Sour Cream vs Greek Yogurt — Nutrition, Calories, Keto & More


Summary
Sour cream is higher in calories, carbs, and fats. It's richer in vitamin A, calcium, and potassium. In comparison, Greek yogurt has a lower glycemic index and is richer in phosphorus, zinc, and vitamins B2, B5, and B12. It has more positive health impacts.
Table of contents
- Introduction
- Are Greek yogurt and sour cream the same thing?
- What are the main differences?
- Taste
- Shelf life
- Culinary world
- Nutritional content comparison
- Water distribution and macronutrients
- Carbs
- Proteins
- Fats
- Saturated fats
- Monounsaturated fats and polyunsaturated fats
- Cholesterol
- Calories
- Vitamins
- Minerals
- Diet and weight loss
- Health impacts
- References
Introduction
This article will compare two dairy products; sour cream and Greek yogurt. These dairy products differ regarding their taste and flavor, nutritional content, and health impacts.
Are Greek yogurt and sour cream the same thing?
Definitely, Greek yogurt and sour cream are not the same. This article will examine their actual differences, nutritional profile, and health impacts in the corresponding sections. First of all, let's have a look at the general differences.
What are the main differences?
The main differences are according to their taste, shelf life, and usage in the culinary world.
Taste
Sour cream has a creamy solid consistency with a milkier taste than yogurt and an acidic undertone. In comparison, Greek yogurt is more solid and has an acidic aftertaste. Both can be classified as having a sour taste, mainly due to the acid that the bacterias produce during fermentation.
Shelf life
They both require refrigeration, yet sour cream has a higher shelf life based on a couple of days more than yogurt. Yogurt lasts up to 2 weeks unopened, whereas sour cream up to 3 weeks. However, once opened, they both remain for up to 1 week.
Culinary world
In the culinary world, yogurt can be used in various ways. It's commonly used as plain yogurt, a cooking ingredient, or a dessert ingredient.
On the other hand, sour cream is most famous in Tex-Mex cuisine in association with Mexican food. In addition, sour cream can be used to make dressing and sauces and in cooking.
Nutritional content comparison
In this section, we will discuss the difference between 100g servings of sour cream and Greek yogurt according to their nutritional content.
Water distribution and macronutrients
Yogurt contains more water as compared to sour cream. In 100g of yogurt, there is 85g of water, whereas sour cream contains 71g. Thus the consistency of sour cream is thicker.
According to the chart shown below, sour cream is significantly richer in fats and carbs, while Greek yogurt is higher in proteins.
Macronutrient Comparison
Contains
more
ProteinProtein
+45.6%
Contains
more
WaterWater
+19.9%
Contains
more
FatsFats
+3515.4%
Contains
more
CarbsCarbs
+94.4%
Contains
more
OtherOther
+25%
Carbs
Sour cream contains twice as many carbs compared to yogurt.
However, Greek yogurt is richer in sugar, thus having a sweeter taste than sour cream.
Proteins
Yogurt has a richer protein content than sour cream. Although the difference is low, it exists: Greek yogurt has 3.2g more protein than sour cream.
Fats
Yogurt is devoid of fats because we are taking into consideration no-fat Greek yogurt in this article. On the other hand, sour cream contains high amounts of fat compared to yogurt. Sour cream contains 14g of fat, which is remarkable considering yogurt is devoid of fat.
In detail, we discuss the major components of fats in this section, considering saturated fats, unsaturated fats, and cholesterol.
Saturated fats
Sour cream contains higher amounts of saturated fats compared to yogurt. Almost half the fat content of sour cream is based on saturated fats.
Monounsaturated fats and polyunsaturated fats
Sour cream is devoid of polyunsaturated fats, but it mainly contains monounsaturated fats regarding the ratio of poly to monounsaturated fat content.
Cholesterol
For both, the cholesterol amounts are categorized as low. However, yogurt contains lower amounts of cholesterol than sour cream.
Fat Type Comparison
Contains
less
Sat. FatSaturated fat
-98.7%
Contains
more
Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat
+7635.8%
Contains
more
Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat
+4066.7%
Calories
Sour cream is higher in calories than yogurt, and the difference that exists between them is quite remarkable.
Sour cream has three times higher calories than Greek yogurt.
