Walnut vs. Pecan — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
It is essential to emphasize that walnuts and pecans are a goldmine of energy and nutrients, so dieticians and nutritionists highly recommend them.
Both of them are rich in unsaturated fats. Pecan is richer in monounsaturated fat, while walnut is richer in polyunsaturated fat, including omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids.
In vitamin content, pecan wins hands down. It is especially richer in vitamin A and vitamin E and considerably higher in vitamins B1 and B5.
It is important to point out the potential risks of allergy, simultaneous medication use, as well as overeating, which can result in obesity or digestive dysfunctions. Enjoy your nuts, and don’t forget about moderation.
Introduction
What kind of snacks do you prefer? Some specialists claim that nuts are the best choice. Among the many other nuts, pecan and walnuts are unique for nutrients and health benefits. Both of them are edible tree nuts. Despite several similarities, they have quite a few differences. Let’s discuss them.
Main Differences
Pecans originated in South Central America and Mexico, dating back to the 16th century, while walnuts owe their origin to Asia and Europe and date back to 7000 B.C. The Romans called walnuts “Jupiter’s royal acorn.”
Did you know that “pecan” means a nut that needs a stone to be cracked because it is extremely hard to do by hand? Pecans also have oval or elongated shells in a dark brown color.
On the other hand, walnut shells are easy to crack or open, even by hand. It is round-shaped and light brown colored. Walnuts look like “little brains” and are famously known for their brain-boosting function.
Pecans are drier and sweeter, while walnuts may be a little bitter due to their rich oil content. That’s why sometimes pecans are used in roasted form.
Both are widely used not only in raw form but also as ingredients in pastries, candies, salads, cookies, and pasta, as well as in producing walnut butter and oil.
Both are widely consumed worldwide; however, pecan is primarily consumed in North America. Prices depend on the territory; pecan is cheaper in North America, and, inversely, walnut is cheaper in Europe and Asia.
Taste and Texture
Compared to other nuts, walnuts are generally more bitter and are utilized to give desserts, salads, granolas, and oatmeal a crunchy consistency, among other things. On the other hand, pecans have a unique flavor and are slightly sweeter in taste.
They both have a hard shell; however, the texture of pecans is somewhat waxy, while walnuts are crunchier.
Nutrition
Pecan is slightly higher in dietary fiber. Conversely, walnut is richer in protein and essential amino acids. It is also worth mentioning that pecan contains less sodium and has a lower glycemic index.
By contrast, walnuts are lower in sugar and saturated fats. Both contain equal amounts of cholesterol.
Minerals
There is no significant difference between these two nuts in terms of mineral content. Nevertheless, walnut is the winner in this category, with a higher content of calcium, magnesium, phosphorus, as well as copper, and iron.
On the other hand, pecans have higher zinc content.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+30.6%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+40%
Contains
more
IronIron
+15%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+32.2%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+24.9%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+28.9%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+46.6%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-100%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+31.8%
Vitamins
From the viewpoint of vitamins, pecan is the king. Pecan is fairly rich in vitamins B1, E, and A and, to a lesser extent, higher in vitamins B5 and K.
At the same time, walnuts are drastically higher in vitamin B6.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+18.2%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+15.4%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+155.7%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+345.5%
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+200%
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+100%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+93.5%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+51.4%
Contains
more
Vitamin KVitamin K
+29.6%
Fats
From the very start, it is necessary to point out that pecan and walnut are rich sources of unsaturated fats. In fact, from the comparison charts below, you can easily see that pecans are extremely rich in monounsaturated fats. On the other hand, walnuts are higher in polyunsaturated fat, including omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids, which we will discuss later. Walnuts are also higher in linoleic acid, alpha-linolenic, and arachidonic acids, essential nutrients that our body can only get from food or supplements
Fat Type Comparison
Contains
more
Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat
+118.3%
Contains
more
Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat
+356.7%
Calories
Both nuts are high in calories. Pecans have 691 calories per 100g, and walnuts have 654 calories per 100g.
Carbohydrates
The nuts' carb content equals 14g per 100g.
Health Benefits
Cardiovascular health
The Dietary Guidelines for Americans state that consuming nuts is directly linked to improved nutrient intake and diet quality and better health outcomes associated with cardiovascular disease (1).
