Zucchini vs. Eggplant — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Eggplant is three times richer in dietary fiber and two times richer in vitamin E.
Zucchini contains eight times more vitamins A and C. It is also rich in vitamins B1, B2, and B6, vitamin K, iron, calcium, potassium, sodium, magnesium, zinc, and phosphorus.
Along with beneficial effects on health, zucchini and eggplant are used in treatments of benign prostatic adenoma and skin cancer, respectively.
Introduction
Zucchini and eggplant are fruity vegetables known and widely used worldwide. They are known for their beneficial impacts on health. This article will compare these two foods to see what they provide us with and their impacts on health.
Classification
Zucchini, otherwise named courgette, or baby marrow, meaning small marrow, belongs to the Cucurbita genus and Cucurbitaceae family. The family includes cucumbers, luffas, squashes, melons, and watermelons.
Eggplant also has many names, including aubergine, brinjal, scientifically Solanum Melongena, and junior synonyms S.ovigerum and S.trongum. It belongs to the Solanum genus and the nightshade family Solanaceae. Eggplant is related to the tomato, potato, and chili pepper.
Aubergine vs. Eggplant
Eggplant and aubergine are the same vegetables, called differently depending on the country.
The word “aubergine” originates from France and is primarily used in Europe, whereas “eggplant” is mainly used in the United States. The name “eggplant” was inspired by the egg-shaped, white varieties of the vegetable that were first brought to the US.
Appearance
Differentiating these two foods is easy. The ordinary zucchini fruits are striped or uniform-colored and can be any shade of green, and the golden zucchini has a deep yellow or orange color.
Eggplant is usually purple and spongy, with smooth flesh. There are also white varieties of this food called Easter white eggplant.
Taste and Use
Zucchini is served in a variety of ways. It is eaten raw, sliced, shredded, or lightly cooked in salads. In different countries, it can be used in the kitchen in various methods, for example, cooked, boiled, grilled, baked, fried, barbequed, or incorporated in other recipes. Zucchini noodles are made from zucchini used as a substitute for spaghetti. Zucchini can also be cooked in different types of bread.
Eggplant is used as a vegetable in cooking; it’s a good absorbent of oils and flavors. It can be steamed, fried, roasted, barbequed, pickled, stewed, or curried. It can be used as a meat substitute in vegan and vegetarian cuisines.
Zucchini has a mild flavor; it is slightly bitter and slightly sweet, which becomes more noticeable when cooked. Eggplant also has a mild flavor and can have some bitterness that becomes tender when cooked, more tasting like the food it’s cooked with.
Varieties
Zucchini comes in many types, each of which has a different color, taste, and appearance. Some of the common types are Black Beauty, Dunja, Gourmet Gold, Cocozelle, Gadzukes, Caserta, Ronde de Nice, Golden Egg, Crookneck, Pattypan, Rampicante, Magda, Zephyr, Raven, Fordhook, Summer Green Tiger, Bush Baby, etc.
Black Beauty is one of the most popular varieties of this food. It’s an easy-growing vegetable, dark green to almost black from the outside, with creamy white flesh inside.
Dunja is straight, with dark green and glossy skin. Dunja is preferred for many people as it is quick and easy to harvest.
Cocozelle produces darker green streaks and is less watery than the other varieties.
Gadzukes is a dark green Italian-type zucchini with light green ridges and star-shaped slices. It has a bland taste, with a sweet and crisp flavor.
Caserta has from light green to grey color, with alternate dark green stripes.
There are also many types of eggplants. Some of its most common types are Globe or American, Italian, Indian, Graffiti, Rosa Bianca, Thai, Japanese, Chinese, White, Fairy tale, Little green, Santana, African Garden Egg, Ping Tung, and others.
Globe eggplants have a deep purple color and are wider, with a meaty and tough texture.
Italian eggplants are smaller, sweeter versions of globe eggplants that often have a teardrop shape.
Indian or baby eggplants are small and round, with a tender texture.
Graffiti (striped or Sicilian) eggplants are known for their purple and white exterior, with tiny seeds and thin skin, making them great for eating whole.
