Whipped cream vs. Ice cream — Nutrition and Health Differences

Summary
Whipped cream provides more vitamins A, D, E, K, and polyunsaturated and monounsaturated fat. On the other hand, ice cream has higher minerals, protein, carbs, vitamins of B-group, vitamin C, and folate. Moreover, ice cream contains over two times less saturated fats, cholesterol, and low GI, whereas whipped cream has over ten times less sodium and low calories.
Introduction
Whipped cream and ice cream are both yummy and creamy desserts.
Whipped cream is usually served at room temperature or slightly cold, while ice cream is served frozen. This article will discuss nutritional differences and their impact on health.
Nutrition
In this part of the article, we will compare the nutritional information for whipped cream and vanilla ice cream. The information is for 100 grams of the food.
Macronutrients and Calories
Overall, whipped cream and ice cream have similar nutritional densities. Both have 61% water. Whipped cream has more calories, whereas ice cream provides more protein, carbs, and low fats.
Macronutrient Comparison
Contains
more
FatsFats
+102%
Contains
more
CarbsCarbs
+89%
Contains
more
OtherOther
+18.4%
Calories
Whipped cream provides more calories per hundred grams compared to ice cream. In a 100g serving, ice cream and whipped cream have 257 calories and 207 calories, respectively.
The serving sizes for whipped and ice cream are one tablespoon (3 grams) and 1/2 cup (66 grams), respectively. One tablespoon of whipped cream has eight calories, and one cup provides 154 calories. One serving of ice cream has 137 calories.
Protein
Ice cream has slightly more protein per hundred grams than whipped cream. A hundred grams of ice cream provides 3.5g of protein, whereas whipped cream has 3.2g.
Fat Type Comparison
Whipped cream provides over two times more fats compared to ice cream. A hundred grams of ice cream provides 11g of fats, whereas whipped cream has 22.22g.
Whipped cream has over two times more monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fat. In contrast, ice cream has two times less saturated fats. The daily need for saturated fat for whipped cream is 35% higher. A hundred grams of whipped cream has 13.8g of saturated fat, while ice cream provides 6.8g.
Fat Type Comparison
Contains
more
Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat
+116.2%
Contains
more
Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat
+82.5%
Contains
less
Sat. FatSaturated fat
-50.9%
Omega-3 Fatty Acids
A hundred grams of whipped cream does not contain omega-3 fatty acids, whereas ice cream has 0.7g of omega-3 EPA.
Cholesterol
Whipped cream has more cholesterol compared to ice cream. In a 100g serving, ice cream and whipped cream have 76 mg and 44mg of cholesterol, respectively.
Carbohydrates
Ice cream is the winner in this category. A hundred grams of ice cream provides 23.6g of carbs, whereas whipped cream has only 12.5g.
In a 100g serving, ice cream contains 22.9g of net carbs and 0.7g of dietary fiber. Whipped cream lacks dietary fiber.
Number of Vitamins
Whipped cream has more vitamins A, D, E, and K. Whipped cream provides over six times more vitamin K. In a 100g serving, ice cream and whipped cream have 0.3µg and 1.9µg vitamin K, respectively. On the other hand, ice cream provides more vitamins B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, and B12. Moreover, whipped cream does not contain vitamin C, whereas ice cream provides 0.6mg.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+59.3%
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+113.3%
Contains
more
Vitamin DVitamin D
+100%
Contains
more
Vitamin KVitamin K
+533.3%
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+10.8%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+269.2%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+65.7%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+90.5%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+17.1%
Contains
more
Vitamin B12Vitamin B12
+34.5%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+66.7%
Number of Minerals
Ice cream wins in this category. Ice cream contains a considerably higher amount of choline, calcium, and manganese and is richer in potassium, zinc, phosphorus, copper, and iron. In contrast, whipped cream contains over ten times less sodium. A hundred grams of whipped cream has 8mg of sodium, whereas ice cream contains 80mg.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-90%
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+27.3%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+26.7%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+35.4%
Contains
more
IronIron
+80%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+130%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+86.5%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+18%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+700%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+28.6%
Glycemic Index
Whipped cream has a glycemic index of 55. The glycemic index of ice cream is 62. That indicates that whipped cream is low-GI food while ice cream is medium-GI food.