According to this study, consuming 30 grams per day of nuts (like walnuts) as part of a Mediterranean diet has been shown to significantly reduce cardiovascular risk (such as myocardial infarction, stroke, and death from cardiovascular disease) by approximately 30% after following this diet for 5 years (2).
The amount of nuts consumed daily, rather than the type, is the main factor in lowering total cholesterol, LDL (“bad” cholesterol) and triglycerides. Stronger effects were observed for consuming at least 60 grams of nuts daily (3).
This study has shown that walnut consumption reduces systolic blood pressure in elderly subjects, especially those with mild hypertension (blood pressure levels of 140-159 mmHg systolic and/or 90-99 mmHg diastolic) (4, 5).
On the other hand, pecans are high in tocopherol, which may help reduce the risk of atherosclerosis, the most common cause of coronary heart disease (6).
Alzheimer’s Disease
It is worth mentioning that walnuts and pecans are among the most important sources of bioactive compounds such as polyphenols and vitamin E, which are famous for their antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities. According to a review published in 2017, the main polyphenol of walnuts is pedunculagin, an ellagitannin (7). Several studies prove the role of ellagitannin against disease development and progression, including neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s disease and different types of cancer (8).
Walnuts are higher in vitamin B6 (pyridoxine), which is essential for many enzyme reactions in our bodies. These include the processing of proteins, carbs, and fats, the formation of red blood cells, and neurotransmitters, which ensure the transmission of impulses in the nervous system. Adequate intake of vitamin B6 may prevent and treat anemia and symptoms of PMS, reduce Alzheimer’s disease risk, and support brain function. It also helps improve our mood.
On the other hand, pecans are higher in vitamin B1 (thiamin), which plays a significant role in energy metabolism and is also involved in transforming proteins, carbohydrates, and fats. Besides the health benefits of vitamin B6 shown above, vitamin B1 also prevents or delays cataracts and contributes to proper digestion by secreting hydrochloric acid. As a powerful antioxidant, thiamin has anti-aging properties (9).
Diabetes
According to a study published in 2016, the consumption of walnut oil by people with type 2 diabetes mellitus was shown to decrease blood glucose levels (10).
According to research, consuming a serving of pecans daily can enhance blood insulin, insulin resistance, and beta-cell activity in at-risk persons (3).
Furthermore, pecans have a low glycemic index, so they do not induce blood sugar spikes, even in diabetics.
You can find more info about pecans and diabetes on this link.
Downsides and Risks
If you are sure that pecans and walnuts are superfoods and are eager to enjoy them, you should wait a minute, as there are some downsides.
Above all, an allergic reaction is the most common risk of pecans, walnuts, and other nuts. The allergy symptoms can vary from hives around the mouth, diarrhea, abnormal breathing, and asthma attacks up to anaphylaxis.
Although dieticians recommend pecans and walnuts as part of different weight-loss diets, you can quickly gain weight if you eat more than the daily recommended quantity.
Certain substances in walnuts called tannins decrease the absorption of other medications. Taking some medications simultaneously with black walnut should be avoided.
And finally, you can get diarrhea and vomiting by eating a large number of nuts due to their high fiber content.