Rosa Bianca has a bulbous shape and an ombre-like appearance. They’re less bitter than most nightshades with a more delicate flavor.
Nutrition
The nutritional values are presented for raw zucchini and raw eggplant.
Macronutrients and Calories
These foods have very similar nutritional contents. Both zucchini and eggplant consist of 93% water, eggplant being only a little denser.
One serving size of zucchini is 1 cup, chopped (124g), whereas one serving size of eggplant is 1 cup in cubes that weighs 82g.
Calories
Both zucchini and eggplant are very low in calories. However, eggplant provides relatively more calories.
A 100g serving of zucchini provides 17 calories, while a 100g serving of eggplant provides 25 calories.
Protein and Fats
These foods are not rich in macronutrients; however, zucchini contains a little more protein than eggplant.
Both foods contain a little from all essential amino acids, making their protein quality high.
Zucchini and eggplant have a very low-fat content. However, zucchini is slightly higher in fats. The predominant fats found in these foods are polyunsaturated fatty acids.
Both of these foods are absent in cholesterol.
Carbohydrates
Eggplant contains two times more carbs than zucchini, making zucchini a better choice for low-carb diets.
Eggplant is three times richer in dietary fiber as well.
Vitamins
Zucchini contains almost two times more vitamins compared to eggplant. Zucchini contains eight times more vitamin C and vitamin A; it is richer in vitamins B1, B2, and B6, and vitamin K too.
Eggplant contains two times more vitamin E, and it is also richer in vitamins B3 and B5.
These foods contain the same amount of folate or vitamin B9 and are absent in vitamins D and B12.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+713.6%
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+900%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+15.4%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+154.1%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+94%
Contains
more
Vitamin KVitamin K
+22.9%
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+150%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+43.9%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+37.7%
Minerals
Zucchini is slightly higher in minerals and is the winner in this category. It has higher iron, calcium, potassium, magnesium, zinc, and phosphorus levels.
Eggplant is richer in copper and is lower in sodium when compared to zucchini.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+28.6%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+77.8%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+14%
Contains
more
IronIron
+60.9%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+100%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+58.3%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+52.8%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-75%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+31.1%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+50%
Glycemic Index
Due to their low sugar content, zucchini and eggplant have low glycemic index values, making them a good choice for people with type 2 diabetes (1).
The glycemic index of eggplant is 30; however, the glycemic index value of zucchini is yet to be calculated.
Acidity
The pH value of eggplant ranges from 5.5 to 6.5.
The pH value of zucchini is calculated for the cooked vegetable, falling from 5.69 to 6.10 (2).
The PRAL value or potential renal acid load value shows how much acid is produced in the organism from the given food.
The PRAL value of zucchini and eggplant are -4.2 and -3.9, respectively. The more negative PRAL value of zucchini shows it is slightly more base-producing.
Weight Loss & Diets
Zucchini and eggplant are great for weight loss diets.
A hundred gram serving of zucchini provides fewer calories than eggplant, making zucchini a better choice for low-calorie diets. Zucchini is a better choice for low-carb diets as well. On the other hand, eggplant is preferred in low-fat diets.
As these foods are low in carbs, fats, and calories, they are a good choice for keto, Atkins, and Mediterranean diets.
Baked zucchini can be used as zucchini chips or courgette crisps during the Dukan diet. Eggplant also can be eaten in phases II-IV in the Dukan diet.
Health Impact
Zucchini and eggplant are low in saturated fats and sugar and high in antioxidants and dietary fiber; therefore, they show beneficial effects on health.
Health Benefits
Cardiovascular Health
These foods are rich in dietary fiber, which is reported to lower the incidence of coronary heart disease. The soluble fiber decreases low-density lipoprotein cholesterol or “bad” cholesterol concentrations, lowering atherosclerosis risk (3).
Most data about their impact on heart health come from animal research. A study on rats on a high-fat diet has shown that increased consumption of zucchini leads to decreased cardiovascular disease risk. The study has also shown decreased levels of “bad” types of cholesterol (total cholesterol, triglycerides, low-density lipoproteins) and increased levels of “good” cholesterol (high-density lipoproteins) (4).