You can click this link to learn more about the glycemic index readings of foods.
Insulin Index
While there is no study on the insulin index of whipped cream, ice cream has an insulin index of 89.
Acidity
The PRAL, or potential renal acid load, is the amount of acid or base produced by meals inside the body. Whipped cream has a PRAL value of 0.2, whereas the PRAL level of ice cream is -0.6. That means whipped cream is acid-forming, while ice cream is alkaline-forming.
Weight Loss & Diets
Between these two, whipped cream is the better choice for a low-carb diet. Unlike it, ice cream might be the better choice for low-fat and low-calorie diets. Moreover, whipped cream can be part of a low glycemic index diet.
Whipped cream has low carbs and is high in fats. It is a great keto diet inclusion, especially when made with heavy cream and sweetened with keto-friendly sweeteners like stevia, erythritol, or monk fruit.
Because of its carbohydrate content, traditional ice cream, which often contains significant amounts of sugar and ordinary milk, is not typically compatible with the keto diet. However, there are keto-friendly ice cream products on the market, as well as homemade varieties that employ low-carb sweeteners and high-fat dairy or dairy substitutes.
Heavy cream, coconut milk, almond milk, or other low-carb milk replacements can be in keto ice cream alternatives, along with natural or artificial low-carb sweeteners.
Health Impact
Diabetes
Low GI foods may lower postprandial glycemia, resulting in more stable blood glucose levels. They also may decrease weight gain in persons with prediabetes or diabetes.
Whipped cream has a lower GI, so it is the better choice for people with Type 2 Diabetes (1).
Lactose Intolerance
Whipped cream and ice cream are dairy products and contain milk as one of their main ingredients. One serving of ice cream contains 2 - 6g lactose, whereas whipped cream has less than 0.5g (2).
Lactose-intolerant people cannot digest considerable amounts of lactose due to a genetically insufficient level of the enzyme lactase. Following the consumption of lactose-containing meals, common symptoms include stomach discomfort and bloating, excessive flatus,, watery stool, and sometimes constipation (3).
Reducing the amount of lactose in the diet by eliminating lactose-containing foods helps to alleviate the disease's symptoms (4).
Allergy
Dairy products that contain milk are the most common cause of allergy. People who are allergic to milk must avoid ice cream and whipped cream. If you are allergic to milk, your immune system recognizes the protein in milk as potentially harmful. Common symptoms are rash, swelling, trouble breathing, wheezing, loss of consciousness, or even it can be fatal (5).
Cardiovascular Health
Regular consumption of whipped cream and ice cream may cause metabolic syndrome with symptoms such as high blood pressure, high triglycerides, and being overweight or obese. It means that cardiovascular risk will be increased in the presence of metabolic syndrome. It means, in turn, that the risk of myocardial infarction and stroke will be increased.
On the other hand, this study found that eating an antioxidant ice cream made from high-polyphenol foods can improve vascular function and physical performance by battling oxidative stress. It can benefit healthy people, athletes, the elderly, and those with chronic or degenerative diseases due to its potent antioxidant properties (6).
Consuming whipping cream and ice cream in moderation is important due to the uncertain findings on the benefits and risks of full-fat dairy. To ensure your safety, limit your saturated fat intake to 5% to 6% of your daily calorie intake, as the American Heart Association recommends. For instance, if you consume around 2,000 calories daily, do not consume more than 120 calories from saturated fat, which is approximately 13 grams of saturated fat per day (7).
Appearance
Ice cream usually has rounded or cylindrical shapes. It has a smooth, creamy texture with various colors. Vanilla ice cream has the hue of light cream or off-white. Chocolate ice cream has a brown or dark brown hue, depending on the chocolate's strength. Pistachio ice cream has a light green color. Ice cream is available in containers, cones, bowls, and as part of a set dessert.
