Whitefish vs. Salmon — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Salmon is high in choline, selenium, omega-3 fatty acids, vitamins A, D, E, K, and most B-groups. On the other hand, whitefish is high in vitamin B2, potassium, phosphorus, calcium, magnesium, and zinc. Moreover, salmon is high in calories, monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats. Salmon provides less saturated fats and sodium. Compared to salmon, whitefish contain more protein and less cholesterol.
Introduction
Fish, salmon, Atlantic, farmed, cooked, dry heat, and Fish, whitefish, mixed species, cooked, dry heat are the specific food kinds considered in this comparison. In this article, we will discuss their nutritional values and health effects.
Classification
Salmon belongs to the family Salmonidae. There are two types of salmon: Pacific and Atlantic. Pacific salmon are members of the Oncorhynchus genus. Atlantic salmon is a member of the Salmo genus. Atlantic salmon are the largest species in the Salmon genus.
The name Pacific salmon refers to five primary species: King (Chinook), Sockeye (Red), Coho (Silver), Pink (Humpback), and Chum (Dog, Silverbrite). The nutritional values of these spices might vary.
Whitefish also belongs to the family Salmonidae and subfamily Coregoninae. There are two species of whitefish: the genus Coregonus and the genus Stenodus.
Appearance
The gill covers of Atlantic salmon contain big dark dots, and the upper body has x- or y-shaped patterns.
Whitefish have sleek bodies with a silvery or light color on their scales. They usually have a distinct lateral line. Whitefish vary in size, although they are typically medium-sized fish.
Taste
Salmon has a particular flavor that is creamy, buttery, and somewhat fishy. The taste of salmon varies based on the variety and method of preparation. Whitefish is mildly sweet with a delicate, clean, and fresh flavor. The flavor can changed by spices or marinades applied throughout the cooking process.
Salmon's texture can also vary, ranging from delicate tender to slightly firm. Whitefish, on the other hand, has a flaky texture.
Nutrition
Macronutrients and Calories
Salmon is high in fats and calories, whereas whitefish has more protein. Moreover, salmon provide less cholesterol compared to whitefish.
Macronutrient Comparison
Contains
more
OtherOther
+266.3%
Contains
more
FatsFats
+64.4%
Calories
Compared to whitefish, salmon provides more calories.
A hundred grams of salmon contains 206 calories, whereas whitefish provide 172 calories per hundred grams.
Protein
Compared to salmon, whitefish has more protein content. A hundred grams of salmon provides 22.1g of protein, whereas the same amount of whitefish provides 24.47g. Both contain all essential amino acids.
Fats
In comparison to whitefish, salmon is high in fats. A hundred grams of salmon provides 12.35g of fats, whereas whitefish 7.51g. Salmon is high in monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats. Whitefish, on the other hand, contain less saturated fats.
Fat Type Comparison
Contains
less
Sat. FatSaturated fat
-51.5%
Contains
more
Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat
+63.4%
Contains
more
Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat
+65.3%
Omega-3 Fats
In comparison to whitefish, salmon provide more omega-3 fats. A hundred grams of salmon contains 2.3g of omega-3 fatty acids, while whitefish contains only 1.8g. Salmon is high in omega-3 DHA and EPA content, whereas whitefish is high in omega-3 DPA.
Cholesterol
Compared to whitefish, salmon contains more cholesterol.
A hundred grams of salmon has 63mg of cholesterol, whereas whitefish has 77mg.
Vitamins
Salmon is high in vitamins B1, B3, B5, B6, B12, and folate. Whitefish, on the other hand, provide more vitamin B2. Salmon also contains vitamins C and E. Salmon contain 3.7mg of vitamin C and 1.14mg of vitamin E, whereas whitefish do not provide them. Moreover, salmon is high in vitamin A.
A hundred grams of salmon contains 230IU of vitamin A, whereas whitefish provides 131IU.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+14.1%
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+76.9%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+98.8%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+109.2%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+70.5%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+87%
Contains
more
Vitamin B12Vitamin B12
+191.7%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+100%
Minerals
Compared to whitefish, salmon contains over 2.5 times more selenium. Salmon provides 41.1µg of selenium, whereas whitefish only 16.2µg. Salmon also contains 90.5 mg of choline. On the other hand, whitefish provides more potassium, phosphorus, magnesium, calcium, and zinc. Both are equal in sodium content.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+40%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+120%
Contains
more
IronIron
+38.2%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+87.8%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+195.3%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+37.3%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+437.5%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+155.6%
Mercury Levels
The amount of mercury in seafood varies depending on the species and the level of pollution in the environment. Canned salmon has a mercury concentration mean (PPM) of 0.014, and fresh salmon has a PPM of 0.022. Whitefish has a mercury concentration mean of 0.089. Compared to salmon, whitefish has a higher mercury content (1).
Acidity
The way to determine the acidity of foods is the potential renal acid load or PRAL. The PRAL value of salmon is 14.7. The PRAL value of whitefish is 11.1. Both of them are acidic.
Weight Loss & Diets
As fish is meat, salmon and whitefish are not considered vegan or vegetarian.
Salmon and whitefish are good options for people who follow the pescetarian diet.
Salmon and whitefish are allowed in the Mediterranean diet.
Salmon and whitefish can be part of the DASH diet in moderation amounts.
As salmon and whitefish do not contain carbs, they are excellent choices for the keto diet.
Both whitefish and salmon are paleo-friendly.
Health Impact
Pregnancy
Salmon and whitefish contain less mercury levels. They are the best choices for pregnant women(2).
According to studies, EPA and DHA are essential for healthy embryonic development, including immunological, neural, and retinal function(3).