Another study on animals has shown that eggplants have heart-protecting effects due to their ability to increase left ventricular function, reduce myocardial infarct size, and heart muscle cell death (5).
Being rich in potassium, zucchini regulates blood flow by dilating blood vessels and blood pressure. Reducing blood pressure decreases cerebrovascular and cardiovascular morbidity and mortality (6,7).
Diabetes
Both zucchini and eggplant are low glycemic index foods containing low sugar. As said before, being used in weight loss diets and having low glycemic index values, these foods reduce the risks of developing type 2 diabetes or the need for medication.
Several studies have shown that foods rich in fiber, such as zucchini and eggplant, may improve blood glucose levels and lower insulin resistance (8,9).
Dietary fiber improves fasting blood glucose, fasting C-peptide (a connective peptide that participates in the synthesis of insulin), triglyceride, and low-density lipoprotein levels as well (10).
For additional information about how eggplant affects diabetes,, you can visit our “Eggplants and Diabetes” page.
Cancer
Zucchini has a potential anticancer activity due to its direct cell-killing effect, which is later enhanced by its antioxidant properties (11). The seed extract inhibits the cell growth of fast-growing cells, such as tumor cells, mainly showing their effect on breast, colon, and prostate cancers (12).
Solasodine rhamnosyl glycosides (SRGs) are chemotherapeutic agents derived from eggplant to treat non-melanoma skin cancers by causing the cells’ death. SRGs in a cream formulation Curaderm BEC5 can be used to treat skin cancers from small to large sizes; even difficult-to-treat areas can be effectively treated (13,14).
The antioxidant nasunin, found in the skin of eggplants, glycoalkaloids, and metabolites, inhibits the growth of human colon and liver cancers (15,16).
Dietary fiber plays a role in reducing the risk of some cancers as well. Several studies suggest dietary fiber reduces the risk of ovarian, breast, esophageal, and stomach cancers (17,18,19,20). On the other hand, study results are contradictory for colorectal cancer.
Digestive Health
Dietary fiber found in zucchini and eggplant shows protective effects against certain gastrointestinal diseases such as inflammatory bowel diseases, constipation, hemorrhoids, colon cancer, gastroesophageal reflux disease, irritable bowel syndrome, duodenal ulcer, diverticulosis, obesity, and diabetes (21).
Dietary fiber leads to increased mechanical stimulation or irritation of the colonic mucosa with increased secretion and peristalsis, leading to increased fecal mass (22).
Short-chain fatty acids are produced by gut microbiota by fermentation of dietary fiber. They lead to mechanisms playing a key role in maintaining homeostasis in the gut and other organs (23).
Urogenital health
Phytotheurapetic compounds in zucchini seed oil play a role in treating benign prostatic hyperplasia by causing a reduction in prostate growth, lower urinary tract symptoms related to benign prostatic hyperplasia, and leading to relaxation of the bladder sphincter for easier urination (24,25).
Downsides and Risks
Allergy
There were reported cases of zucchini causing allergy, resulting from primary sensitization to the fruit or cross-reactions to the allergen protein called profilin and cross-reacting carbohydrate determinants (26).