Vitamins
Sour cream is richer in vitamin A compared to yogurt. However, yogurt has a richer and more diverse vitamin profile. Yogurt is richer in vitamin B12 and mainly satisfies the recommended daily value by 94% when 300g of Greek yogurt is consumed. In addition to that, it is also richer in vitamins B2, B5, and B6.
Below, the vitamin coverage chart highlights the difference between them.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+15.8%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+197.1%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+215%
Contains
more
Vitamin B12Vitamin B12
+150%
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+11800%
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+3900%
Contains
more
Vitamin DVitamin D
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+73.9%
Contains
more
Vitamin KVitamin K
+∞%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+57.1%
Minerals
Sour cream is richer in calcium and potassium, whereas yogurt is richer in phosphorus and zinc. It is important to discuss the calcium content of both these foods since they are dairy-based foods, and they are one of the main foods known to be rich in calcium.
Based on the consumption of 300g of each food, when sour cream is consumed, 43% of the RDV is satisfied, whereas when yogurt is consumed, 33% of the RDV is satisfied.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
IronIron
+16.7%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+70%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+92.6%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+58.8%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-48.6%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+∞%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+136.6%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+28.2%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+49.6%
Diet and weight loss
Vegan
They are not part of the vegan diet since they are dairy products.
Keto
Yogurt is low caloric and has a low glycemic index; thus, it can be eaten during the keto diet. However, in this article, we discuss reduced-fat sour cream, which is high in carbs and cannot be eaten during the keto diet. However, normal fat content sour cream, which has more fat than the reduced sour cream, can be eaten during the keto diet.
Lactose intolerance
Lactose intolerance symptoms are triggered at a particular amount of lactose ingestion. Most lactose-intolerant people can meet their calcium needs by eating small amounts of yogurt without developing intolerance symptoms.
Sour cream is similarly low in lactose and may be consumed by most lactose-intolerant people. However, if bloating, abdominal pain, diarrhea, and flatulence appear, consumption of these products must be stopped.
Health impacts
Cardiovascular health
Sour cream consumption does not contribute to the development of cardiovascular diseases. In addition to that, the consumption of dairy, including sour cream, is associated with positive effects on the cardiovascular system (1).
On the other hand, sour cream is richer in saturated fats, as mentioned above. Foods with high amounts of saturated fats may result in high LDL cholesterol levels in blood flow, increasing cardiovascular disease risk (2).
Consumption of yogurt has been found to lower the risk of developing cardiovascular disease in hypertensive individuals (3).
Another study found that eating yogurt regularly lowers mortality risk from cardiovascular disorders (4).
In summary, Greek yogurt is generally considered a healthier choice for heart health compared to sour cream due to its lower saturated fat content, higher protein content, and potential probiotic benefits. However, it's essential to choose low-fat or fat-free varieties of Greek yogurt and watch out for added sugars or artificial ingredients. Incorporating Greek yogurt into the diet as a substitute for sour cream in recipes or as a snack can contribute to a heart-healthy eating pattern.
Diabetes and metabolic disorders
The following study demonstrates a link between dairy consumption and a lower risk of developing type 2 diabetes. However, this is dose-dependent, so reasonable amounts must be consumed without added sweeteners or flavorings (5).
Yogurt is a probiotic that keeps the usual gut microorganisms healthy and active, which helps to regulate blood glucose levels. As a result, the risk of type 2 diabetes is reduced (6).
Consumption of full-fat dairy products has been linked to the development of pre-diabetes, which, if not regulated, can lead to type 2 diabetes (7).
Cancer
Research on postmenopausal women in a discussion about breast cancer in relation to dairy intake was done. Dairy consumption is not related to breast cancer development in this statistical population; however, overall, high calcium consumption is positively associated with breast cancer development in postmenopausal women. Thus it is important to maintain a balanced diet. In this comparison, sour cream is richer in calcium than yogurt. However, these numbers need to be higher to cause any harm (8).
Consumption of yogurt decreased cancer development risks in gastric, colorectal, breast, and bladder cancers. However, as mentioned above, high calcium consumption is associated with cancer development (9).
Another study looks at the effects of yogurt and how it can lower the incidence of upper aerodigestive tract cancer (10).
Muscle recovery and healthy weight
In contrast to sour cream, Greek yogurt is an excellent option for athletes as a pre-workout snack. Its protein content is beneficial for muscle protein synthesis, therefore, its gain and recovery (11) (12). Moreover, yogurt consumption is linked with healthy weight and low-fat muscle mass gain (13).
