatoes.
Both of them are absent in vitamin D and vitamin B12.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin KVitamin K
+∞%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+381.8%
Minerals
Tomatoes are higher in zinc, magnesium, copper, and choline.
At the same time, persimmons contain more significant amounts of calcium, iron, and potassium.
Both have a low amount of sodium, although persimmons have a lower sodium content than tomatoes.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+∞%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+∞%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+∞%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+∞%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+170%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+30.8%
Contains
more
IronIron
+825.9%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-80%
Phytochemicals
One of the most important phytochemicals found in tomatoes is lycopene, which is a red carotenoid pigment. 100g of tomatoes contain 12 mg lycopene(1).
Bioactive compounds found in persimmon include proanthocyanidins, flavonoids, tannins, polyphenols, and carotenoids. Tannins are one of the most significant phytochemicals in persimmons(2).
Both lycopene and tannin have antioxidant effects(1)(3).
Glycemic Index
Tomato has a glycemic index of 23, whereas persimmon has a glycemic index of 61.
So tomato is classified as a low glycemic index food, whereas persimmon is a medium glycemic food.
Glycemic Load
The glycemic load of tomatoes is equal to 1. The glycemic load of persimmon is equal to 5.
As we can see, persimmons tend to have a higher glycemic load than tomatoes. However, the glycemic load of both tomato and persimmon falls in the low category.
Insulin Index
There are no specific insulin index values for tomatoes. The insulin index of persimmon is 47.
Acidity
Persimmon ranges from 4.42 to 4.70 (4). Tomato acidity has been determined to be -4.1 based on the PRAL, making it alkaline. Tomatoes have a pH of 4.3-4.9. Persimmon has an alkaline PRAL of -5.5.
Weight Loss & Diets
Tomatoes are low in sugar, low in carbs, and practically fat-free. That makes them an excellent choice for people following a keto diet. In contrast, persimmon contains more carbs and is not a good option for this type of diet.
As tomatoes contain fewer carbs than persimmons, they are more suitable for the Atkins diet, though you can consume persimmons in moderate amounts.
While tomatoes are allowed to your Dukan diet from the Cruise phase, you can only add persimmons during the Consolidation phase in moderation amounts.
Both tomatoes and persimmons are recommended in the DASH diet.
Tomatoes and persimmons are an excellent choice for the Paleo diet.
Moreover, both are suitable for vegan, vegetarian, and pescetarian diets.
Health Benefits
In this part, we will compare the health benefits of tomatoes and persimmons, focusing on the differences and similarities.
Cardiovascular Health
There is Chinese literature on the use of dietary therapy to manage hypertension. Both of these products are on this food therapy list (5).
According to studies, tomato and persimmon consumption may reduce LDL (bad cholesterol) levels in the blood. In addition, persimmon may inhibit HMG-CoA reductase activity, similar to antihyperlipidemic drugs (statins) (2.6.7).
Both tomatoes and persimmons may decrease the risk of platelet aggregation and lower the risk of cardiovascular disease (3.8).
Diabetes
Persimmon peel, rich in antioxidants and dietary fiber and has anti-diabetic effects, could be used as a nutritional supplement to help with diabetes complications and hyperglycemia(9).
Consuming lycopene, which contains in tomatoes, on the other hand, may help reduce the risk of obesity and diabetes due to their anti-inflammatory and antioxidant characteristics, according to research. Furthermore, lycopene effectively manages diabetic neuropathy, nephropathy, and other complications(10).
Cancer
As mentioned above, tomatoes contain lycopene. Lycopene has been suggested as a potential cancer preventive agent, notably for prostate cancer(1).
Persimmons, conversely, are thought to be beneficial in treating prostate and breast cancers, oral carcinoma cells, human lymphoid leukemia cells, and female precancerous colon polyps(9).
Nervous system
Overall, both foods have a neuroprotective effect.
Bioactive tomato constituents, such as polyphenols and carotenoids, play a protective modulator role in the pathogenetic mechanisms, cognitive symptoms, and behavioral manifestations of Alzheimer's disease(11).