References
- Dietary Instruction Sheet
- pH values of foods and food products
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16407729/
- https://www.scirp.org/html/1-2702747_98189.htm#txtF5
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21894326/
- https://journals.physiology.org/doi/full/10.1152/ajpregu.00491.2005
- Does potassium supplementation lower blood pressure
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26923351/
- https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/nejm199602293340906
- https://www.spandidos-publications.com/10.3892/etm.2016.3377
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5537869/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26976217/
- https://www.scirp.org/html/8-2100267_17880.htm
- http://www.curadermbec5.com/The%20Eggplant%20Cancer%20Cure.pdf
- https://tahomaclinic.com/Private/Articles3/BEC5
- https://www.vri.org.nz/dmsdocument/73-f001435658
- https://academic.oup.com/nutritionreviews/article/71/7/474/1807346
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30376840/
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0923753419387320
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0016508513004927
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24876314/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28731144/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27113407/
- https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Liubov-Ben-Noun-nun/publication/335542665
- https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/87559129.2018.1482496
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10932084/
Infographic
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
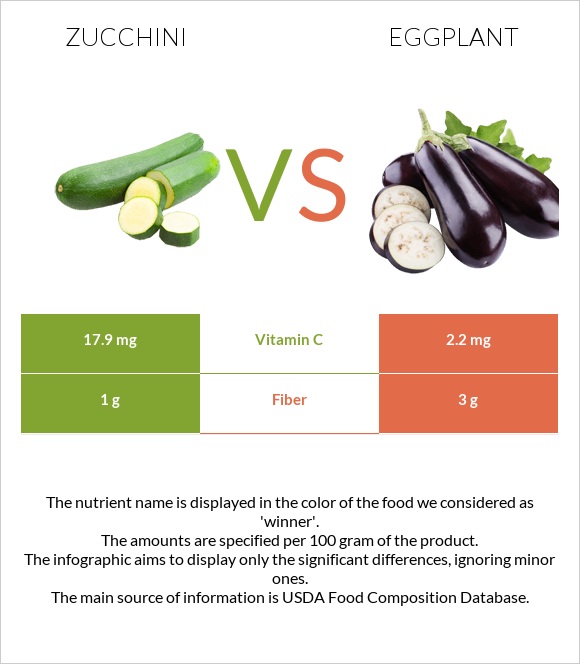
| Vitamin C | 17.9mg | 2.2mg | 17% |
| Fiber | 1g | 3g | 8% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.163mg | 0.084mg | 6% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.094mg | 0.037mg | 4% |
| Copper | 0.053mg | 0.081mg | 3% |
| Iron | 0.37mg | 0.23mg | 2% |
| Phosphorus | 38mg | 24mg | 2% |
| Manganese | 0.177mg | 0.232mg | 2% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.204mg | 0.281mg | 2% |
| Carbs | 3.11g | 5.88g | 1% |
| Magnesium | 18mg | 14mg | 1% |
| Calcium | 16mg | 9mg | 1% |
| Potassium | 261mg | 229mg | 1% |
| Zinc | 0.32mg | 0.16mg | 1% |
| Vitamin A | 10µg | 1µg | 1% |
| Vitamin E | 0.12mg | 0.3mg | 1% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.045mg | 0.039mg | 1% |
| Vitamin B3 | 0.451mg | 0.649mg | 1% |
| Vitamin K | 4.3µg | 3.5µg | 1% |
| Folate | 24µg | 22µg | 1% |
| Calories | 17kcal | 25kcal | 0% |
| Protein | 1.21g | 0.98g | 0% |
| Fats | 0.32g | 0.18g | 0% |
| Net carbs | 2.11g | 2.88g | N/A |
| Sugar | 2.5g | 3.53g | N/A |
| Sodium | 8mg | 2mg | 0% |
| Selenium | 0.2µg | 0.3µg | 0% |
| Choline | 9.5mg | 6.9mg | 0% |
| Saturated fat | 0.084g | 0.034g | 0% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 0.011g | 0.016g | 0% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.091g | 0.076g | 0% |
| Tryptophan | 0.01mg | 0.009mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 0.029mg | 0.037mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 0.044mg | 0.045mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 0.071mg | 0.064mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 0.067mg | 0.047mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.018mg | 0.011mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 0.043mg | 0.043mg | 0% |
| Valine | 0.054mg | 0.053mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.026mg | 0.023mg | 0% |
| Fructose | 1.38g | 1.54g | 0% |
| Omega-3 - ALA | 0.061g | N/A | |
| Omega-6 - Linoleic acid | 0.03g | N/A |
Macronutrient Comparison
| Contains more ProteinProtein | +23.5% |
| Contains more FatsFats | +77.8% |
| Contains more CarbsCarbs | +89.1% |
| Contains more OtherOther | +15.8% |
Fat Type Comparison
| Contains more Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat | +19.7% |
| Contains less Sat. FatSaturated fat | -59.5% |
| Contains more Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat | +45.5% |
Carbohydrate type comparison
| Contains more SucroseSucrose | +420% |
| Contains more GlucoseGlucose | +47.7% |
| Contains more FructoseFructose | +11.6% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Zucchini - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/169291/nutrients
- Eggplant - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/169228/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.