References
- https://blogs.cdc.gov/nchs/2014/12/17/2558/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34579146/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26561616/
- https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.118.12766
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26713565
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27719661/
- https://www.journals.uchicago.edu/doi/abs/10.1086/692168
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28115966
Infographic
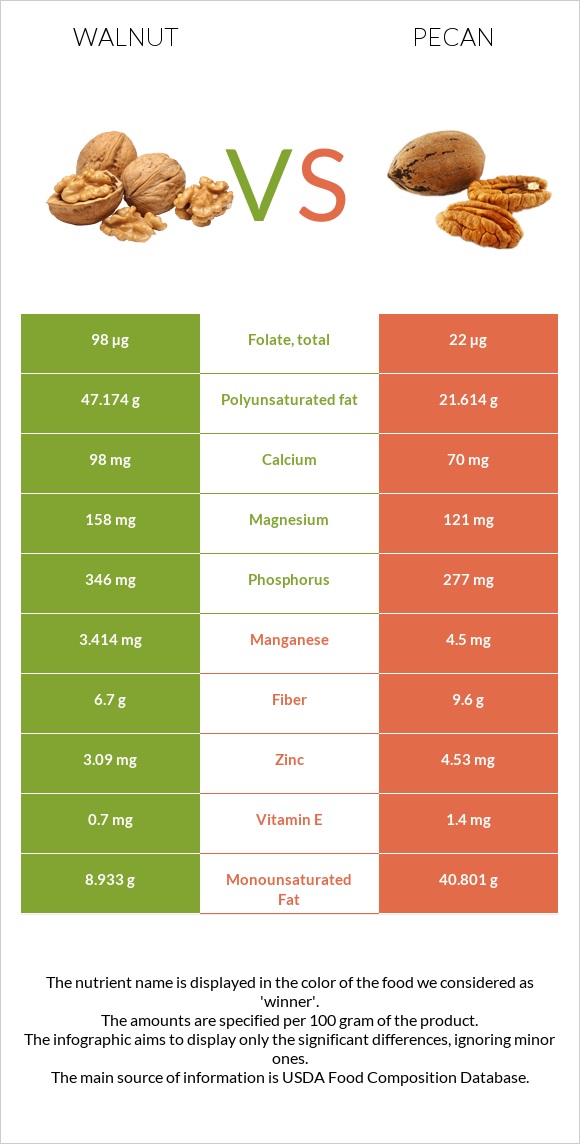
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 47.174g | 21.614g | 170% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 8.933g | 40.801g | 80% |
| Manganese | 3.414mg | 4.5mg | 47% |
| Copper | 1.586mg | 1.2mg | 43% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.341mg | 0.66mg | 27% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.537mg | 0.21mg | 25% |
| Folate | 98µg | 22µg | 19% |
| Zinc | 3.09mg | 4.53mg | 13% |
| Protein | 15.23g | 9.17g | 12% |
| Fiber | 6.7g | 9.6g | 12% |
| Fats | 65.21g | 71.97g | 10% |
| Phosphorus | 346mg | 277mg | 10% |
| Magnesium | 158mg | 121mg | 9% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.57mg | 0.863mg | 6% |
| Iron | 2.91mg | 2.53mg | 5% |
| Vitamin E | 0.7mg | 1.4mg | 5% |
| Calcium | 98mg | 70mg | 3% |
| Calories | 654kcal | 691kcal | 2% |
| Selenium | 4.9µg | 3.8µg | 2% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.15mg | 0.13mg | 2% |
| Potassium | 441mg | 410mg | 1% |
| Vitamin K | 2.7µg | 3.5µg | 1% |
| Protein per 100 calories | 2.3287461773700304g | 1.3270622286541245g | N/A |
| Calories per 10 g protein | 429.4156270518713kcal | 753.5441657579062kcal | N/A |
| Vitamin C | 1.3mg | 1.1mg | 0% |
| Net carbs | 7.01g | 4.26g | N/A |
| Carbs | 13.71g | 13.86g | 0% |
| Sugar | 2.61g | 3.97g | N/A |
| Starch | 0.06g | 0.46g | 0% |
| Sodium | 2mg | 0mg | 0% |
| Vitamin A | 1µg | 3µg | 0% |
| Vitamin B3 | 1.125mg | 1.167mg | 0% |
| Choline | 39.2mg | 40.5mg | 0% |
| Saturated fat | 6.126g | 6.18g | 0% |
| Tryptophan | 0.17mg | 0.093mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 0.596mg | 0.306mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 0.625mg | 0.336mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 1.17mg | 0.598mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 0.424mg | 0.287mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.236mg | 0.183mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 0.711mg | 0.426mg | 0% |
| Valine | 0.753mg | 0.411mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.391mg | 0.262mg | 0% |
| Fructose | 0.09g | 0.04g | 0% |
Macronutrient Comparison
| Contains more ProteinProtein | +66.1% |
| Contains more WaterWater | +15.6% |
| Contains more OtherOther | +20.3% |
| Contains more FatsFats | +10.4% |
Carbohydrate type comparison
| Contains more GlucoseGlucose | +100% |
| Contains more FructoseFructose | +125% |
| Contains more StarchStarch | +666.7% |
| Contains more SucroseSucrose | +60.5% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Walnut - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/170187/nutrients
- Pecan - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/170182/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.