Whipped cream, in contrast, contains air bubbles and has a fluffy texture. It keeps its shape when piped or spooned. Whipped cream is frequently white or faintly colored. Whipped cream is occasionally flavored or colored with additives such as vanilla extract, chocolate, or food coloring. That can result in variations such as pale beige or light pastel hues.
Ingredients
While whipped cream is a dairy-based, natural, handmade, or store-bought choice, the cool whip is a non-dairy, ready-made topping.
Whipped cream is made from heavy whipping cream, sugar, and sometimes vanilla extract. Cool Whip is made from water, hydrogenated vegetable oil, high-fructose corn syrup, skim milk, light cream, and natural and artificial flavors.
Heavy whipping cream has 36% milk fat, whereas whipping cream (without the word "heavy") has 30% milk fat. Fat crystals solidify whipped cream, ice cream, butter, and margarine.
Whipped cream is usually created by whisking or mixing heavy cream until it's light and frothy. Whisk the sugar, vanilla, and heavy cream at a medium-high speed. Whipping cream works best at this speed because it incorporates air into the mixture at a moderate speed. The perfect sweet spot is soft whipped cream. It has a smooth, billowy texture. Over-mixed whipped cream has a gritty texture and stiff peaks. As you whip the heavy cream, the volume of the cream doubles.
Ice cream is composed of cream, milk, sugar, and frequently eggs.
Six steps are involved in the production of commercial ice cream: In stainless steel vats, milk, cream, milk solids, sugars, modifying agents, and flavorings are combined. The mixture is blended to get a constant texture. After that, it is pasteurized by heating at 82-85°C for 15 seconds and then cooling to kill microorganisms.
Taste and Use
Whipped cream made with heavy cream tastes rich, creamy, and slightly sweet. Adding sugar and vanilla makes it taste sweeter and smell better. It's light and easy to eat, which makes it a nice change from heavier desserts or drinks.
Ice cream tastes cold, creamy, and sweet with a smooth texture. Depending on the flavor, ice cream can have added tastes like fruit (blueberries, strawberries, raspberries), chocolate, nuts, or other things mixed in, which make its flavor more interesting.
Whipped cream is typically used as a topping, whereas ice cream is eaten alone or with desserts, such as sundaes, milkshakes, or floats.
Whipped cream has an airy and billowy texture and is the ideal topping for pies, cakes, cupcakes, crepes, cheesecake, and trifles. You can add some flavoring such as powdered sugar, coffee, orange zest, chocolate, and vanilla extract.
Ice cream is available in different flavors and can include extra components such as fruits, nuts, chocolate, or cookies.
Varieties
Several types of ice cream and whipped cream are available, each with a unique flavor, texture, and application.
Gelato, sherbet, sorbet, frozen yogurt, soft serve, and ice popsicles are common types of ice cream.
Sweetened, flavored, dairy-free, sugar-free, and stabilized whipped creams are common types of whipped cream.