References
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4006120/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29898882/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29462263/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31968071/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3719038/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28615384/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29498341/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2959158/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22081693/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22179690/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5852800/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6503736/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4856732/
Infographic
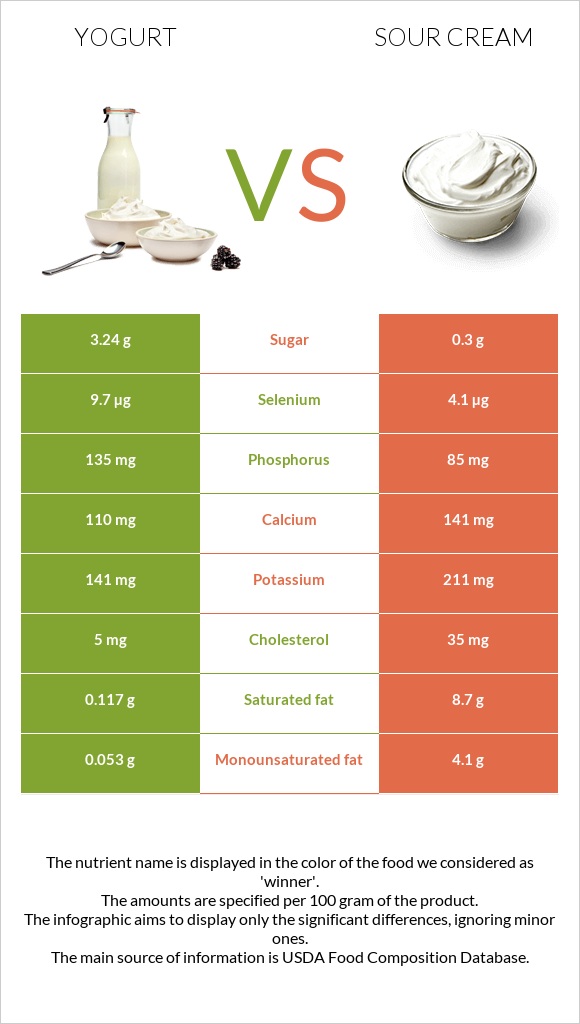
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Saturated fat | 0.117g | 8.7g | 39% |
| Fats | 0.39g | 14.1g | 21% |
| Vitamin B12 | 0.75µg | 0.3µg | 19% |
| Vitamin A | 1µg | 119µg | 13% |
| Cholesterol | 5mg | 35mg | 10% |
| Selenium | 9.7µg | 4.1µg | 10% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 0.053g | 4.1g | 10% |
| Phosphorus | 135mg | 85mg | 7% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.331mg | 7% | |
| Calories | 59kcal | 181kcal | 6% |
| Protein | 10.19g | 7g | 6% |
| Calcium | 110mg | 141mg | 3% |
| Vitamin E | 0.01mg | 0.4mg | 3% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.278mg | 0.24mg | 3% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.063mg | 0.02mg | 3% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.012g | 0.5g | 3% |
| Potassium | 141mg | 211mg | 2% |
| Zinc | 0.52mg | 0.27mg | 2% |
| Vitamin D | 0µg | 0.3µg | 2% |
| Vitamin C | 0mg | 0.9mg | 1% |
| Carbs | 3.6g | 7g | 1% |
| Vitamin D | 0 IU | 10 IU | 1% |
| Copper | 0.017mg | 0.01mg | 1% |
| Sodium | 36mg | 70mg | 1% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.023mg | 0.04mg | 1% |
| Vitamin B3 | 0.208mg | 0.07mg | 1% |
| Vitamin K | 0µg | 0.7µg | 1% |
| Folate | 7µg | 11µg | 1% |
| Choline | 15.1mg | 19.2mg | 1% |
| Net carbs | 3.6g | 7g | N/A |
| Magnesium | 11mg | 11mg | 0% |
| Iron | 0.07mg | 0.06mg | 0% |
| Sugar | 3.24g | 0.3g | N/A |
| Manganese | 0.009mg | 0% | |
| Trans fat | 0.006g | N/A | |
| Omega-3 - ALA | 0.001g | N/A | |
| Omega-6 - Linoleic acid | 0.01g | N/A |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Yogurt - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/170894/nutrients
- Sour cream - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/173442/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.