The other review describes the importance of tannin as an essential compound against Alzheimer's disease(12).
Sources
- https://www.journal-of-agroalimentary.ro/admin/articole/84481L12_Liana_Alda_Vol.4_540-542.pdf
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4817420/
- https://www.torrossa.com/en/resources/an/2209326#
- https://www.clemson.edu/extension/food/food2market/documents/ph_of_common_foods.pdf
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27852126/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12587984/
- https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10068-017-0031-4
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28129549/
- https://www.hindawi.com/journals/jchem/2016/3424025/
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1043661820312743
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33577362/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28176625/
Infographic
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
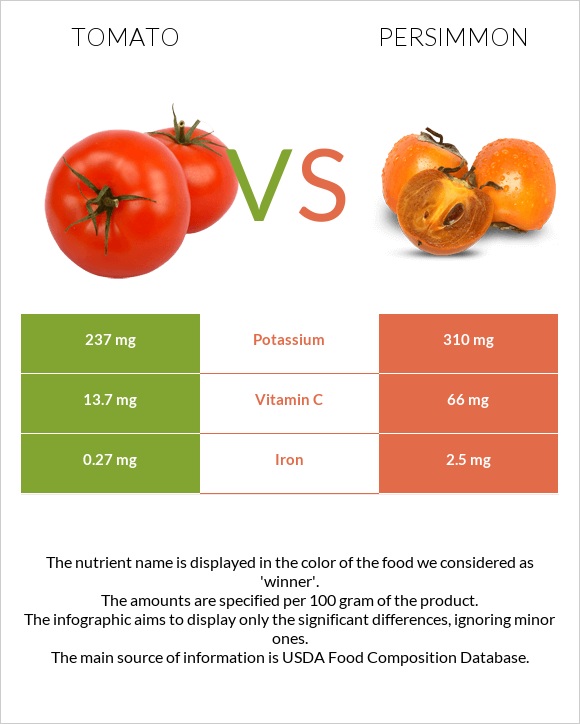
| Vitamin C | 13.7mg | 66mg | 58% |
| Iron | 0.27mg | 2.5mg | 28% |
| Carbs | 3.89g | 33.5g | 10% |
| Copper | 0.059mg | 7% | |
| Vitamin K | 7.9µg | 7% | |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.08mg | 6% | |
| Calories | 18kcal | 127kcal | 5% |
| Fiber | 1.2g | 5% | |
| Vitamin A | 42µg | 5% | |
| Manganese | 0.114mg | 5% | |
| Vitamin E | 0.54mg | 4% | |
| Vitamin B3 | 0.594mg | 4% | |
| Folate | 15µg | 4% | |
| Magnesium | 11mg | 3% | |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.037mg | 3% | |
| Calcium | 10mg | 27mg | 2% |
| Potassium | 237mg | 310mg | 2% |
| Zinc | 0.17mg | 2% | |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.089mg | 2% | |
| Fructose | 1.37g | 2% | |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.019mg | 1% | |
| Choline | 6.7mg | 1% | |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.083g | 1% | |
| Protein | 0.88g | 0.8g | 0% |
| Fats | 0.2g | 0.4g | 0% |
| Net carbs | 2.69g | 33.5g | N/A |
| Sugar | 2.63g | N/A | |
| Phosphorus | 24mg | 26mg | 0% |
| Sodium | 5mg | 1mg | 0% |
| Saturated fat | 0.028g | 0% | |
| Monounsaturated fat | 0.031g | 0% | |
| Tryptophan | 0.006mg | 0.014mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 0.027mg | 0.041mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 0.018mg | 0.035mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 0.025mg | 0.058mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 0.027mg | 0.045mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.006mg | 0.007mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 0.027mg | 0.036mg | 0% |
| Valine | 0.018mg | 0.042mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.014mg | 0.016mg | 0% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Tomato - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/170457/nutrients
- Persimmon - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/169943/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.