Cardiovascular Health
According to the study, eating salmon reduced systolic, diastolic, and mean arterial blood pressure. Salmon consumption also decreased LDL-cholesterol and increased HDL-cholesterol(4).
In patients with known coronary heart disease, omega-3 fatty acids reduce the risk of sudden cardiac death and mortality(5).
Omega-3 fatty acids may also improve cardiovascular function, including inflammation, peripheral artery disease, major coronary events, and anticoagulation(3).
Neurodegenerative Diseases
Supplementation of fish products rich in omega-3 fatty acids, such as salmon or whitefish, may slow or prevent neurodegenerative disorders. As mentioned above, salmon contains more omega-3 fatty acids.
A diet high in polyunsaturated omega-3 fatty acids may lower the risk of Parkinson's disease.
According to the study, fatty fish consumption is inversely associated with the incidence of dementia and Alzheimer's disease(6).
Diabetes
Fish high in omega-3 fatty acids is a good choice for people with diabetes. Compared to whitefish, salmon is high in omega-3 DHA and omega-3 EPA.
Consumption of fatty fish, as well as EPA and DHA, was not linked to an increased risk of type 2 diabetes(7). It may reduce inflammation. People with diabetes may choose baked or grilled fish and avoid fried fish(8).
Infographic
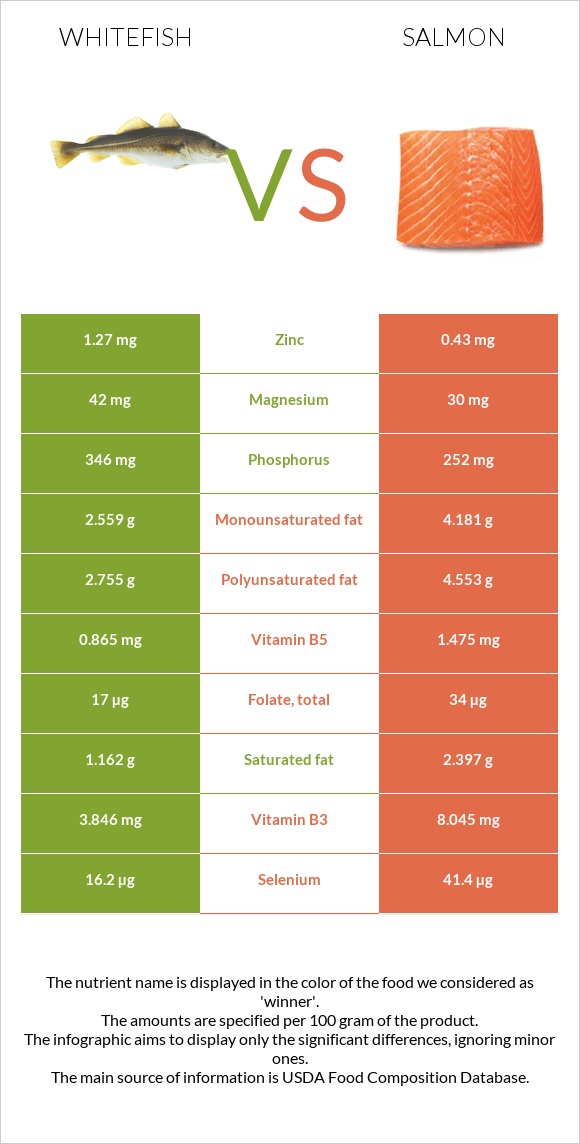
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Vitamin B12 | 0.96µg | 2.8µg | 77% |
| Vitamin D | 526 IU | 66% | |
| Vitamin D | 13.1µg | 66% | |
| Selenium | 16.2µg | 41.4µg | 46% |
| Vitamin B3 | 3.846mg | 8.045mg | 26% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.346mg | 0.647mg | 23% |
| Choline | 90.5mg | 16% | |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.171mg | 0.34mg | 14% |
| Phosphorus | 346mg | 252mg | 13% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.865mg | 1.475mg | 12% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 2.755g | 4.553g | 12% |
| Zinc | 1.27mg | 0.43mg | 8% |
| Vitamin E | 1.14mg | 8% | |
| Fats | 7.51g | 12.35g | 7% |
| Saturated fat | 1.162g | 2.397g | 6% |
| Protein | 24.47g | 22.1g | 5% |
| Cholesterol | 77mg | 63mg | 5% |
| Copper | 0.092mg | 0.049mg | 5% |
| Vitamin C | 0mg | 3.7mg | 4% |
| Folate | 17µg | 34µg | 4% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 2.559g | 4.181g | 4% |
| Magnesium | 42mg | 30mg | 3% |
| Vitamin A | 39µg | 69µg | 3% |
| Manganese | 0.086mg | 0.016mg | 3% |
| Calories | 172kcal | 206kcal | 2% |
| Calcium | 33mg | 15mg | 2% |
| Iron | 0.47mg | 0.34mg | 2% |
| Potassium | 406mg | 384mg | 1% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.154mg | 0.135mg | 1% |
| Sodium | 65mg | 61mg | 0% |
| Vitamin K | 0.1µg | 0% | |
| Tryptophan | 0.274mg | 0.248mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 1.073mg | 0.969mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 1.128mg | 1.018mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 1.989mg | 1.796mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 2.248mg | 2.03mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.724mg | 0.654mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 0.955mg | 0.863mg | 0% |
| Valine | 1.261mg | 1.139mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.721mg | 0.651mg | 0% |
| Omega-3 - EPA | 0.406g | 0.69g | N/A |
| Omega-3 - DHA | 1.206g | 1.457g | N/A |
| Omega-3 - DPA | 0.209g | 0.17g | N/A |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Whitefish - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/174246/nutrients
- Salmon - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/175168/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.