Sources
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31374573/
- https://med.virginia.edu/ginutrition/wp-content/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12018807/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK532285/
- https://www.foodallergy.org/resources/milk-allergy-vs-lactose-intolerance
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0899900716301289
- https://www.heart.org/en/healthy-living/healthy-eating/eat-smart/fats/saturated-fats
Infographic
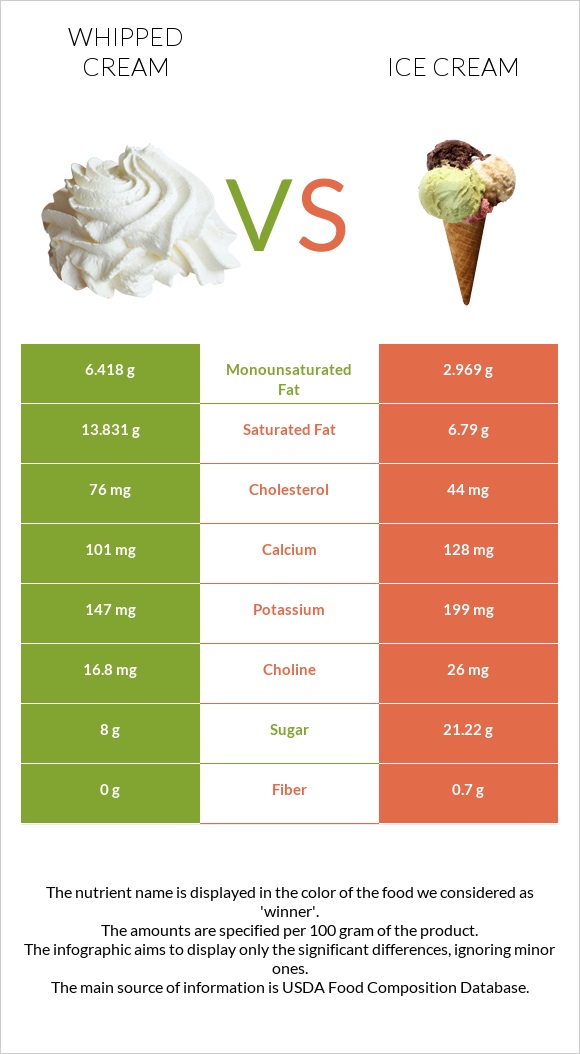
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Saturated fat | 13.831g | 6.79g | 32% |
| Fats | 22.22g | 11g | 17% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.065mg | 0.24mg | 13% |
| Cholesterol | 76mg | 44mg | 11% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 6.418g | 2.969g | 9% |
| Vitamin A | 188µg | 118µg | 8% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.305mg | 0.581mg | 6% |
| Carbs | 12.49g | 23.6g | 4% |
| Vitamin B12 | 0.29µg | 0.39µg | 4% |
| Calories | 257kcal | 207kcal | 3% |
| Calcium | 101mg | 128mg | 3% |
| Fiber | 0g | 0.7g | 3% |
| Zinc | 0.37mg | 0.69mg | 3% |
| Sodium | 8mg | 80mg | 3% |
| Potassium | 147mg | 199mg | 2% |
| Phosphorus | 89mg | 105mg | 2% |
| Vitamin E | 0.64mg | 0.3mg | 2% |
| Choline | 16.8mg | 26mg | 2% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.825g | 0.452g | 2% |
| Protein | 3.2g | 3.5g | 1% |
| Vitamin C | 0mg | 0.6mg | 1% |
| Vitamin D | 16 IU | 8 IU | 1% |
| Magnesium | 11mg | 14mg | 1% |
| Iron | 0.05mg | 0.09mg | 1% |
| Copper | 0.01mg | 0.023mg | 1% |
| Vitamin D | 0.4µg | 0.2µg | 1% |
| Selenium | 1.4µg | 1.8µg | 1% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.041mg | 0.048mg | 1% |
| Vitamin K | 1.9µg | 0.3µg | 1% |
| Folate | 3µg | 5µg | 1% |
| Net carbs | 12.49g | 22.9g | N/A |
| Sugar | 8g | 21.22g | N/A |
| Manganese | 0.001mg | 0.008mg | 0% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.037mg | 0.041mg | 0% |
| Vitamin B3 | 0.07mg | 0.116mg | 0% |
| Tryptophan | 0.045mg | 0.045mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 0.144mg | 0.146mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 0.194mg | 0.195mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 0.313mg | 0.316mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 0.254mg | 0.258mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.08mg | 0.081mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 0.154mg | 0.157mg | 0% |
| Valine | 0.214mg | 0.217mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.087mg | 0.088mg | 0% |
| Omega-3 - EPA | 0g | 0.003g | N/A |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Whipped cream - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/170860/nutrients
- Ice cream - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/167575/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.






